What Is a Permanent Magnet Motor?
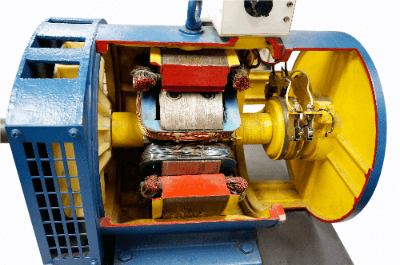 A Permanent Magnet Motor is a motor that incorporates a permanent magnet with an electromagnet in the rotor. Motors are classified into AC motors and DC motors, and permanent magnet motors are one type of AC motor. AC motors are further divided into induction motors, which are driven by induction electromotive force, and synchronous motors, which are driven by magnetic attraction. A permanent magnet motor is a type of synchronous motor.
A Permanent Magnet Motor is a motor that incorporates a permanent magnet with an electromagnet in the rotor. Motors are classified into AC motors and DC motors, and permanent magnet motors are one type of AC motor. AC motors are further divided into induction motors, which are driven by induction electromotive force, and synchronous motors, which are driven by magnetic attraction. A permanent magnet motor is a type of synchronous motor.
Induction motors are inexpensive and widely used motors, and permanent magnet motors are characterized by their higher efficiency compared to induction motors. However, PM motors are more complex and expensive due to the number of parts used, such as permanent magnets.
Increased carbon dioxide emissions due to the increased use of fossil fuels has increased the need for global warming countermeasures, and energy conservation has become a focus of attention. As a result, motors that consume electricity are required to be even more efficient. Against this backdrop, the use of permanent magnet motors are being considered in a wide range of fields.
Uses of Permanent Magnet Motors
Permanent Magnet Motors are used in industrial applications and small components. The following are examples of permanent magnet motor applications:
- For vertical movement of elevators
- For powering robot arms, etc.
- For driving electric vehicles
- For winders of synthetic fiber manufacturing machinery
Permanent Magnet Motors are highly efficient and require precise positioning in many applications. Therefore, they are often used with an inverter or servo controller as the power source to control the number of revolutions and angle of rotation.
Elevators and robot arms require high positioning accuracy, for which permanent magnet motors are suitable.
In recent years, electric vehicles are becoming more and more popular, and high-efficiency permanent magnet motors are also attracting attention.
Principle of Permanent Magnet Motor
Permanent Magnet Motor is composed of a stator, a rotor, and a housing.
1. Stator
The stator consists mainly of coils coated with varnish. Coils of different phases surround the rotor, and a magnetic field is generated when an electric current is applied. The generated magnetic field changes in a rotating manner as the power supply phase changes.
2. Rotor
A permanent magnet is fixed to the rotor, which is attracted to the magnetic field of the stator. Since the magnetic field of the stator is changing so that it rotates, a force is applied to the rotor so that it rotates. This is the principle of rotation of the permanent magnet motor.
3. Housing
Since voltage is applied to the stator to carry current, it is insulated by a housing to prevent ground fault. The stator also generates heat due to the current, which is cooled by the fins of the housing.
Types of Permanent Magnet Motors
Permanent Magnet Motors can be broadly classified into SPM and IPM motors.
1. SPM Motors
SPM motors have permanent magnets installed on the surface of the rotor. SPM stands for “Surface Permanent Magnet Motors”.
SPM motors are characterized by a large effective magnetic flux and low torque ripple. Therefore, although SPMs can be used in high-performance servo applications, they are not suitable for high-speed rotation due to concerns about magnet dropout. To address this issue, the cogging torque can be reduced by improving the super magnetic force distribution.
2. IPM Motors
IPM motors are products with permanent magnets embedded inside the rotor. IPM stands for “Interior Permanent Magnet” and is also called an embedded magnet synchronous motor.
Since there is a large degree of freedom in the shape and arrangement of the magnets, the maximum speed can be flexibly controlled at the design stage. Recently, PM motors are used in HV and EV motors, and are also applied to refrigerators and air conditioners.
Other Information on Permanent Magnet Motor
History of Permanent Magnet Motor
When permanent magnet motors were first developed, they had a stator winding structure with a full section winding system similar to that of induction motors. Later, a brushless type was developed for DC motors. The winding system was the concentrated winding system, which was also used in the permanent magnet motor.
As a result, energy loss due to winding resistance could be suppressed, resulting in higher efficiency and energy savings. The IPM motor allows flexible control of the maximum speed.
Thus, as the permanent magnet motor has undergone technological innovation, new products have been developed one after another, contributing to higher efficiency.