What Is a Seam Welder?
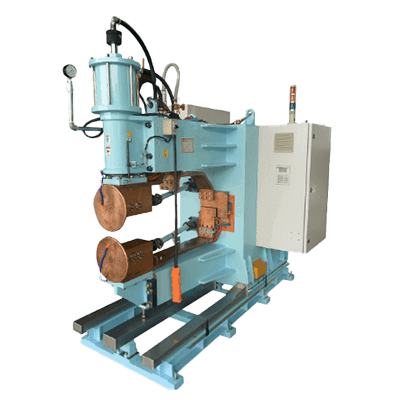
A seam welder is a machine that performs welding by pressure welding. It is used in fusion welding, pressure welding, and brazing, applying pressure to heated metals to join them. Seam welders enable high-precision welding with less dependence on the welder’s technical skills.
Uses of Seam Welders
Seam welders are essential for manufacturing products requiring airtight seals, such as canned juice, food, and fuel tanks. They are also used in producing cases for sensors and electronic devices that must be sealed from the outside air. This includes quartz devices and MEMS, which integrate semiconductors, sensors, actuators, and electronic circuits. In the automotive industry, seam welding is utilized to enhance the rigidity of fuel tanks and structural components, offering continuous joints that increase body strength compared to spot welding.
Principle of Seam Welders
Seam welders join materials by sandwiching them between two roller electrodes that transmit an electric current, melting and fusing the parts with applied pressure. The process achieves continuous sealing by rotating the rollers, with the machine settings, such as welding speed and current magnitude, predetermined for automatic operation. Suitable for welding thin plates, seam welding is a type of resistance welding that relies on electrical resistance to generate heat.
Other Information on Seam Welders
1. Advantages of Seam Welding
- Accessible to operators without advanced skills, thanks to preset conditions on the seam welder.
- The pre-joining accuracy of the flange portion is less critical, as it is adjusted between rollers during welding.
- Offers a safer working environment with no sparks or flashes common in other welding processes.
2. Disadvantages of Seam Welding
Seam welding requires significant initial investment due to the size and cost of seam welders, and the process consumes considerable electricity due to the heat generated by electrical resistance.