What Is Isobutane?
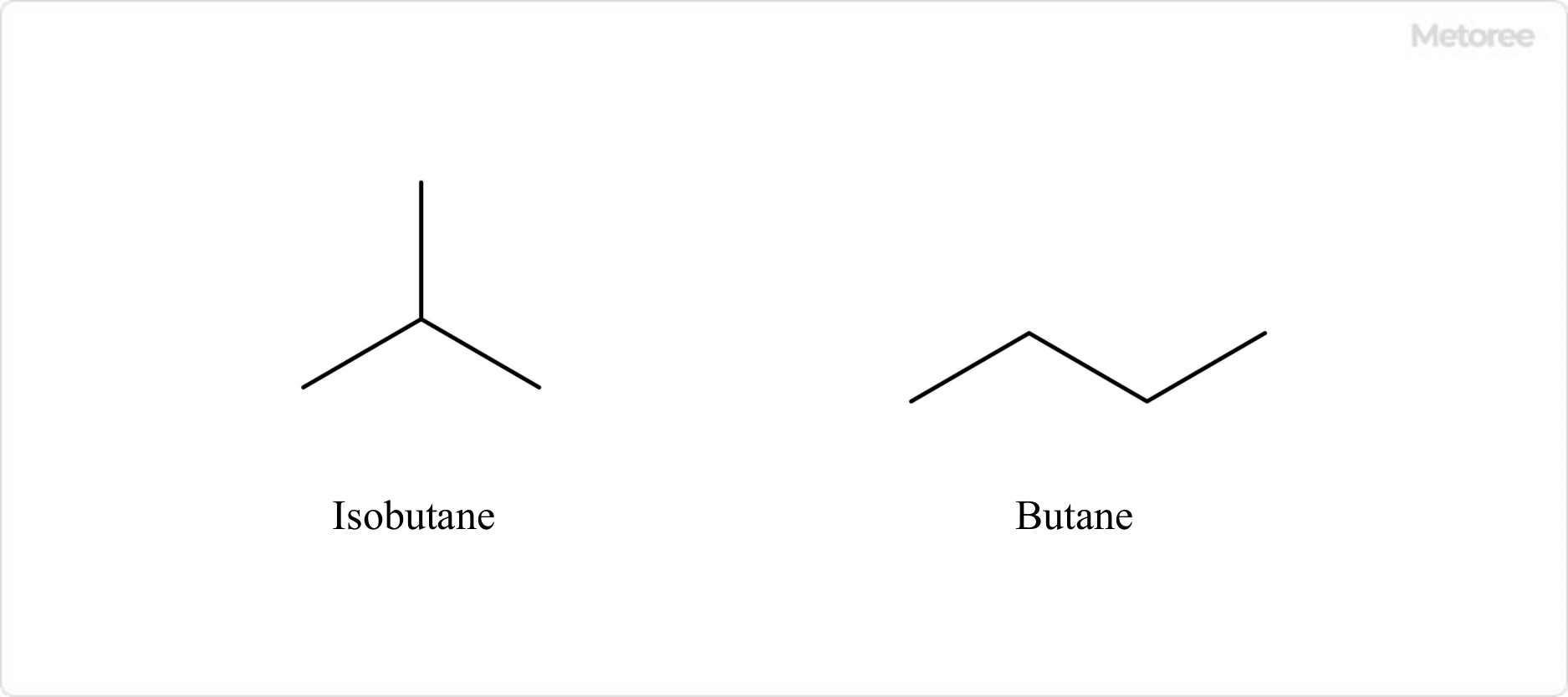
Figure 1. Isobutane and structural isomer (Butane)
Isobutane is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C4H10.
Its CAS number is 75-28-5. It is also known as 2-methylpropane and trimethylmethane. It is a structural isomer of butane and is found in the cracked gases of wet natural gas and petroleum hydrocarbons. It is synthesized mainly by isomerization of butane.
Under the Industrial Safety and Health Law, it is classified as a hazardous substance (flammable gas) in Appendix 1 of the Enforcement Order, and as a hazardous and toxic substance that should be labeled or notified by name. It is not regulated by the Labor Standards Law, the PRTR Law, the Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law, or the Fire Service Law.
Uses of Isobutane
Isobutane is mainly used as a substitute for CFC gas, as a refrigerant in air conditioners and refrigerators, and in sprays. Its refrigerant number, which is a number indicating the type of refrigerant as defined by the American Society of Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Engineers, is R600a.
Isobutane is also a substance used as a liquefied gas for household and industrial fuels because of its flammability and explosive properties. It is mainly used in cassette gases and lighters for outdoor use.
Its boiling point temperature is lower than that of butane, making it suitable for use in cold climates and winter mountaineering. Other uses include organic synthesis raw materials and atomizers. Isobutane is also used as a raw material for synthesis of isoparaffins, among others.
Properties of Isobutane
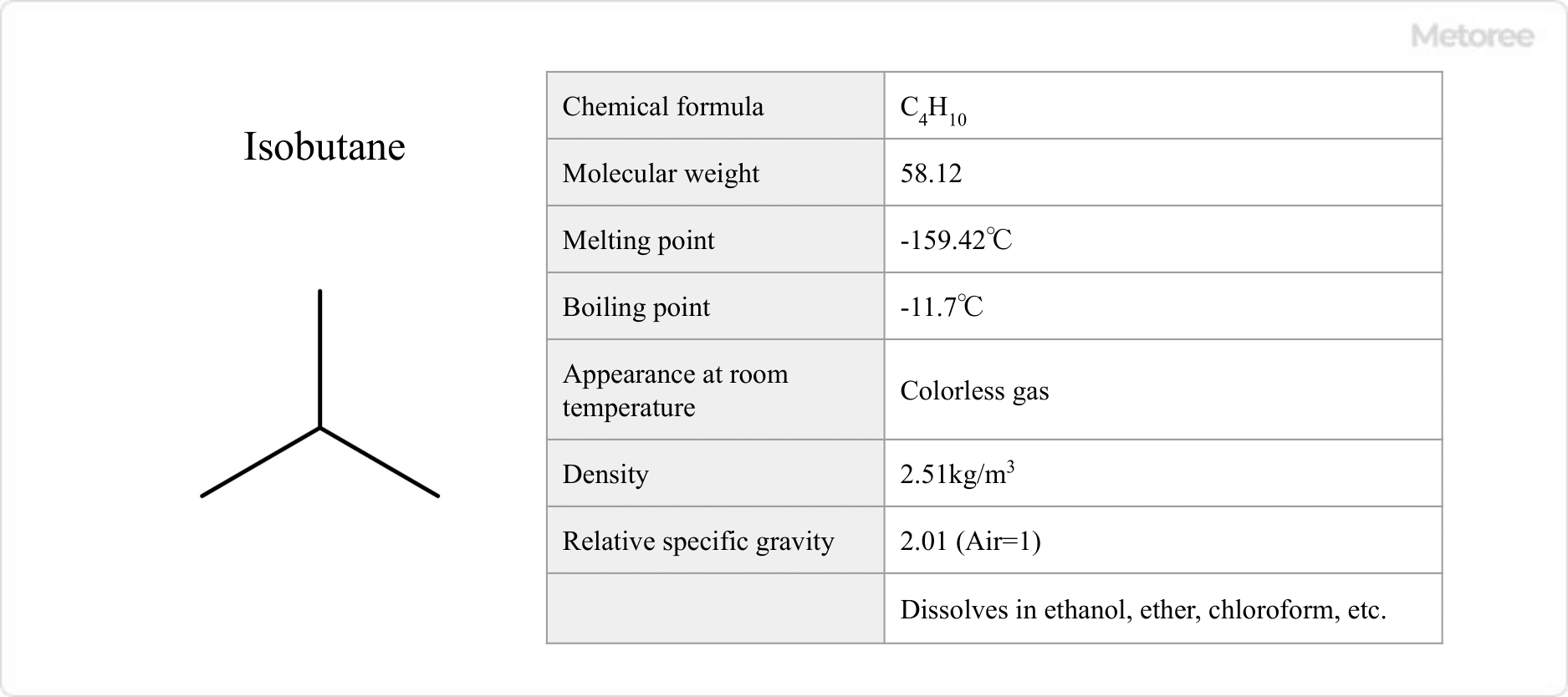
Figure 2. Basic information on isobutane
Isobutane has a molecular weight of 58.10, a melting point of -159.42°C, and a boiling point of -11.7°C. It is a colorless gas at room temperature.
It has a relative specific gravity of 2.01 with air as 1 and a density of 2.51 kg/m3. It is soluble in ethanol, ether, and chloroform. Its solubility in water is 48.9 mg/L.
Types of Isobutane
Isobutane is sold mainly as a high-pressure gas for industrial use. Products used for foaming polystyrene, polyethylene, etc., and special products include standard gases for calibration of flammable and toxic gas detectors.
The containers are welded steel containers, which are sold in the form of so-called gas cylinders. The contents can be 50 kg, 500 kg, etc. Standard gases for calibration of flammable and toxic gases are used for calibration of gas detectors at sites where flammable gases are used, and are diluted with air. It is available in 3.4L, 10L, 47L, etc.
Other Information on Isobutane
1. Reactivity of Isobutane
Isobutane reacts with strong oxidizers, acetylene, halogens, and nitrogen oxides to create fire and explosion hazards. Since isobutane is heavier than air, it moves along the ground and may generate static electricity due to flow, agitation, etc. Therefore, isobutane may ignite over long distances. Therefore, there is a high possibility of distant ignition.
2. Chemical Reaction of Isobutane
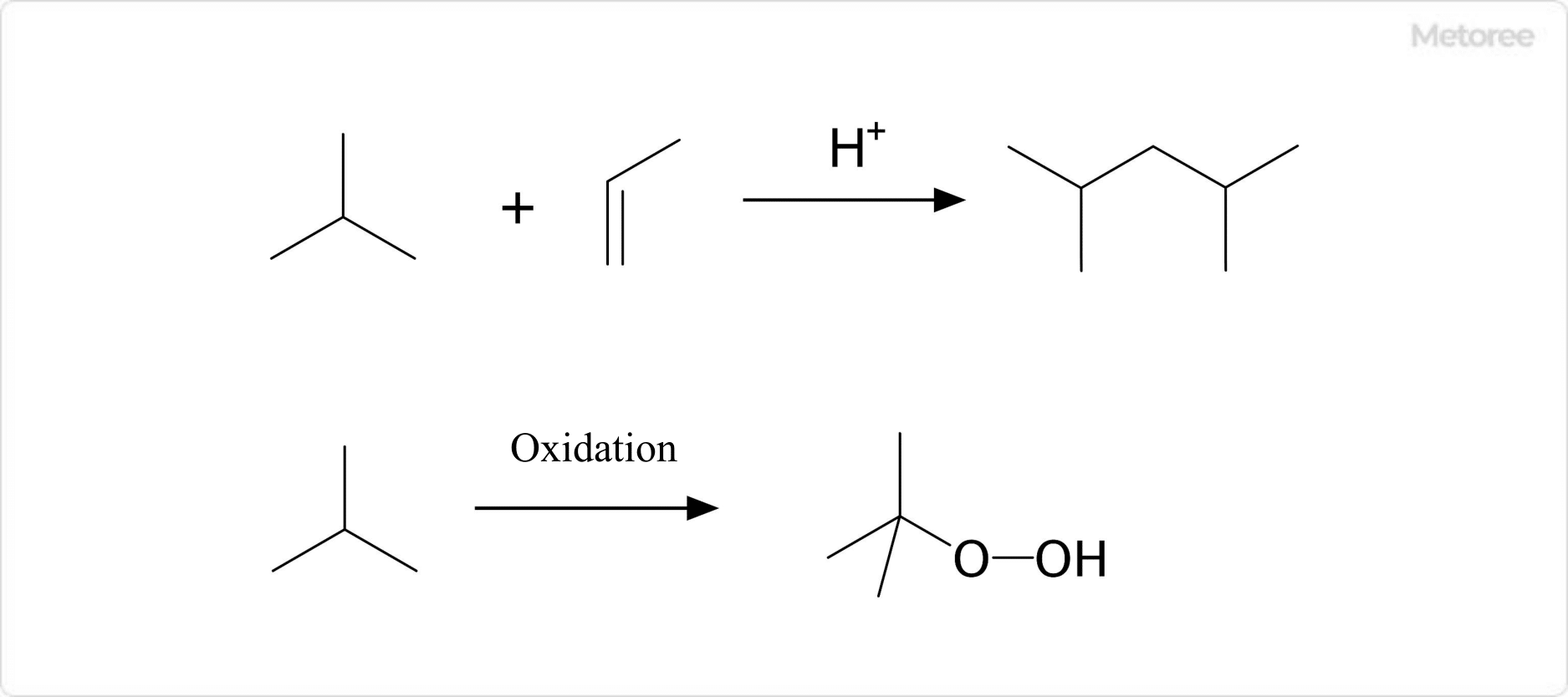
Figure 3. Chemical reaction of isobutane
Isobutane reacts with low molecular weight alkenes to form hydrocarbons under acidic conditions. This reaction is used in the petroleum industry to synthesize 2,4-dimethylpentene and 2,2,4-trimethylpentane.
Oxidation also yields tert-butyl hydroperoxide. This substance can be reacted with propylene to produce propylene oxide.
3. Hazards of Isobutane
The main hazards of Isobutane include the following
- Highly flammable/flammable
- Hazards to the circulatory system
- May cause drowsiness or dizziness
The GHS classification classifies isobutane as follows
- Flammable/flammable gas: Category 1
- Specific target organ toxicity (single exposure): Category 1 (circulatory system), Category 3 (anesthetic effect)
4. Regulatory Information on Isobutane
Isobutane is designated by the Industrial Safety and Health Law as a “Hazardous and Noxious Substance to be Labeled or Notified” and a “Hazardous and Flammable Gas” due to the above hazardous properties. It is important to handle isobutane properly in compliance with laws and regulations.