What Is a Power Transformer?
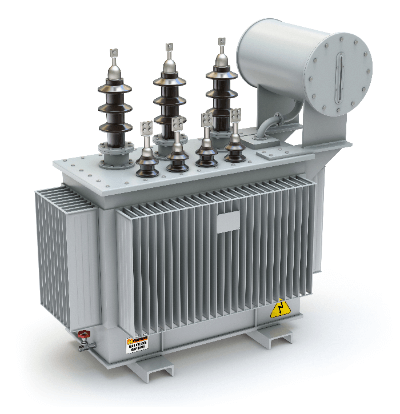 A power transformer is a transformer that transforms electrical AC voltage using electromagnetic induction.
A power transformer is a transformer that transforms electrical AC voltage using electromagnetic induction.
The official name is transformer, but the word power transformer is already well established. Electrical products, for example, are powered by AC outlets, but there are many components in those products, such as motors, that are used with DC electricity instead of AC.
Also, many of those components that can be used in AC are too high voltage to be used with the 100V voltage from the outlet. For this reason, electrical products incorporate small power transformers for the purpose of varying the voltage and current, so that they always operate at the optimum voltage.
Uses of Power Transformers
The primary use of power transformers is as electrical equipment for boosting and lowering the voltage of alternating current.
Larger ones are used at substations to reduce the high AC voltage values sent from power plants and other sources, while smaller ones are used as transformers to change the voltage of electrical outlets to the proper value at shavers and other overseas destinations.
Power transformers are used in a wide range of applications, both industrial and residential, and are indispensable for converting voltage values to appropriate values.
Principle of Power Transformer
The principle of a power transformer is based on the laws of electromagnetic induction.
It is based on the physical phenomenon that the electromotive force, due to the magnetic field fluctuation generated in a coil, is proportional to the number of turns of the power transformer. Power transformers generally consist of two coils wound around an iron core, with the primary coil on the input side and the secondary coil on the output side. The coil generates an electromotive force by changing the strength of the magnetic field within the coil; applying an AC voltage to the primary coil generates a magnetic field in the iron core, and the electromagnetic induction effect of this magnetic field induces a current in the secondary coil, generating an electromotive force.
The magnitude of the electromotive force generated in the secondary coil and the number of coil turns are in a proportional relationship, and the magnitude of the voltage can be changed by the number of turns of the secondary coil relative to the primary. In an ideal Power Transformer, the capacitance of the input and output sides should be the same, but in reality, there is a power loss due to resistance, which is mostly dissipated as heat.
Types of Power Transformers
1. Power Transformer
Power transformers are used in AC commercial power supplies to isolate the power line from the equipment power supply to ensure safety.
Power transformers with INPUT: 100V / OUTPUT: 100V are used for equipment whose power supply is 100V AC. The commercial power supply is 100V or 200V AC power, but the power supply from the power company is a much higher voltage power source up to the nearest column transformer, which is grounded by taking out 100V in the positive and reverse phases at the secondary side of the column transformer and 0V at the neutral line. If a leakage current occurs in equipment that does not use power transformers, the leakage voltage of 100 V to ground is applied to the equipment, and if a person touches the equipment, he or she will receive an electric shock. In such cases, Power Transformers can prevent electric shock by insulating both the 100V side and the neutral wire side from the 100V side and the neutral wire side of the commercial power supply.
2. Power Transformer on a Pole
Power transformers are installed on utility poles, which are often seen in the city, in addition to holding the power lines that supply electricity. Power transformers may be installed slightly below the low-voltage lines.
The power transformer receives 6600V from the high voltage line and supplies 100V to the low voltage side. The low-voltage side (secondary side) has a positive-phase 100V and a reverse-phase 100V, so that 200V can be obtained between the positive and reverse phases (single-phase 200V / voltage to ground is 100V).
The high-voltage lines on the poles transmit power at 6600V, but even higher voltages are used on the towers that transmit power over longer distances. The reason for transmitting power at high voltage is to reduce transmission losses. Electric wires have electrical resistance, albeit slight, and voltage loss occurs in proportion to the current flowing through them. To reduce transmission loss, it is necessary to reduce the current as much as possible, and power is transmitted at a high voltage to maintain a constant transmission power.
Other Information on Power Transformers
Silicon steel or amorphous steel is used for the internal iron core of power transformer structures, but because of the higher cost of amorphous steel, a laminated iron core made of stacked silicon plates with a silicon content of about 4% and a thickness of 0.35 mm is often used.
Power transformer coils can be single or double wound. Double winding is usually used because the primary and secondary coils can be insulated, but single winding is sometimes used for reasons such as larger size and higher cost.
Power transformers need to be cooled to prevent heat generation due to voltage conversion losses. Power transformers, for this purpose, are oil-filled transformers or dry-type (molded) transformers. The former is cooled by soaking the inside of the transformer with insulating oil, while dry or molded Power Transformers that incorporate a cooling mechanism using varnish or epoxy resin are widely used in hospitals and office buildings from the standpoint of disaster prevention.