What Is a Clamp-On Meter?
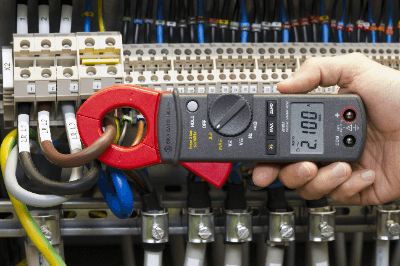
A clamp-on meter is an instrument that measures the current flowing in a circuit.
Ordinary ammeters must be built into the current circuit, and the circuit must be stopped once. On the other hand, a Clamp-on meter can measure current by simply clamping the wire section from the outside. The work can be done quickly and safely without the need to interrupt the circuit.
Uses of Clamp-On Meters
Clamp-on meters are used in situations where the value of the current flowing in a circuit needs to be determined simply. The following are examples of use.
- Pre-checking and post-checking of current flow during electrical work
- Checking the energized part of an electric circuit to investigate the cause of a breakdown
- Checking the operating status of electric equipment
Another feature of clamp-on meters is that they can be used without power interruption. It can be applied to equipment in continuous operation.
Principle of Clamp-On Meters
Clamp-on meters do not measure the current but measure the magnetic field generated by the current and output it as a current equivalent value.
The clamp part of the clamp-on meters has a magnetic core that detects the magnetic field and converts it to a current value. Since the polarity of the magnetic field differs between AC and DC, the principle is different.
Among the various measurement methods, the Hall element method can detect both DC and AC. In this method, a Hall element is built into the magnetic core to measure the magnetic field of the circuit under test as a voltage, which is converted to a current value via a built-in amplifier.
How to Select Clamp-On Meters
Current circuits include both DC and AC circuits. It is important to select an appropriate clamp-on meter according to the current component of the circuit you wish to measure and the accuracy at which you wish to measure.
If you do not require great accuracy, a Hall element-type clamp-on meter that can handle both DC and AC circuits is a safe choice. However, it is assumed that the clamp may not clamp well, depending on the installation position of the circuit.
For AC, select a Rogowski-type clamp-on meter without a core, which allows measurement while bending the clamping section.
Other Information on Clamp-On Meters
1. How to Measure Leakage Current
Leakage current is an essential inspection item in the maintenance of electrical equipment because it can cause electric shock. A leakage current clamp-on meter is used to measure leakage current.
The leakage current is a very small current, and the leakage current clamp-on meters are equipped with a sensitive current transformer. Permalloy, which has high magnetic permeability and is suitable for detecting minute currents, is used for the current transformer.
Leakage current is measured in two ways: “measurement of zero-phase current” and “measurement of earth line current.”
Measurement of Zero-Phase Current
In the measurement of zero-phase current, all phases are clamped together. The clamp-on meters detect the magnetic field caused by the current and convert it into a current value, but the magnetic fields caused by the current flowing against the load cancel each other out. However, if there is a leakage current, the magnetic fields become unbalanced, and a current value is displayed on the clamp-on meters. By reading this current value, the magnitude of the leakage current can be measured.
Measuring Ground Wire Current
Electrical equipment is grounded with a ground wire. In the event of leakage current, the leakage current flows through the ground wire to the earth, so the current value can be measured by directly clamping the ground wire.
2. Accuracy of Clamp-On Meters
There are two types of AC measurement methods: “average value type” and “effective value type”.
Average value type
In the average value type, the current value for a half cycle of AC is averaged, and the average value is multiplied by the waveform factor to obtain the measurement value.
RMS value type
In the RMS value type, the current value is periodically sampled and measured, and the RMS value is obtained by performing the RMS operation on the measured value.
In current measurement, if the current to be measured is a sinusoidal wave, the value is the same regardless of the measurement method. However, if the current to be measured is a distorted wave, the harmonic component prevents the average value type clamp-on meters from obtaining the correct RMS value.
On the other hand, RMS value-indicating clamp-on meters can be measured without any loss of measurement accuracy if the sampling frequency is sufficiently high. As described above, if the current to be measured contains distortion waves, RMS-type clamp-on meters should be used. However, inexpensive clamp-on meters are of the moving coil type of the average value type.