What Is Structural Analysis Software?
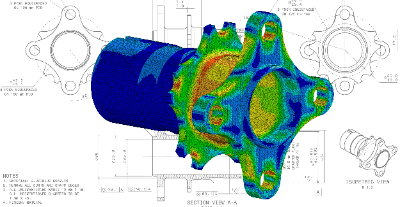 Structural analysis software is a series of processes that calculate the physical quantities that change when loads are applied to the structure under analysis, and evaluate and analyze them based on the obtained calculation results.
Structural analysis software is a series of processes that calculate the physical quantities that change when loads are applied to the structure under analysis, and evaluate and analyze them based on the obtained calculation results.
The physical quantities calculated include deformation, internal forces (stresses), heat and vibration frequencies. The purpose of structural analysis software is to reduce the risk of failure by predicting the results before actually creating the desired structure.
It also provides hints on how to make a better structure. Structural analysis software can also be used to predict the results of large structures that cannot be easily tested.
Uses of Structural Analysis Software
Areas where structural analysis software is often used include the development and production of automobiles, the architectural and civil engineering fields, production studies of metal processing, and the development of rubber products.
1. Automotive
Structural analysis software is an indispensable technology in the development of today’s automobiles. Structural analysis software is used for many components to improve driving performance, ensure safety, conserve energy, and lower costs.
2. Architecture and Civil Engineering
Structural analysis software is used in the architectural and civil engineering fields to design the strength, earthquake resistance, wind resistance, and fire resistance of various buildings. In architecture, it is almost impossible to make prototypes like machine parts. Structural analysis software must be used effectively.
3. Metalworking
In metalworking, plastic forming and pressing are used. In the past, products with a high degree of difficulty were made by the experience of experienced workers. Today, the effective use of structural analysis software enables more advanced manufacturing as well as the transmission of skills.
4. Rubber Products
Rubber products are subject to large deformation under load and contact with other products during deformation. Among Structural analysis software, nonlinear analysis is often used.
Principles of Structural Analysis Software
Structural analysis software consists of the following steps: drawing the object to be analyzed, cutting the mesh, modeling, inputting physical quantities, analysis, and output.
1. Drafting the Object to Be Measured
The analysis target is drawn using CAD or other software. Mainly 3D CAD is used. If you are using a CAD software, it is recommended to check if the file format of the CAD software is compatible with the structural analysis software to be used.
2. Cutting a Mesh
The analysis target is decomposed into a grid called a mesh. The accuracy of this decomposition will affect the accuracy and speed of the calculation, so care should be taken.
3. Modeling
To model the analysis object, it is common to consider the boundary surface of each mesh as a spring.
4. Input Physical Quantities
Input Young’s modulus, specific heat, expansion coefficient, density, etc. of the object to be analyzed. These physical quantities should be measured in advance by experiments or other means. 5.
5. Analysis
There are several types of analysis: static analysis based on Hooke’s law, f=kx, and dynamic analysis based on Newton’s equation of motion, F=ma.
The concept of time exists in kinetic analysis, and it can be divided into implicit analysis, which is relatively easy, and explicit analysis, which solves complex simultaneous linear equations.
6. Output
Most structural analysis software can visualize the results of the analysis. By visualizing the results, it is possible to discover the displacements of the analyzed object and the locations where concentrated forces are applied.
Types of Structural Analysis Software
There are various types of Structural Analysis Software.
Typical examples are as follows:
1. Static Analysis
Static analysis software calculates the deformations and stresses in a structure when forces are applied to it. It provides hints on how to shape the part to be suitable for the way it is used.
2. Eigenvalue Analysis
Eigenvalue analysis calculates the eigenvalues of an object. Eigenvalue is the frequency at which resonance occurs, and if the eigenvalue is high, it can be determined that resonance is unlikely to occur.
In the case of precision equipment mounts, vibration affects their functions, so eigenvalue analysis is performed to determine the shape so that the eigenvalues are as high as possible.
3. Heat Transfer Analysis
Heat transfer analysis calculates the heat distribution of an object. For example, by calculating the temperature distribution of a heater plate, the temperature uniformity can be predicted, allowing optimal design without fabricating parts.
Other Information on Structural Analysis Software
Points to Note About Structural Analysis Software
Structural analysis software is used to perform structural analysis, but there are a few items to keep in mind in order to obtain analysis results that are close to actual conditions.
1. How to Create a 3D model
Making the model exactly the same as the actual geometry may cause errors in mesh processing or take too much time for analysis, and may not produce good analysis results. Depending on what is to be analyzed, the model must be created in detail and the parts to be omitted must be used separately.
2. Analysis Conditions
There are a variety of conditions, and if these settings are not properly made, analysis results will be far from the actual values. Even if the analysis software is excellent, if the model and condition settings are poor, results that are close to reality cannot be obtained.
It is important to attend seminars of analysis software companies and use methods that are appropriate for the software. If experiments are available, correlation between structural analysis software results and experimental results (collation analysis) is also an important technique.