What Is EPDM Rubber?

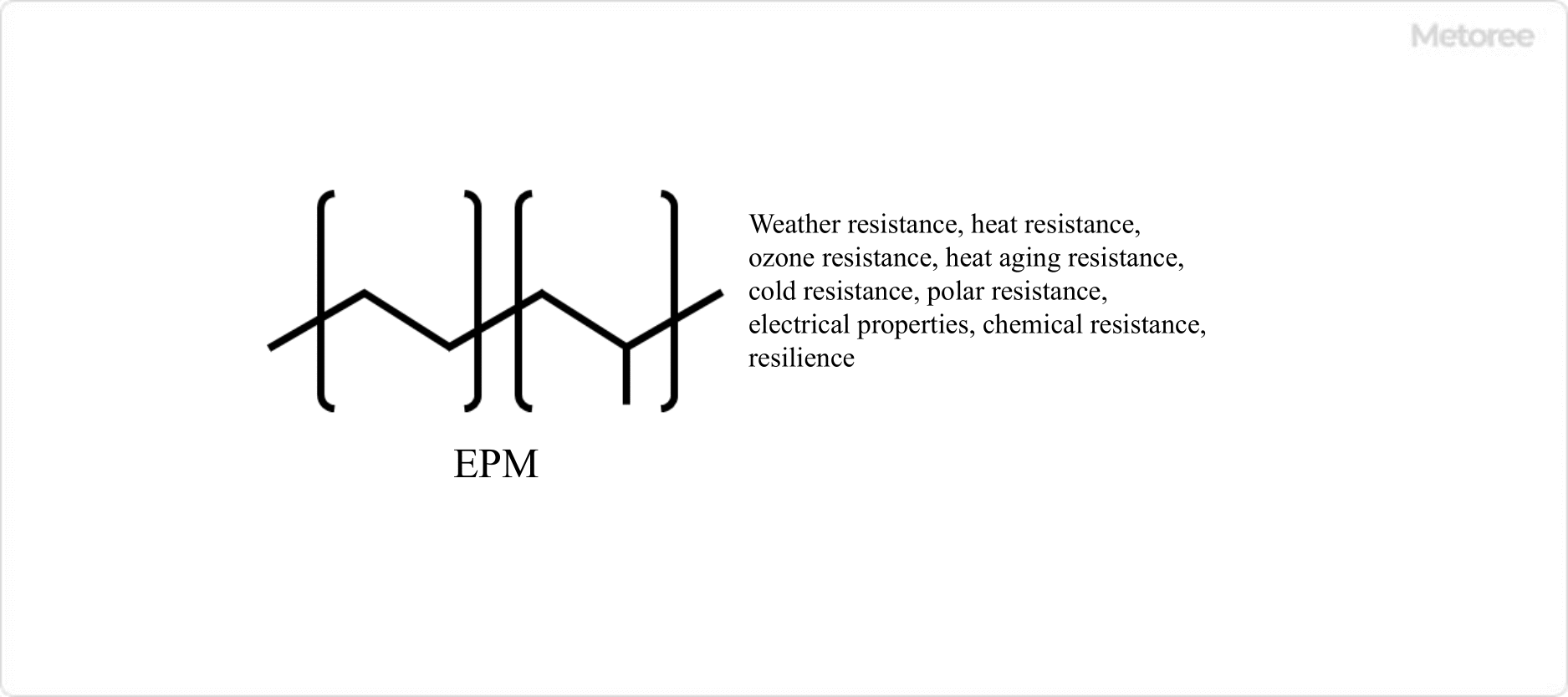
Figure 1. Structure of EPM
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EDPM) Rubber is a copolymer of ethylene and propylene.
Those that do not have unsaturated bonds in the main chain and cannot be vulcanized by sulfur are called EPMs. It has various excellent properties. On the other hand, ethylene propylene diene rubber copolymerized with a small amount of monomer having unsaturated bonds to enable sulfur vulcanization is called EPDM.
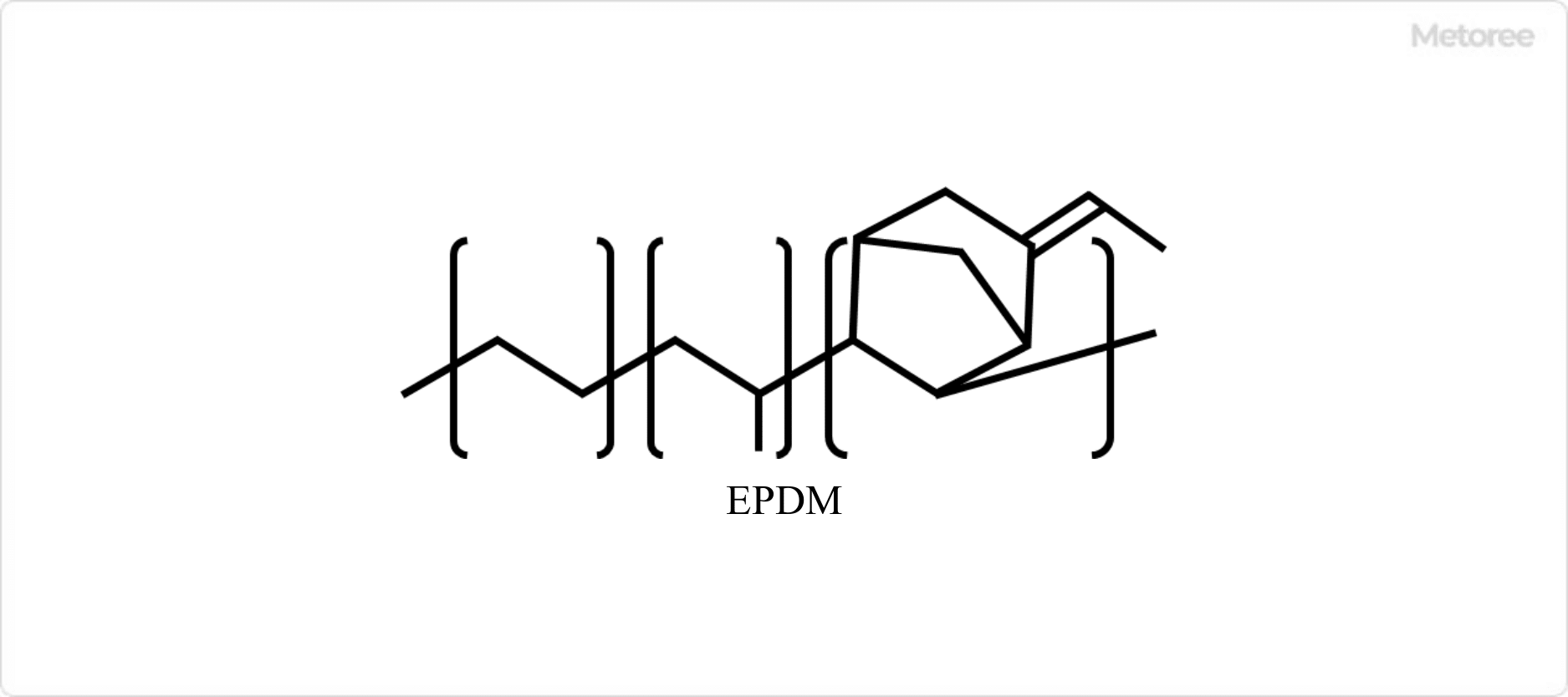
Figure 2. Structure of EPDM
Various diene compounds have been considered as monomers with unsaturated bonds, but three types are still in industrial production worldwide: ethylidene norbornene, 1,4-hexadiene, and dicyclopentadiene. Of these, ethylidene norbornene is the most used.
These monomers are selected based on their reactivity ratio during polymerization, their effect on polymerization speed and catalyst life, ease of recovery in the polymerization process, ease of vulcanization, and their effect on the physical properties of the product. For example, ethylidene norbornene is excellent because its reactivity ratio to the polymerization reactivity of propylene is very large and the double bonds in the ring are highly selective during polymerization.
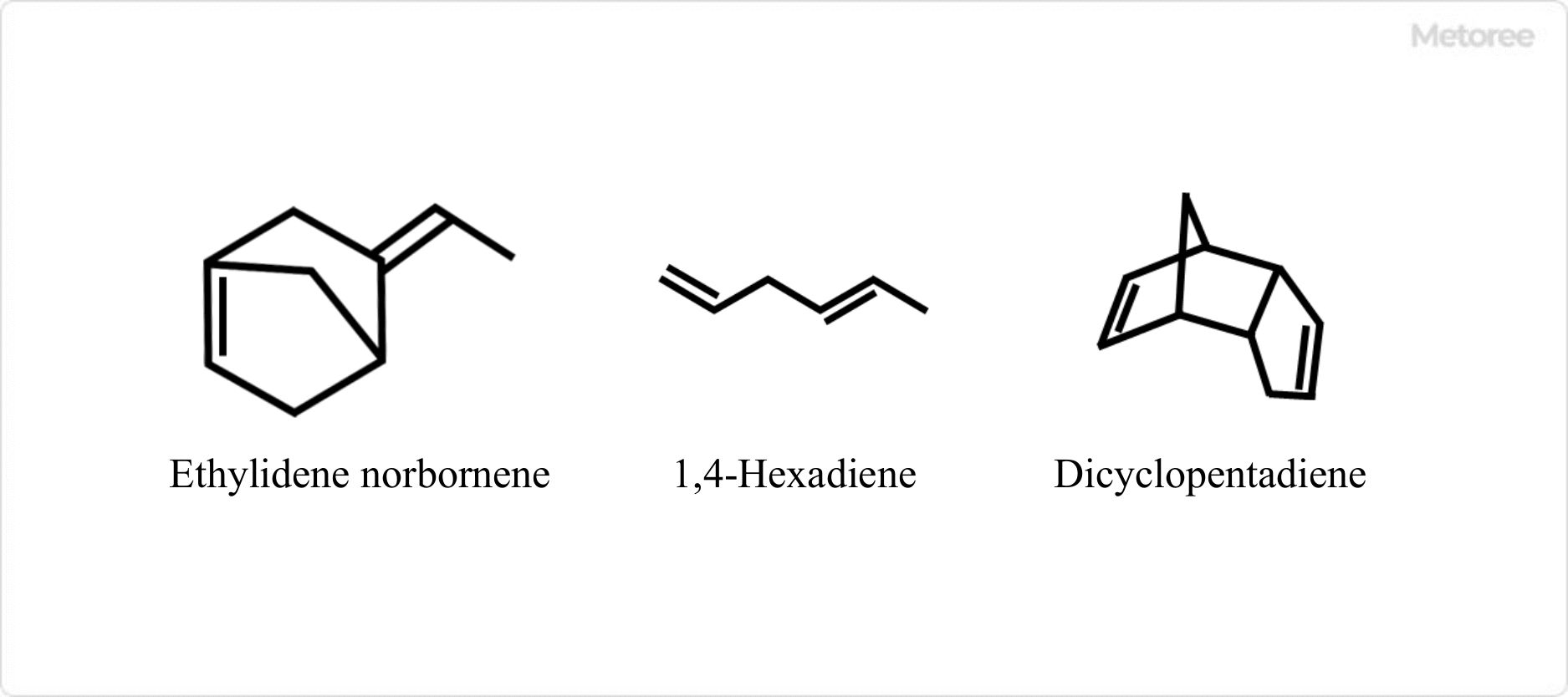
Figure 3. Structure of diene monomer used in EPDM
EP stands for ethylene propylene, EPD for ethylene propylene diene, and M for polymethylene-type rubber with a saturated main chain.
Uses of EPDM Rubber
1. Uses of EPM
EPM cannot be cross-linked by sulfur, so it is vulcanized by peroxide and used in the same way as other rubber products such as tires and hoses. EPM is also used as an impact modifier added to general-purpose olefin resins such as polypropylene.
EPDM can also be modified with maleic anhydride, etc., and used as a modifier for polyamide, polyester, etc.
2. Uses of EPDM
While other rubber products are easily degraded by direct sunlight and cold, EPDM Rubber is suitable for outdoor use due to its excellent weather and cold resistance. Familiar applications include wire sheathing covers, rubber for window frames, and automotive rubber products.
Properties of EPDM Rubber
Polyethylene, which is polymerized only from ethylene, is difficult to handle due to its high crystallinity. EPDM Rubber is a polymer made by copolymerizing propylene with a methyl group on the side chain, which reduces the crystallinity by weakening the intermolecular interaction between polymer chains, making it easier to handle.
EPDM Rubber has no double bonds in its main chain, which makes it excellent in weather resistance and heat resistance. It also has excellent ozone resistance, heat aging resistance, cold resistance, polar resistance, electrical properties, chemical resistance, and repulsive elasticity, and is widely used second to styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR, BR).
Other Information on EPDM Rubber
1. Production Process of EPDM
EPDM is often produced by solution polymerization using metallocene or vanadium catalysts. EPDM with different characteristics can be synthesized by selecting catalysts and polymerization conditions. One of the characteristics of EPDM is that it can be produced in various types depending on the purpose.
Synthesis with metallocene catalyst
EPDM with a narrow molecular weight distribution can be obtained using a metallocene catalyst, which acts while the catalyst is dissolved in the reaction solution (homogeneous catalyst). The narrow molecular weight distribution is advantageous in terms of physical properties such as tensile strength, but its inflexibility and poor processability are disadvantages.
Synthesis with vanadium catalyst
On the other hand, vanadium catalysts have lower catalytic activity than metallocene catalyst and the polymerization process is more complicated, but the resulting EPDM has excellent processability and shows high rubber elasticity even under low temperature conditions.
2. Vulcanization Method
Vulcanization methods include sulfur vulcanization, peroxide vulcanization, oxime vulcanization, and radiation vulcanization, but the two most commonly used are sulfur vulcanization and peroxide vulcanization.
Sulfur vulcanization
This is the most commonly used vulcanization method for EPDM. The reaction proceeds at a high temperature of 150°C or higher during vulcanization. The higher the reaction temperature, the less likely it is to cause reversion (return of vulcanization) and the higher the productivity.
Peroxide Vulcanization
This is the vulcanization method used when EPM is used for wires and cables that require flexibility.