What Is Myrcene?
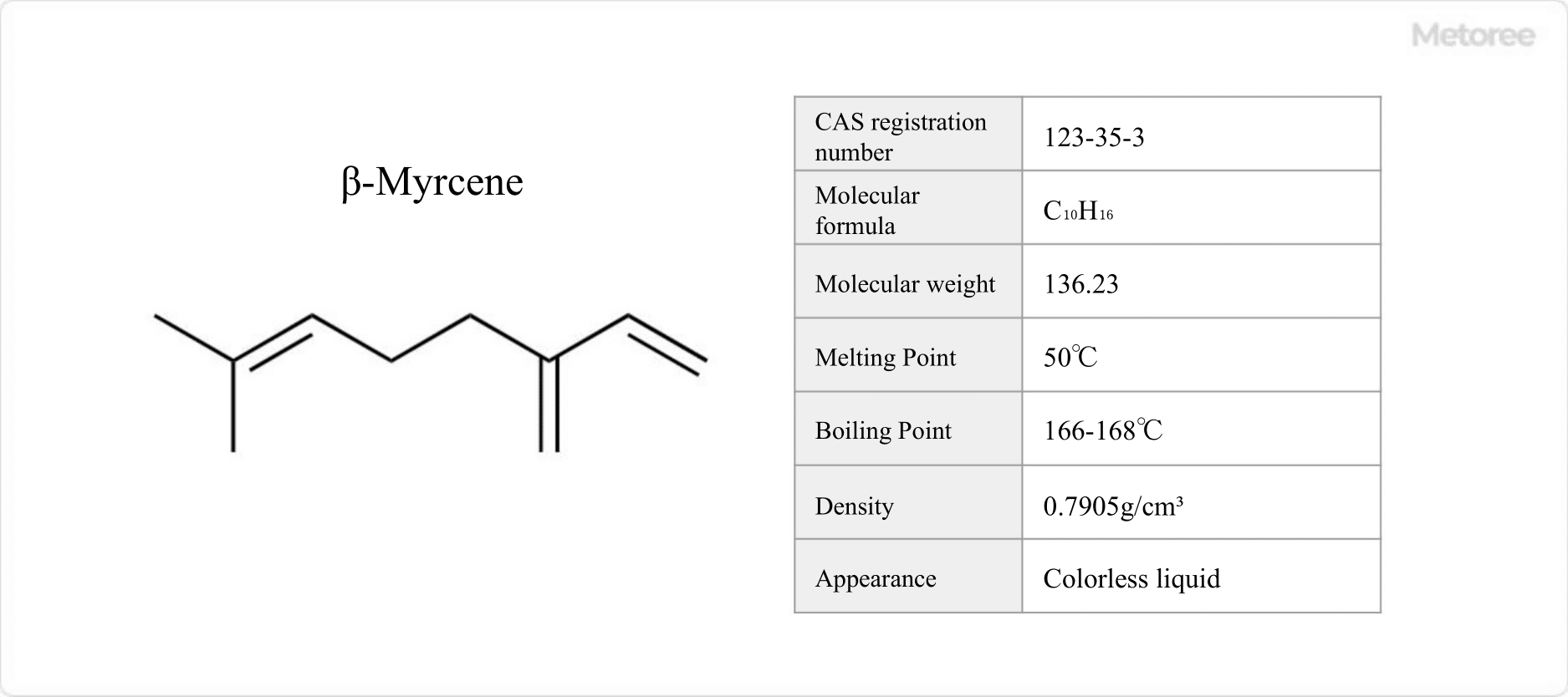
Figure 1. Basic Information on Myrcene
Myrcene, a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula C10H16, is notable for its presence in laurel, pine, wormwood, and mints. As β-myrcene, it serves as a pheromone for woodlice and an attractant, while being handled carefully due to its classification under fire laws.
Uses of Myrcenes
Valued for its muscle relaxant, sedative, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties, myrcene is utilized in dietary supplements, aroma oils, and the fragrance industry. It’s a precursor for various fragrances like menthol and citral and is involved in resin production.
Properties of Myrcenes
Myrcene exhibits a fresh coniferous aroma, with a melting point of 50°C and a boiling point of 166-168°C. It tends to polymerize at room temperature, enhancing its chemical interest.
Structure of Myrcenes
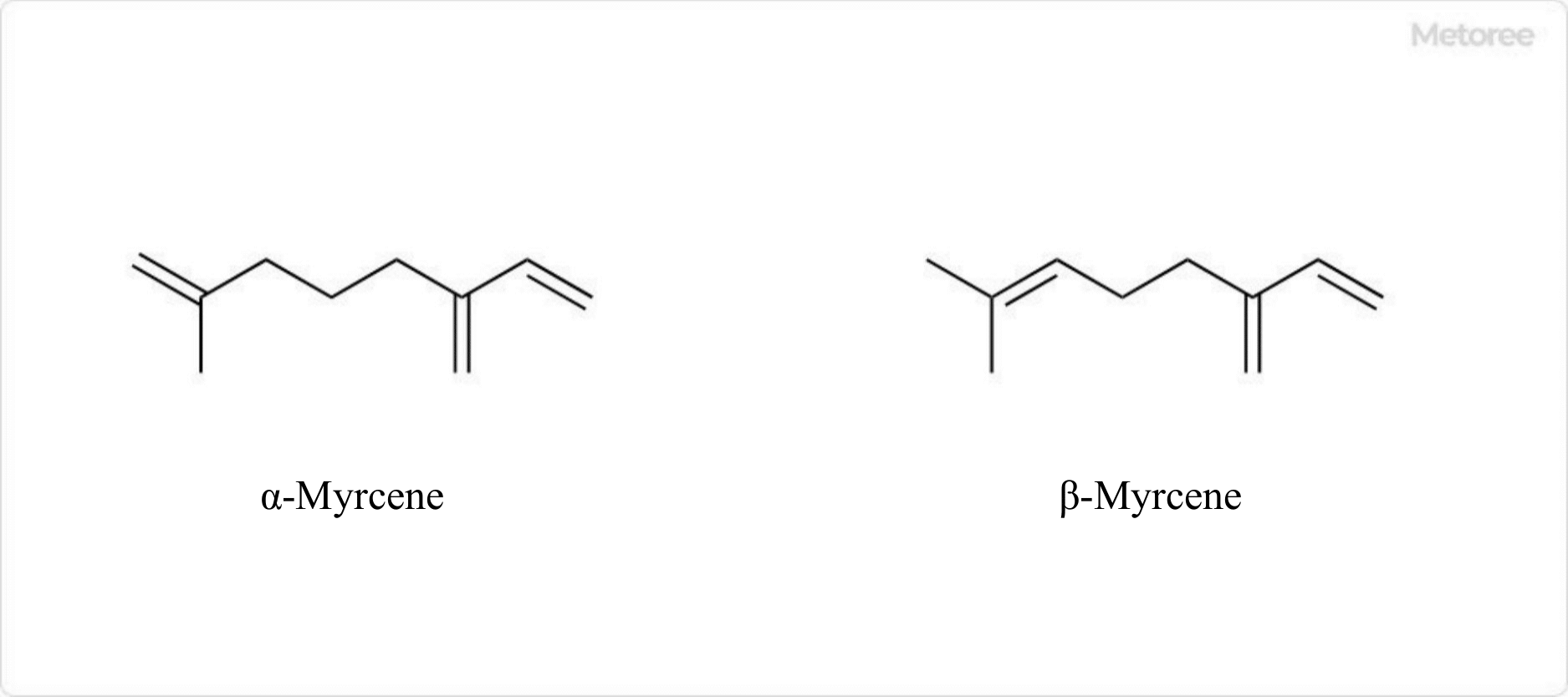
Figure 2. Myrcene Structure
As a monoterpene, myrcene consists of two isoprene units, with α-myrcene and β-myrcene as isomers. β-myrcene, predominant in nature, differs from α-myrcene by the position of its double bond.
Other Information on Myrcenes
1. Synthesis of Myrcenes
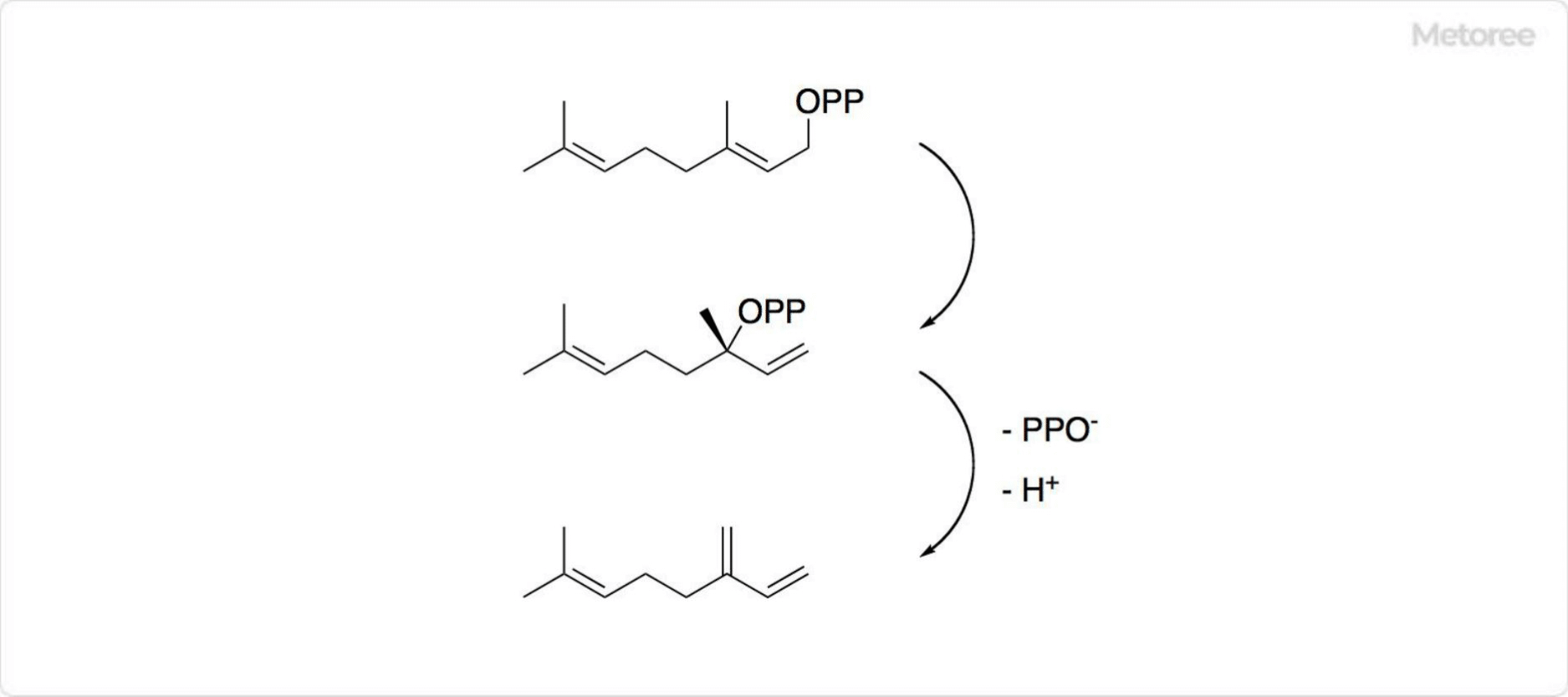
Figure 3. Synthesis of Myrcenes
Commercially, myrcene is mainly produced from the pyrolysis of β-pinene from turpentine oil, with a biosynthesis route involving geranyl diphosphate in plants.
2. Myrcene Reaction
Myrcene is convertible to myrcenol through hydroamination, followed by hydrolysis and amine removal via a palladium catalyst. It participates in Diels-Alder reactions, producing derivatives like hydroxymethylpentylcyclohexenecarboxaldehyde, known as Lyral.