What Is a RTD?
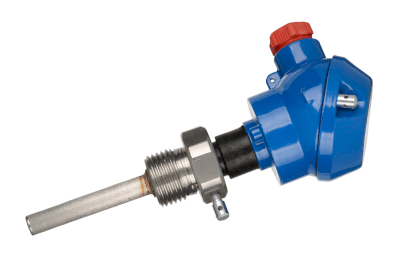
RTD stands for resistance temperature detector. It is a type of temperature sensor, also called a resistance thermometer.
RTD is a temperature sensor that utilizes the property of electrical resistance of metals to increase with increasing temperature.
The RTD element, which is the temperature sensing part of RTD, is made of a metal with a large temperature coefficient of electrical resistance and good linearity, such as platinum, nickel, or copper. Because the relationship between the resistance of the metal and the temperature is precisely known, RTDs can measure temperature with high accuracy.
Uses for RTDs
Because RTD is a highly accurate, stable, and reproducible temperature sensor, it can be used to measure the temperature of pipes, ducts, and rooms of air conditioning in buildings and factories. They are used to monitor the condition of solar power generation. They are also used to control the temperature in clean rooms, refrigerators, and freezers in semiconductor factories, saunas, swimming pools, hot springs, and plastic greenhouses; and to measure the internal temperature of food.
In particular, RTDs are often used for precise measurement of ambient temperatures around motors, motors, and high-voltage equipment in factories because of their low susceptibility to electrical noise.
Characteristics of RTDs
The electrical resistance of metals generally varies almost in proportion to temperature. This is because, as temperature rises, the movement of metal atoms becomes more active, making it more difficult for electrons to pass through and increasing electrical resistance.
RTDs use this principle to measure temperature. Specifically, a constant current is applied to the RTD, the potential difference between the two ends of the RTD is measured, the resistance is calculated from Ohm’s law (E=IR), and the temperature is determined from the standard resistance table for the metal used in the RTD element.
There are three conductor formats for measuring the resistance of RTDs: 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire, each with a different measurement circuit.
The 2-wire type is inexpensive, but the internal resistance of the conductors is added to the measured resistance, resulting in a large measurement error for RTDs with low resistance.
The 3-conductor type is most often used for industrial measurements because the conductor resistance is offset at both ends of the bridge in the measurement circuit, making conductor resistance virtually negligible.
The 4-conductor type is even more precise than the 3-conductor type because the current supply and voltage detection terminals exist separately and are not affected by conductor resistance.
While RTDs have advantages, such as high accuracy, excellent stability, and good sensitivity to temperature, making them suitable for temperature measurements near room temperature. They also have disadvantages, such as being unsuitable for high-temperature measurements and being susceptible to mechanical shock and vibration due to their minute internal structure.