What Is a Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)?
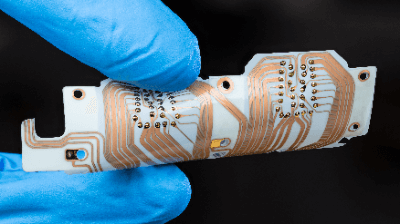 A Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a substrate with a wiring pattern made of bendable copper on a base film. The base film is composed of an insulating and bendable resin.
A Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a substrate with a wiring pattern made of bendable copper on a base film. The base film is composed of an insulating and bendable resin.
Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB) can be made thinner and can be bent freely while maintaining its electrical characteristics.
Uses of Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards can be used as a circuit board by mounting components, etc., and can also be used as a connecting member like a cable by forming only wiring patterns.
Due to its thin and soft characteristics, it is often used for moving parts that require bending and folding, and for connecting parts, and together with flexible rigid substrates, it is also used for three-dimensional circuits.
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards are often used not only in the space exploration and military fields where it was originally intended, but also in familiar fields such as smartphones, cell phones, typing keyboards, and calculators that require thinness and lightness.
Principle of Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards consist of a wiring pattern formed by bendable copper on a base film made of a bendable resin such as polyimide.
There are also rigid printed circuit boards with wiring patterns on a rigid, non-flexible insulating base
board. Flexible Printed Circuit Boards differs from rigid PCB in that the base is a thin film and the base is bendable. As with rigid substrates, components can be mounted on the wiring pattern.
Types of Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards have a single-sided structure in which only one layer of the wiring pattern is formed on one side of the base film, and a double-sided structure in which one layer is formed on both sides of the base film. There is also a multi-layered Flexible Printed Circuit Board with two or more layers of wiring patterns on each side of the base film.
1. Single-Sided Structure
The single-sided structure of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards is one in which a single-layer wiring pattern is formed on only one side of the base film. Single-sided structure is often used in moving parts because of its light weight, flexibility, and durability against movement.
2. Double-Sided Structure
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards with a double-sided structure have a single-layer wiring pattern formed on both sides of the base film. The double-sided structure is superior in that it is compact and allows high-density wiring patterns to be formed, and more functions can be mounted. However, compared to the single-sided structure, it is inferior in flexibility and durability, making it unsuitable for use in moving parts.
3. Multilayered Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
Multilayered Flexible Printed Circuit Boards are multilayered flexible printed circuit board. Flexible Printed Circuit Boards, like rigid PCB, can have two or more layers of wiring patterns on the surface of the base film.
In this case, in order to efficiently multilayer, two or more wiring patterns are stacked on both sides of the base film with an insulating layer in between. This multilayered Flexible Printed Circuit Board with a protective layer is called a Flex Rigid Board.
This multilayered Flexible Printed Circuit Board is lightweight, but has the same high mechanical strength and circuit formation capabilities as rigid substrates, making it suitable for use in three-dimensional circuits. It is an indispensable component for reducing the size of electronic devices to a compact size.
Other Information on Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
1. Manufacturing Method of Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
The manufacturing method of Flexible Printed Circuit Board is explained using a single-sided flexible printed circuit board as an example.
- Application of photoresist
Photoresist is applied to CCL, which is an insulating base film such as polyimide film with copper foil laminated to it. - Formation of photomask
A photomask with a predetermined wiring pattern shape is placed over the CCL. At this time, the photomask is shaped in the same way as in printing and photographic techniques, with the wiring pattern portion removed. - UV curing of the photomask
UV light is irradiated from the top of the photomask, and only the portion corresponding to the wiring pattern is UV cured. - Photoresist removal
The photomask is removed, and uncured photoresist is removed using a chemical solution. - Copper foil removal
The next process is called etching. In the etching process, a chemical solution is used to remove the copper foil, leaving only the copper foil in the area protected by the photoresist, i.e., the wiring pattern area, where the wiring pattern is formed. - Removal of cured photoresist
The cured photoresist covering the wiring pattern is removed with a chemical solution. - Formation of coverlay
An insulating layer called a coverlay is formed to protect the wiring pattern.
The production of such Flexible Printed Circuit Board requires a great deal of chemical knowledge. Knowledge of inorganic chemistry is required for the etching process, which leaves only the wiring pattern, and the coverlay formation process, which protects the wiring pattern.
The wastewater from the rinsing process contains a wide variety of hazardous substances, so advanced wastewater treatment technology based on chemical knowledge is required.
2.Global Trends in Flexible Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards are manufactured worldwide by about 2,500 companies, with Taiwanese manufacturers topping the list in 2018, followed by Japan, Korea, China, and some other leading manufacturers in East Asia.
Flexible Printed Circuit Board demand is expected to continue to grow in a variety of sectors, including public and private military and industrial machinery, the space industry, and the automotive and telecommunications sectors.
Some observers predict that China will have the most momentum due to its investment in improving its technological capabilities and its abundant rare metal resources. Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea, the top group, are moving toward higher unit price niche fields, while China is currently increasing sales centered on low-priced PCBs, but the gap in technological capabilities is shrinking, and it is only a matter of time before China will join the top group in the future.