What Is a DC Servo Motor?
A DC Servomotor is a servomotor that operates on DC.
DC Servomotors are used in precision equipment, etc. Since DC Servomotors are controlled by detecting the motor’s speed and position, they are generally integrated with a motor and a sensor that detects speed and position, such as an encoder or resolver. The motor is controlled by a sensor that detects the speed and position of the motor.
To rotate a DC motor, current supplied to the motor must be passed to the rotating shaft by a component called a brush, which wears out due to wear and tear on the brush, requiring periodic maintenance.
Uses of DC Servo Motors
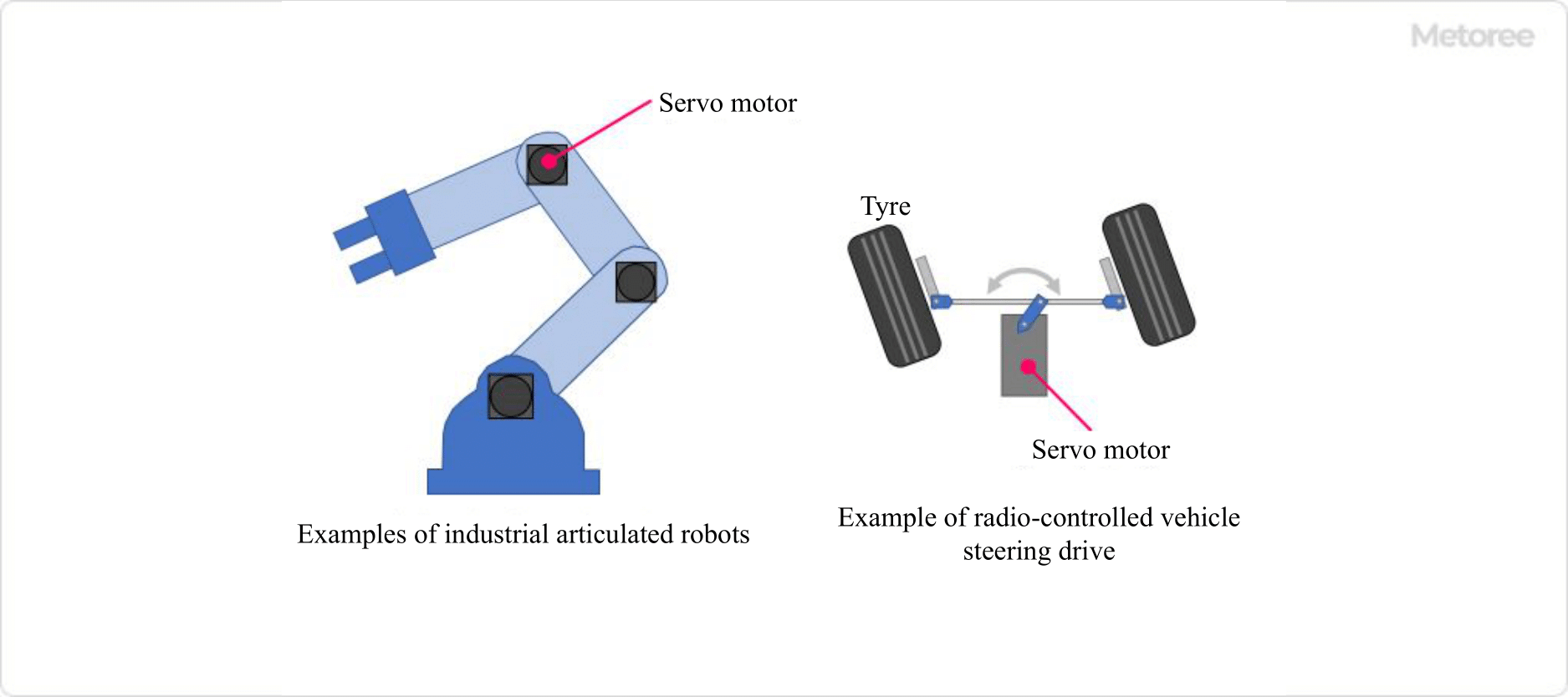
Figure 1. Uses of DC servo motors
DC servo motors are widely used in industrial robots that require precise control. Compared to general-purpose motors, DC servo motors respond more quickly to signals from robot controllers of industrial robots to output rotation speed and torque, and function as actuators for precise movement of robot arms and other parts.
DC servo motors are also used for the steering angle drive of radio-controlled vehicles, XYZ axis drive of machine tools, positioning drive of precision equipment, etc. It is important to select a DC servo motor appropriately according to the level of output and torque capacity, accuracy, and response speed required by the equipment to be used.
Principle of DC Servo Motor
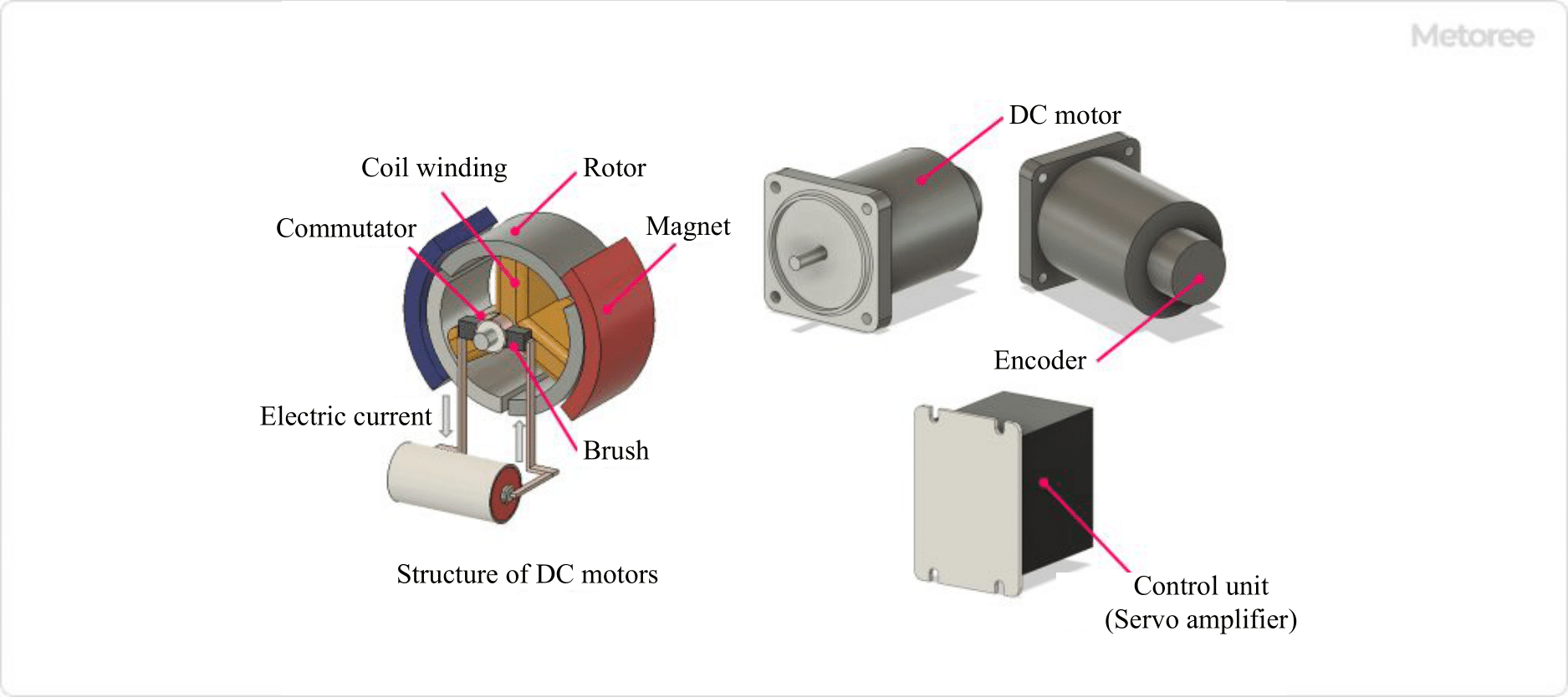
Figure 2. Principle of DC servo motors
A DC servo motor consists of a “motor,” an “encoder,” and a “controller.” It is composed of a permanent magnet, an iron core (rotor) divided into two or more parts, coils wound around each iron core, electrodes, and brushes that pass current through the coils.
The principle of operation of a DC servo motor is explained separately for the motor and other functions.
1. Motor
The motor is made to rotate by the Lorentz force generated from two sources: the current flowing in the coil and the magnetic field from the permanent magnet, which causes the iron core to rotate. When applying current to the coils, direct current from the outside is passed through brushes to the iron core and then transmitted to the coils. Since the current is passed directly to the coil, the Lorentz force can be quickly controlled and the response speed is fast.
2. Other Functions
DC servo motors use command signals transmitted from an external controller to rotate the motor to achieve a commanded target value. The encoder attached to the motor sends speed and position information to the controller, which performs feedback control based on the position and speed information from the encoder in response to commands sent from the controller so that the motor’s rotation speed and rotation position approach the target values.
Control of DC Servo Motor
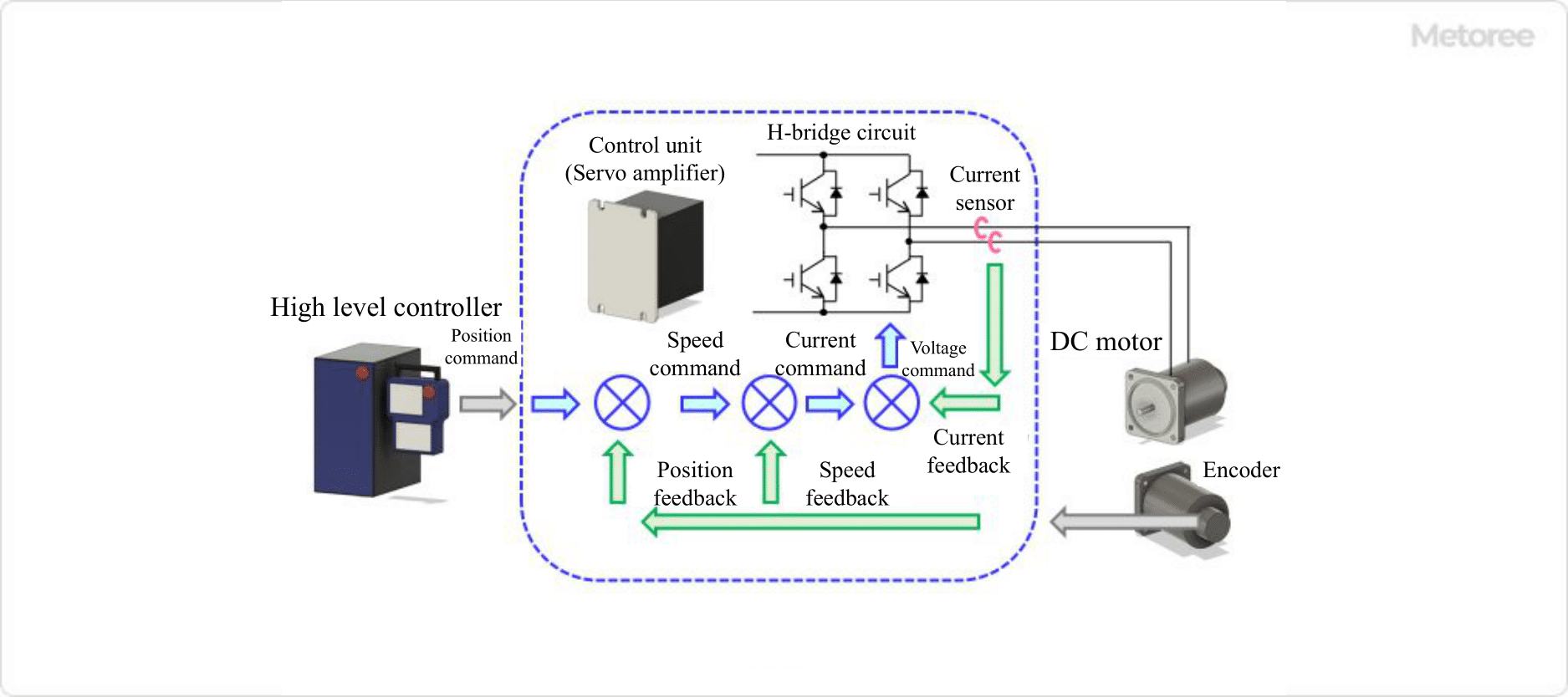
Figure 3. Control of DC servo motors
DC servo motors can be controlled in the following three ways
1. Position Control
DC servo motors are equipped with an encoder, a sensor that detects rotation angle and position and feeds back the detected rotation speed and position to the controller. If a position deviation from the command position is detected, a position correction command is issued by applying a gain to the amount of deviation to enable highly accurate control that moves the motor to the desired position and then stops the motor.
2. Speed Control
The simplest way to control the speed of a DC motor is to vary the voltage applied to the motor. In the case of a DC servo motor, a variable resistor is used to control the speed of the motor.
For DC servo motors, instead of a variable resistor, the voltage applied to the motor is controlled via an H-bridge composed of power semiconductors such as IGBTs and FETs that are incorporated in the servo amplifier.
On the other hand, the speed control of AC motors requires changing not only the voltage applied to the motor but also the drive frequency, whereas DC motors are widely used in small motors for speed control because they only change the voltage.
3. Torque Control
Torque control of the DC Servomotor is based on the proportional relationship between current and torque. Therefore, the current is controlled to maintain the torque at a constant value by detecting the current from the voltage value of the current sensor or current shunt resistor and feeding back the current command.
Other Information on DC Servomotor
Types of Servo Motors
Servomotors are constructed to be more durable than ordinary motors to operate repeatedly even in harsh environments and can be broadly classified into two types: DC Servomotors and AC Servomotors.
1. DC Servo Motor
DC Servomotor is a servomotor driven by a DC power supply. DC Servomotor is used in a wide variety of applications because it is easier to control rotation and more efficient than AC Servomotor, and its simple mechanical structure makes it inexpensive. However, the disadvantage of DC servomotors is that they have mechanical wear parts called “brushes” that require periodic replacement and maintenance.
2. AC Servo Motor
AC Servomotors are servo motors driven by an AC power source. Compared to DC motors, AC Servomotors are more complicated to control, but they are used in equipment in almost all industrial fields due to their high practicality, such as the progress in control technology and the trend toward smaller and lighter robots.
There are two types of AC motors: synchronous (SM) motors that use permanent magnets and induction (IM) motors that do not use permanent magnets, but currently synchronous motors are mainly used.