What Is a Ball Screw?
 A ball screw is a type of feed screw that converts rotational motion into linear motion to move the position of a component. The screw shaft and nut are actuated by a ball. As the screw shaft and nut rotate relative to each other, the balls roll in an endless cycle. The sliding resistance between the screw and nut is much lower than that of conventional trapezoidal screws.
A ball screw is a type of feed screw that converts rotational motion into linear motion to move the position of a component. The screw shaft and nut are actuated by a ball. As the screw shaft and nut rotate relative to each other, the balls roll in an endless cycle. The sliding resistance between the screw and nut is much lower than that of conventional trapezoidal screws.
The precision grade of the screw and ball allows for precise motion, resulting in high positioning accuracy. They are used in automotive steering devices and precision machine tools.
Uses of Ball Screws
Ball screws are machine elements that convert the rotational motion of a motor, etc., into linear motion. Major applications include transportation and positioning of products and parts, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, industrial robots, and machine tools. Since the amount of travel (lead) per revolution of a ball screw can be precisely reproduced, high positioning accuracy can be achieved by combining it with a stepping motor.
In NC-controlled machine tools, ball screws are used to configure the feed mechanism and obtain precision positioning accuracy. Ball Screws are also used in food machinery, medical equipment, robots, injection molding machines, printing equipment, amusement equipment, automobiles, trains, aircraft, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, and inspection equipment.
Principle of Ball Screws
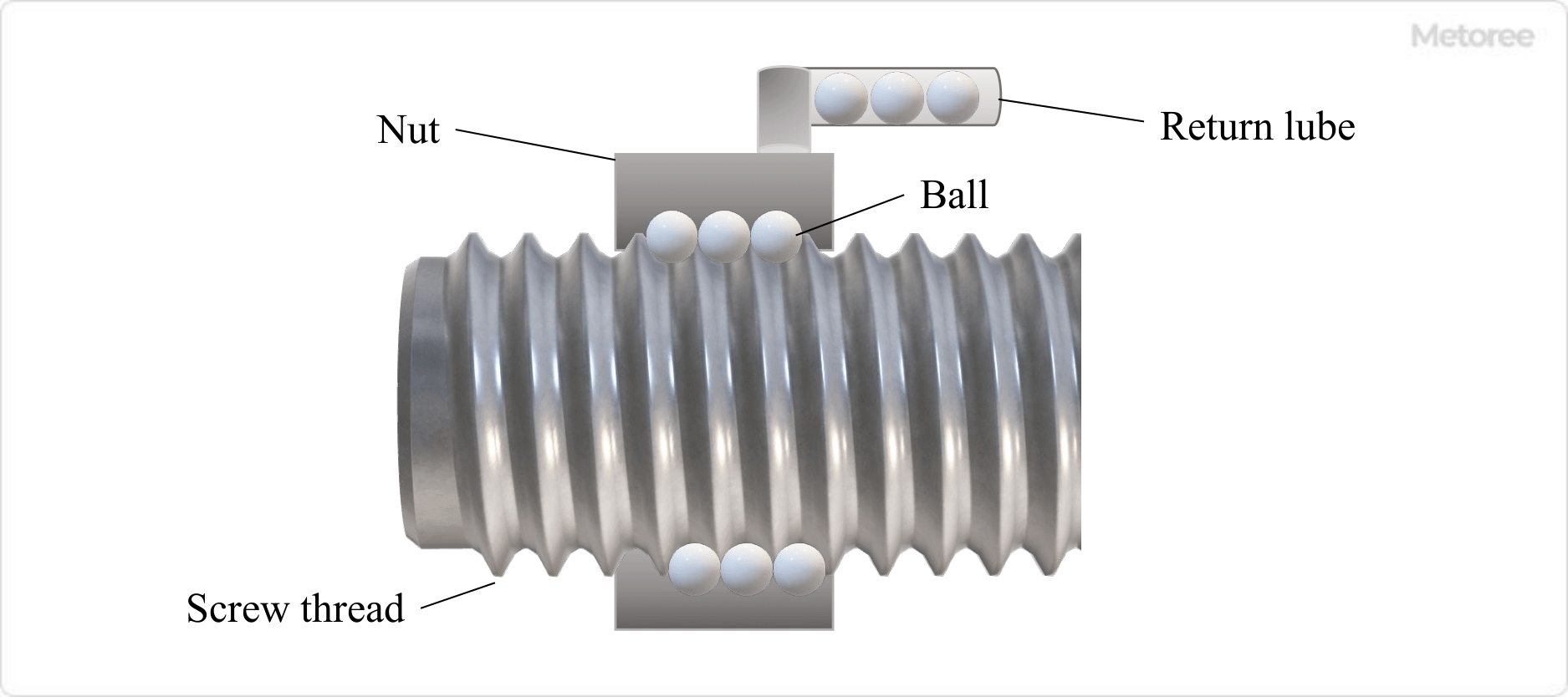
Ball screws are machine element parts consisting of a screw shaft, nut, and ball, which convert rotational motion into linear motion or linear motion into rotational motion. This component uses tribology technology that allows a ball to be placed between the screw shaft and nut and to roll lightly. It converts sliding contact motion on the screw surface into rolling contact motion. Balls need to circulate infinitely, so circulating parts are required.
There are several types of recirculation systems, such as return tube type, end deflector type, end cap type, and piece type, as well as return plate type, and their applications are classified according to size and precision. When using ball screws, a guide rail is required to guide the nut. Guide rails bear vertical loads and moment loads other than the axial load applied to the nut.
The threaded shaft is made to move with high accuracy by combining the length of the lead, which is the amount of movement per nut revolution, with the number of threaded strips. The ball is pressurized to eliminate any nut backlash, and high positioning accuracy can be obtained without uneven rotation of the screw shaft or nut.
Other Information on Ball Screws
1. Characteristics of Ball Screws
Ball screws are capable of converting the rotational motion of a machine into a linear motion. Conversely, it can also convert linear motion into rotational motion. The torque to drive the screw shaft rotation can be reduced to 1/3 or less compared to that of an ordinary screw. Therefore, the motor that drives the Ball Screw can be made smaller and lighter.
The difference between starting frictional torque and kinetic frictional torque is small, and a stick-slip phenomenon can be avoided, enabling high-precision machine control. Nuts can be preloaded by using two nuts or by using balls with a larger diameter in advance. Backlash is eliminated and rigidity is increased, resulting in better controllability.
The wear life and rolling fatigue life of ball screws can be predicted by calculation, thus increasing operational reliability. The coefficient of friction at the contact surface between the screw and nut is about 0.1 to 0.2 for a sliding screw, whereas it is 0.002 to 0.004 for a Ball Screw. Therefore, the transmission efficiency is high and over 90%.
Since dimensions and accuracy are internationally standardized and mass-produced in dedicated factories, they are easy to use and cost-effective. On the other hand, ball screws have the disadvantage of being vulnerable to impact. Since the sliding parts are in point contact, they are prone to leave dents and other marks when subjected to impact. In addition, foreign matter entering the sliding parts may cause malfunctions or failures. When used as a slide shaft of a machine tool, it is necessary to cover it with a cover, etc., to prevent chips from getting into it.
2. Manufacturing Method of Ball Screws
Ball Screws can be classified into “rolling” and “grinding” depending on the method of production.
Rolling Ball Screw
In this method, a round bar is pressed against a tool called a rolling die while rotating to form a threaded groove by plastic deformation. Compared to grinding, the accuracy grade tends to be lower.
Ground Ball Screw
This method uses a machine tool called a thread grinder to form the thread groove by grinding. Since cylindrical grinding is performed after heat treatment, the surface is smoother than that of rolling. This method is used when high-precision machine control is required, such as for slide axes of small machine tools for precision instruments.