What Is Memory?
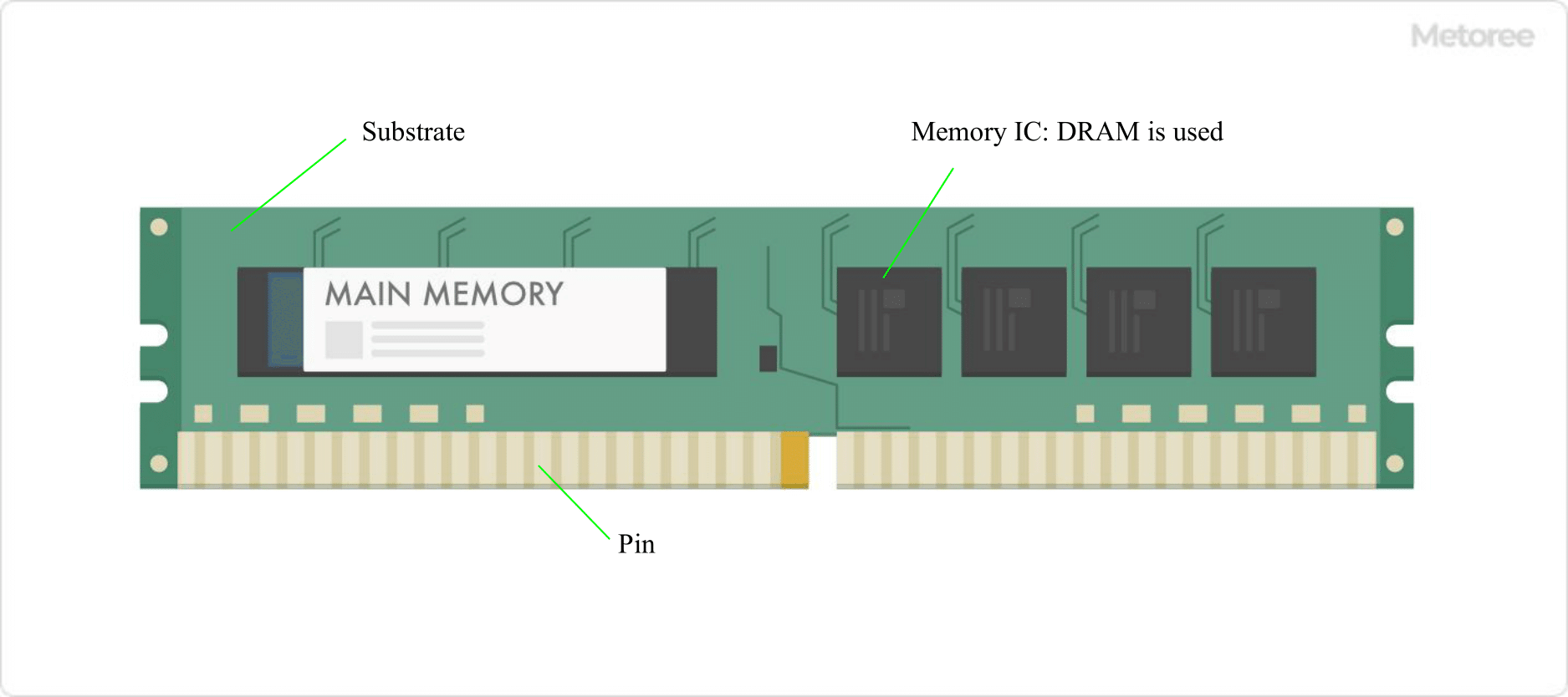
Figure 1. Memory outline drawing
Memory is a storage device composed of semiconductors that is used to record various data and programs.
Most of today’s computers are made of a configuration known as the Neumann type. The Neumann type is said to have been proposed by the American mathematician John von Neumann. The method proposed by Neumann is called a program-embedded computer, in which programs are stored in the computer’s memory and instructions are executed one at a time.
Memory is a device that stores data and programs and communicates with the CPU.
Uses of Memory
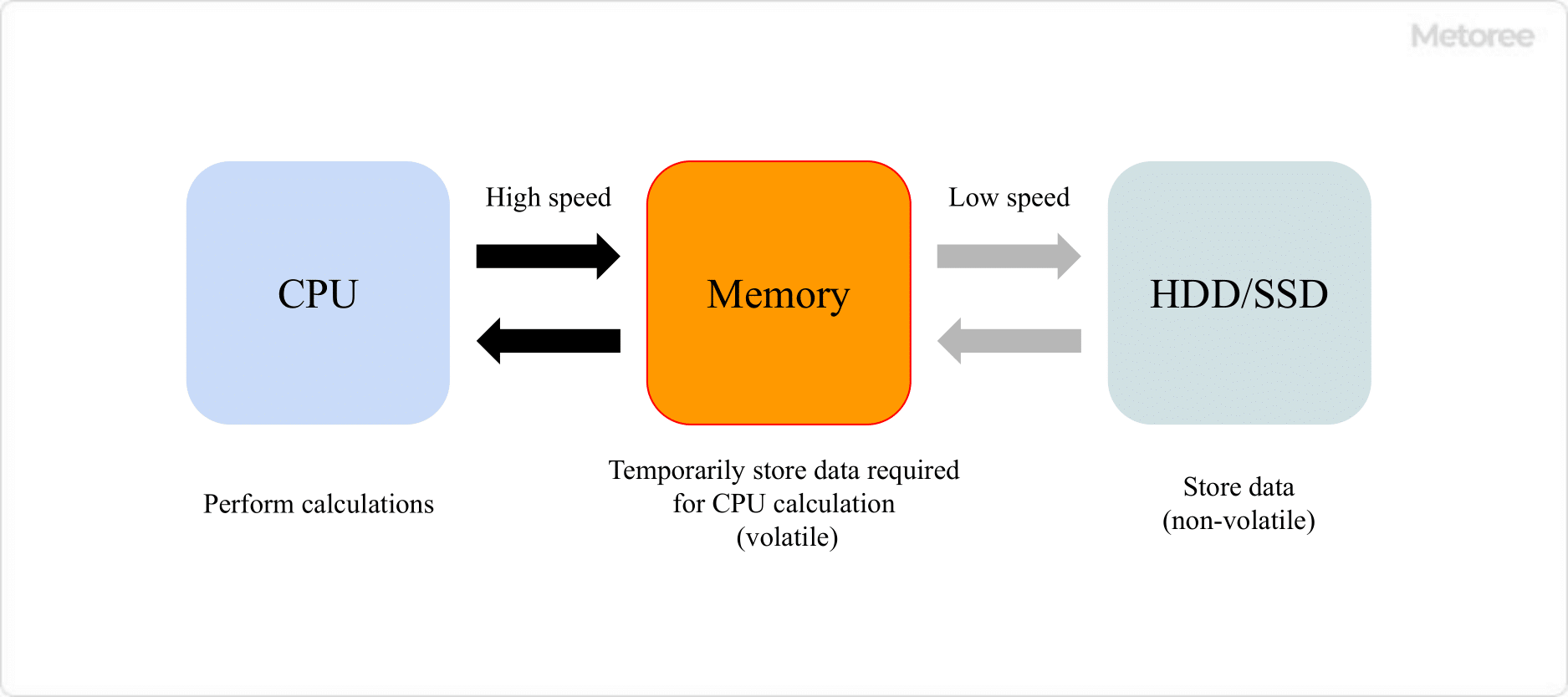
Figure 2. Components of a computer
A computer consists mainly of a CPU (central processing unit), memory (storage device), and HDD (hard disk drive). Program instructions and data are exchanged between the CPU and memory for processing. For this reason, almost all electronic devices with CPUs have memory.
Computers have the following five functions:
- Input Functions
Input is provided by a mouse or keyboard. - Output Function
Outputs the results of programmed processing to a monitor or other device. - Memory Function
Stores programs and data. - Arithmetic Functions
Performs four arithmetic operations and comparison processing. - Control Function
Controls input devices, output devices, memory devices, and arithmetic devices according to the program
The storage capacity of memory can be compared to the size of a work desk. The larger the memory capacity (the larger the working table), the more work can be performed in parallel.
If memory capacity is small, data that cannot be stored will be written to the HDD, but reading/writing data from the HDD will take longer than from memory, thus reducing the overall processing speed.
Principle of Memory
Memory is a storage device composed of semiconductors, and is classified into RAM and ROM according to function and form. Generally speaking, memory refers to RAM.
1. RAM
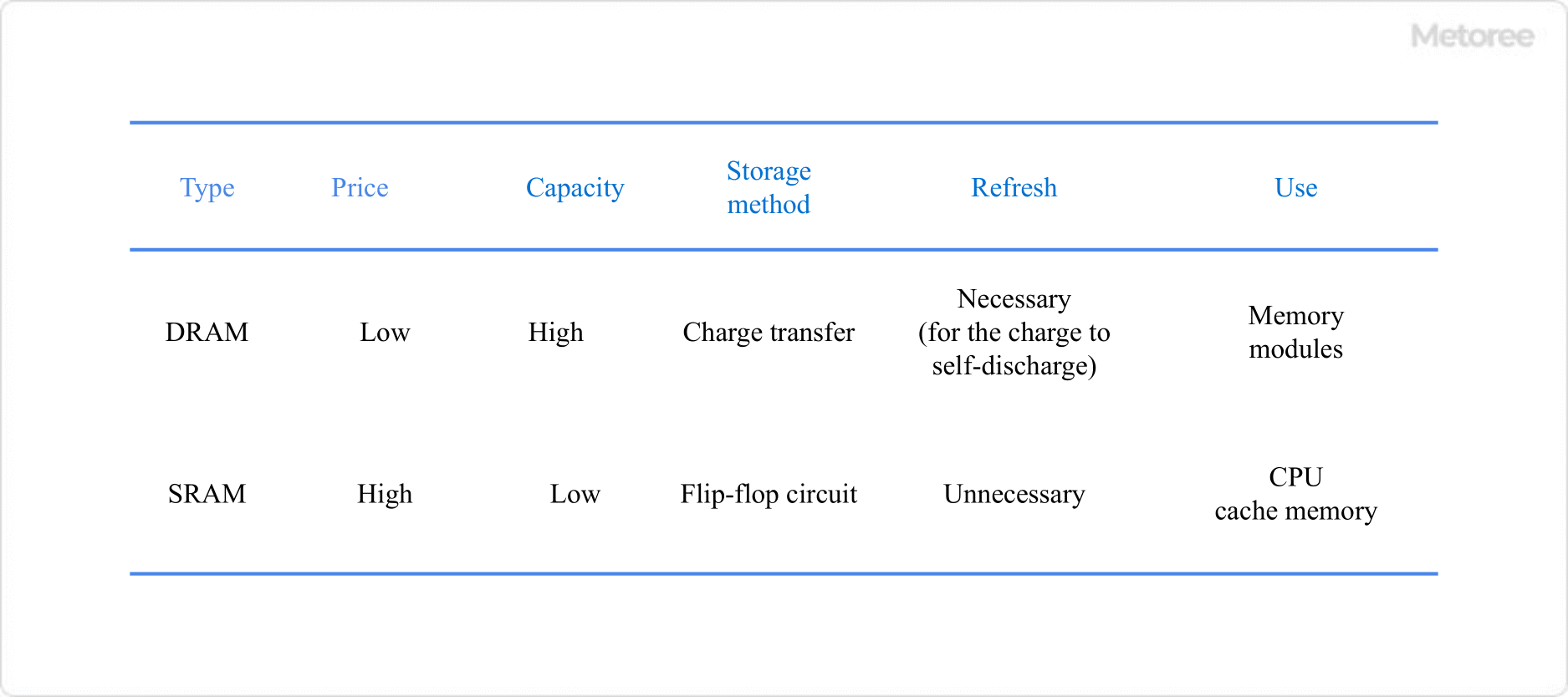
Figure 3. DRAM vs. SRAM
RAM stands for Random Access Memory and is used as the main memory, which is frequently accessed by the CPU to store programs and data temporarily. RAM is broadly classified into DRAM and SRAM.
DRAM stands for Dynamic RAM, which has a larger capacity than SRAM, but is slightly slower and requires recharging (refresh/recharge).
SRAM is an abbreviation for Static RAM, which is characterized by the fact that there is no charge transfer, and is faster and easier to use than DRAM, but has a smaller capacity. SRAM is used for cache memory in CPUs because of its high speed.
2. ROM
ROM is an abbreviation for Read Only Memory. ROM is a non-volatile memory that does not lose its data even if the power is turned off. For this reason, it is often used to record internal firmware, such as BIOS, HDDs, and routers. ROMs are classified into the following types according to whether they are writable or not.
- Mask ROM
Data is written at the time of manufacture and cannot be rewritten later. - EEPROM
A ROM whose contents can be rewritten. Recently, the internal memory of smartphones is sometimes referred to as ROM, and this ROM refers to this EEPROM. Flash memory, which is now widely used in USB devices, is an improved version of EEPROM that was developed earlier.