What Is a Tube Fuse?
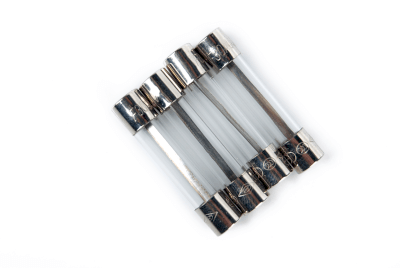
Tube fuses are safety devices used to protect electrical circuits by interrupting current flow when it exceeds safe levels. They contain a fusible metal wire within a glass or ceramic tube that melts (blows) under excessive current, thereby breaking the circuit.
Applications of Tube Fuses
Widely used in consumer electronics, automotive circuits, industrial machinery, and more, tube fuses safeguard against electrical faults. They are particularly valuable in systems where frequent current fluctuations occur, offering protection without the need for constant replacement.
Principle of Tube Fuses
The operation of tube fuses is based on the melting of a fuse element made from materials like lead, tin, or silver, whose composition determines the fuse’s melting point. This feature allows tube fuses to cater to a broad spectrum of rated currents, from low-power applications to those requiring currents of 30A or more.
Types of Tube Fuses
- Normal Fusing Type: Standard fuse for household electronics.
- Fast-Acting Fusing Type: Designed for quick response, suitable for semiconductor protection.
- Time Lag Fusing Type: Delays blowing for applications like motors, accommodating initial power surges.
- Glass Tube Fuse: Offers a visual indication of fuse status through a transparent glass body.
- Ceramic Tube Fuse: Provides higher breaking capacity and additional safety features like arc suppression.
How to Choose a Tube Fuse
Selection involves ensuring the fuse’s rated current exceeds the normal operational current of the circuit but responds appropriately under fault conditions. Factors such as material type, fusing speed, and application-specific requirements guide the choice of the appropriate tube fuse.