What Is an NPT Thread?
An NPT thread is a type of American National Standard Taper Pipe Thread, which is used for pipe end threads and pipe fittings.
The following types of NPT threads are used for pipe joints:
Uses of NPT Threads
NPT threads, like other tapered pipe threads, are primarily used in joints where tightness is required. They are particularly useful for joints in machinery, equipment, and plant piping that are designed and manufactured by the manufacturer according to American and ANSI/ASME standards.
Typical examples of use are pipe fittings used for threaded pipe joints. Note that there are various types of threaded pipe fittings with NPT threads.
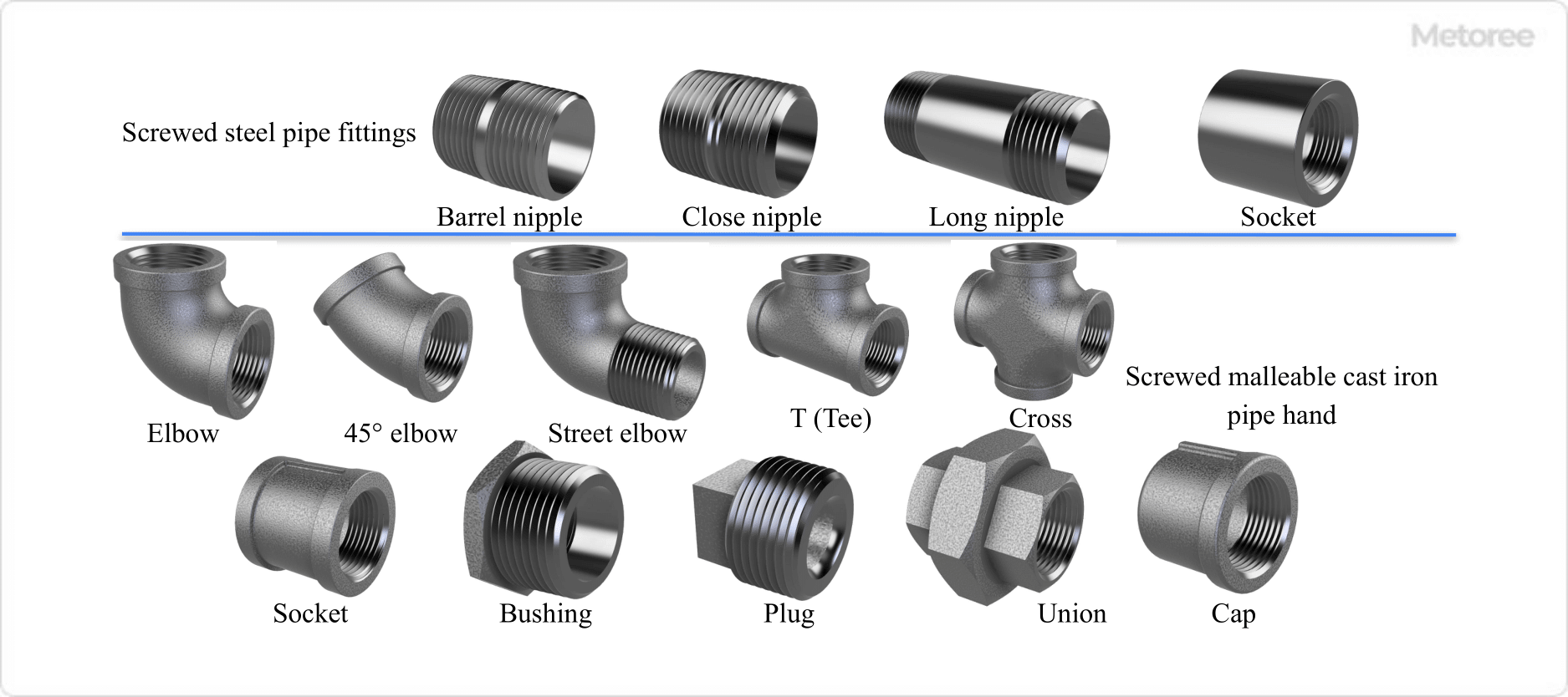
Figure 1. Threaded pipe fittings with NPT (National Pipe Taper) screws
NPT threads are also used in many piping assemblies, such as NPT female threads on valve joints and NPT male threads on pipe (tube) ends.
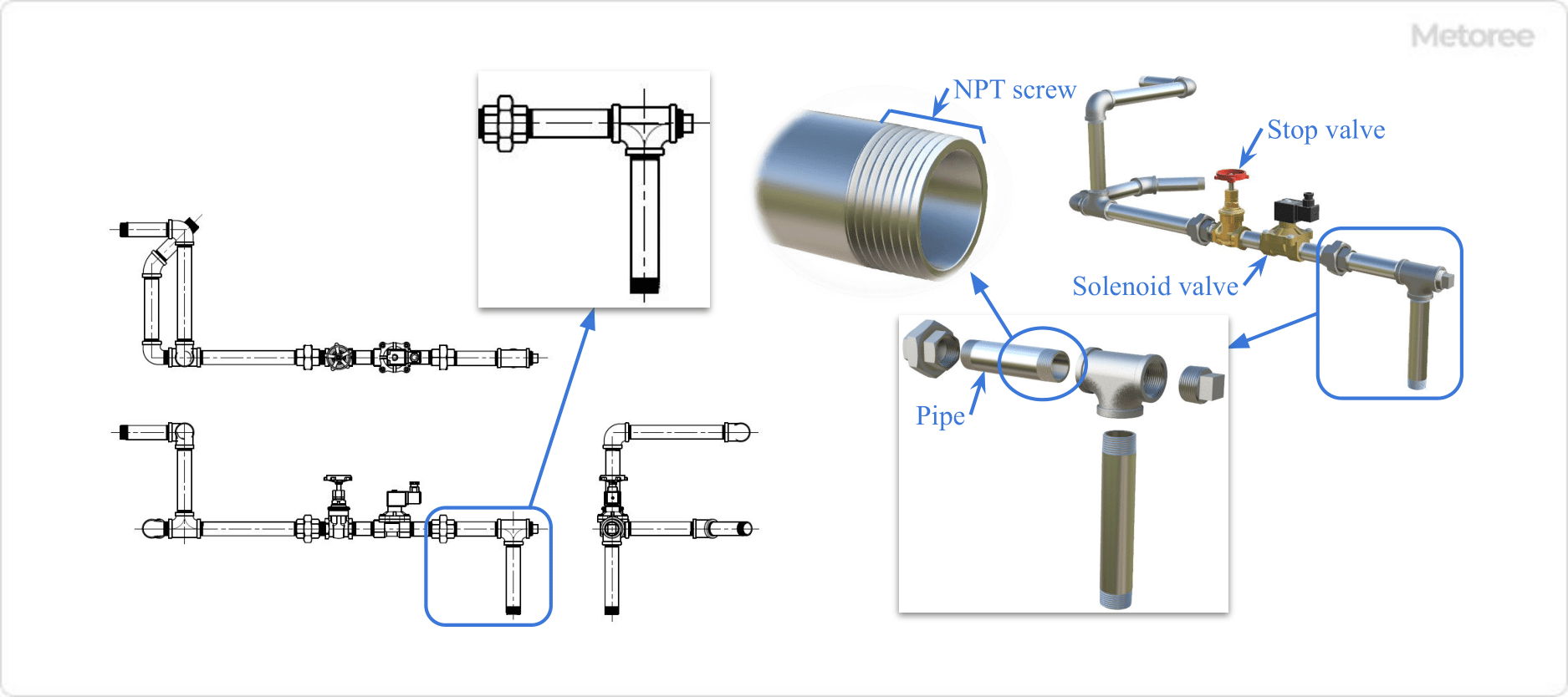
Figure 2. NPT screw piping assembly use cases
Principle of the NPT Thread
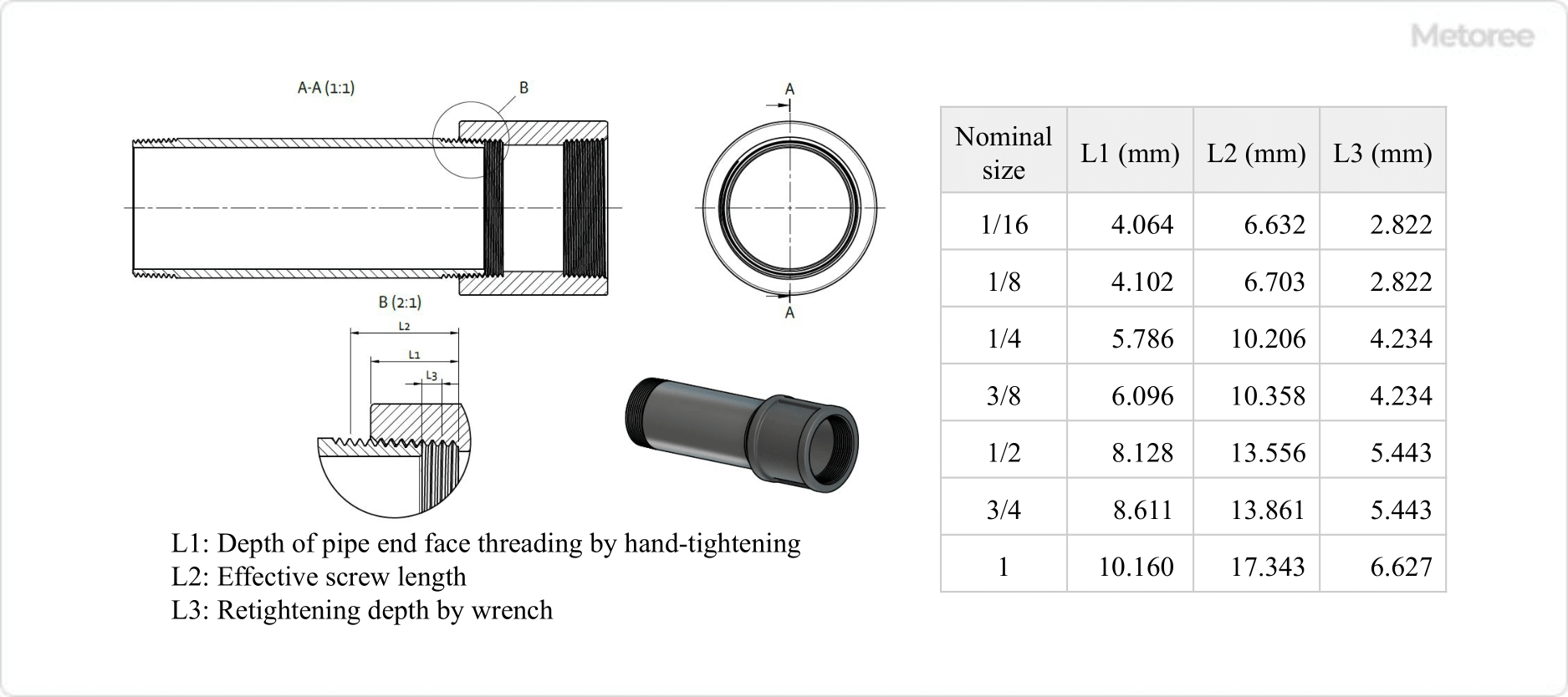
Figure 3. Tightening depth dimensions of NPT screw
The taper of an NPT thread is such that the line connecting the tops of adjacent threads (or the bottom of a thread trough) and the thread center axis are angled rather than parallel. This angle causes the male thread to taper toward the tip and the female thread to narrow from the end face of the hole to the back.
The deeper the NPT thread is tightened, the smaller the gap between the male and female threads becomes, and the stronger the tightening. However, care should be taken not to over-tighten the screw as this may result in damage to the screw.
The ANSI standard specifies the L1 dimension for each screw size as the tightening depth when hand-tightening. However, this dimension is only a guide and varies depending on the processing accuracy of the screw.
Torque control and tightening depth control are performed at each site.
Other Information on NPT
1. Standard Mountain Shape of NPT Thread
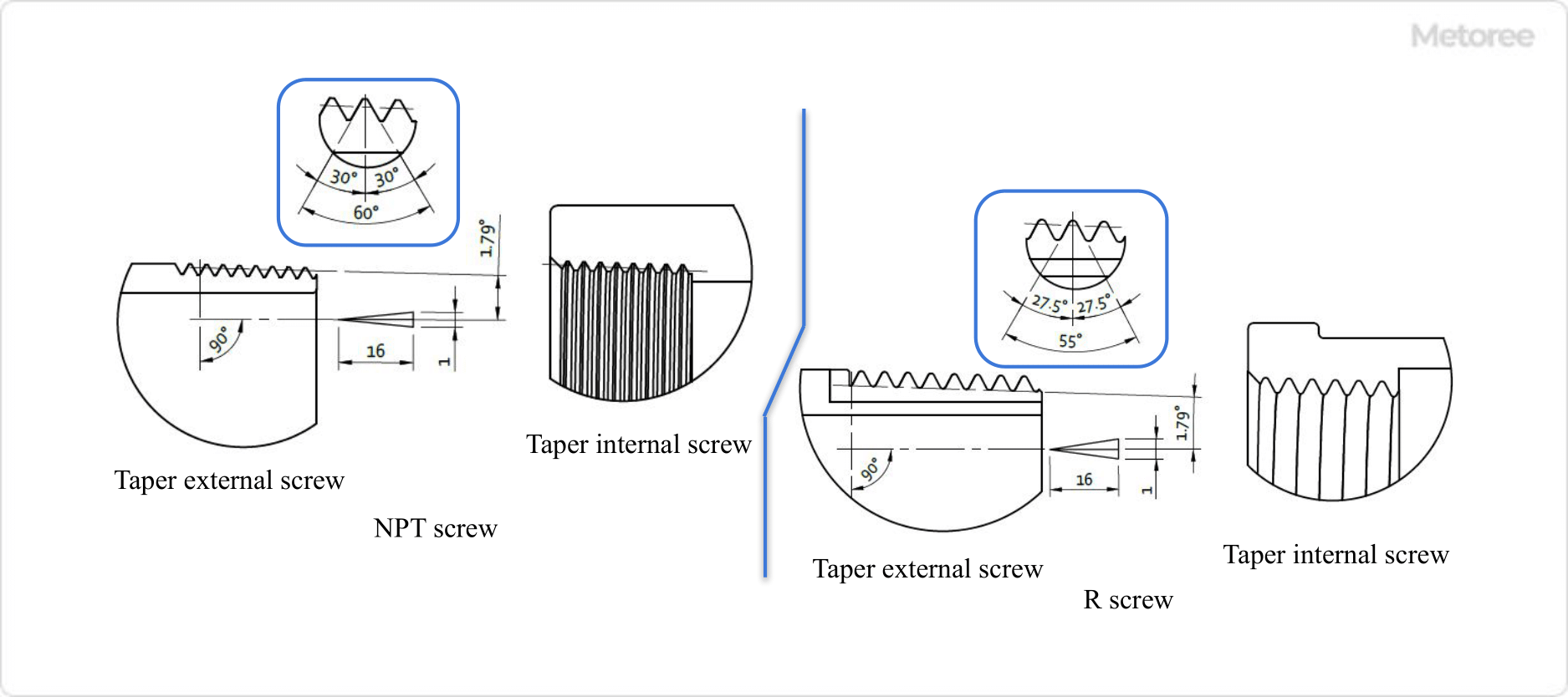
Figure 4. Reference mounting style for NPT and R screws
The reference profile of the NPT thread has a 1/16th taper to the center of the thread axis with an angle of 3.576° (1/32, 1.789° on one side) and a thread crest or trough angle of 60°. The reference profile of the NPT thread and R thread have the same 1/16th taper angle but a different crest or trough angle of 55°. Therefore, NPT threads and R threads are not interchangeable.
Taper ratio = 1/16 is a slope of 1 inch in the diameter direction for a thread center axial length of 16 inches.
2. Taper and Parallel Threads
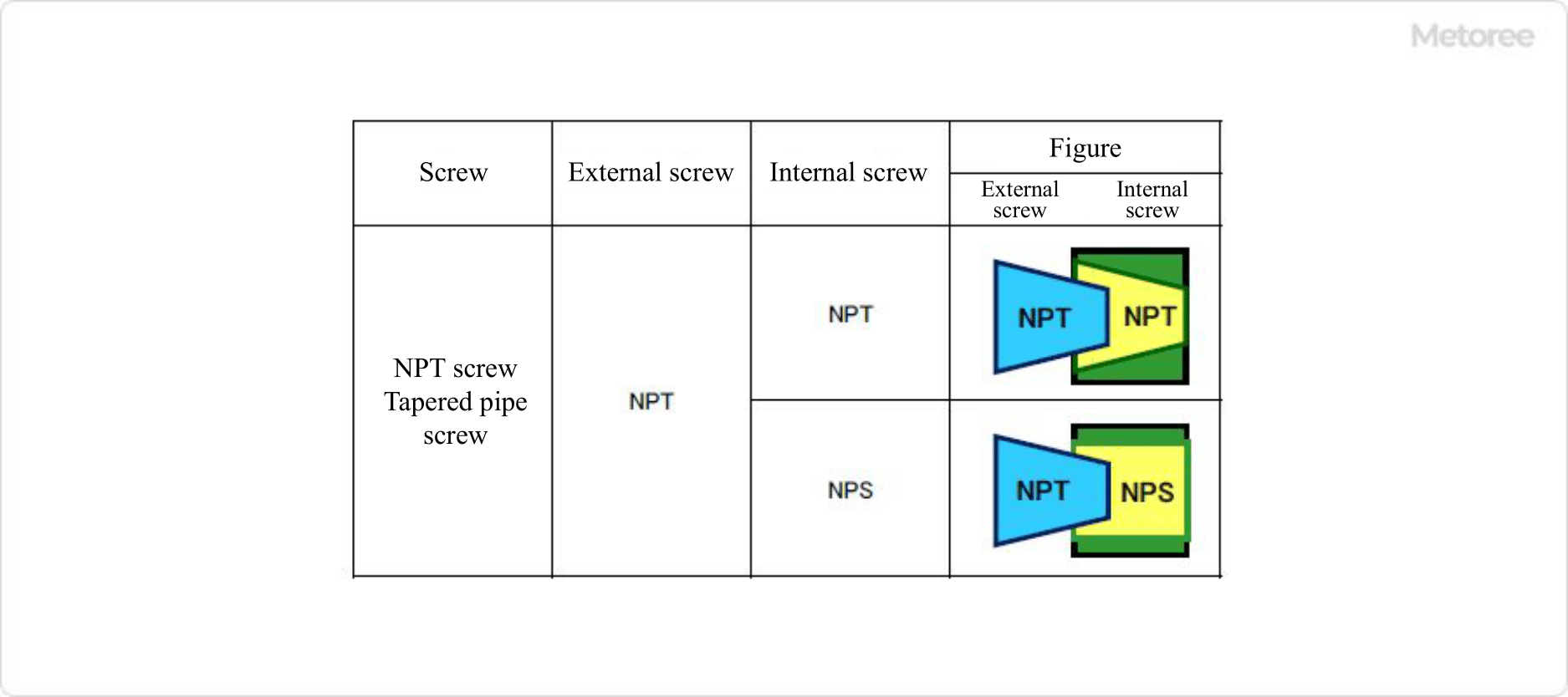
Figure 5. Combination of NPT and NPS screws
Generally, when tightening an NPT thread, wrap sealing tape or similar material around the male thread side to improve sealing. However, in addition to the NPT thread, the ANSI standard includes the NPTF thread (Dryseal USA Standard Taper Pipe Thread) as a taper thread for pipes, which can ensure tightness without the use of sealing material.
In contrast to the taper thread, there is the NPS thread (National Pipe Straight Pipe Thread), which is a parallel thread for pipes and is specified under the same ANSI standard number as the NPT thread.
3. Standards for NPT Threads
NPT threads are specified by the following standards:
ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 Pipe Threads, General Purpose (Inch)
ANSI (American National Standards Institute) is a representative standardization organization of the United States. ASME is the American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
A similar thread to the NPT thread is the R thread in the ISO standards, and is specified in the following:
JIS B0203, Taper Pipe Threads
ISO 7-1, Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads-Part 1: Dimensions, tolerances, and designation.
4. Taper Pipe Threads Other Than NPT
The taper threads used in Japan are almost always JIS R threads, although ANSI/ASME NPT threads are also used in some cases. However, NPT threads and JIS R threads are not interchangeable and cannot be used in combination in the same joint.
Therefore, care must be taken not to mistake NPT threads for other tapered screws during maintenance and servicing work. (Note that NPT threads can be identified by using an NPT thread gauge.