What Is Phosphonic Acid?
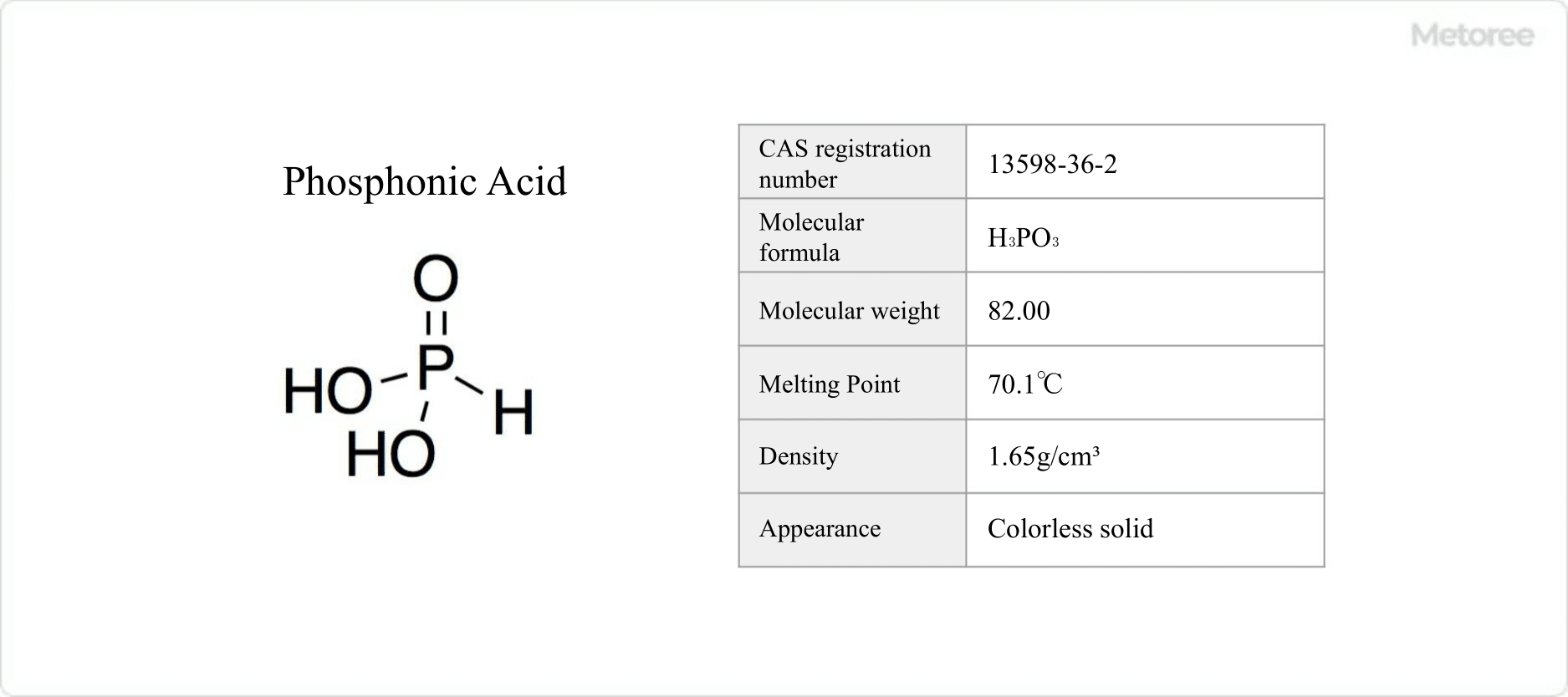
Figure 1. Basic Information on Phosphonic Acid
Phosphonic acid is an oxoacid of phosphorus with an oxidation number of +3, and chemical formula of H3PO3.
It has a molecular weight of 82.00 g/mol and a density of 1.65 g/cm3. Phosphonic acid is obtained through the hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride. In solution, it exhibits tautomerism with phosphorous acid.
In organophosphorus chemistry, phosphonic acid refers to a series of compounds with the general formula RR-P(=O)(OH)2, where R represents an organic group.
Uses of Phosphonic Acid
Phosphonic acid possesses strong reducing properties and serves as a reducing agent in electroless plating. Silver and copper can be plated from aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and copper sulfate, respectively.
P-alkylphosphonate dialkyl esters (R-P(=O)(OR’)2) are significant intermediates in industry. They are known as Horner-Emmons reagents and are utilized as raw materials for alkenes, fragrances, and pharmaceuticals.
Properties of Phosphonic Acid
Phosphonic acid melts at 70.1°C and appears as colorless, odorless crystals. Upon heating to 200°C, it decomposes into phosphine and phosphoric acid
It is insoluble in water, except for its alkali and calcium salts. The acid dissociation constants are pKa = 1.5 and 6.79.
Structure of Phosphonic Acid
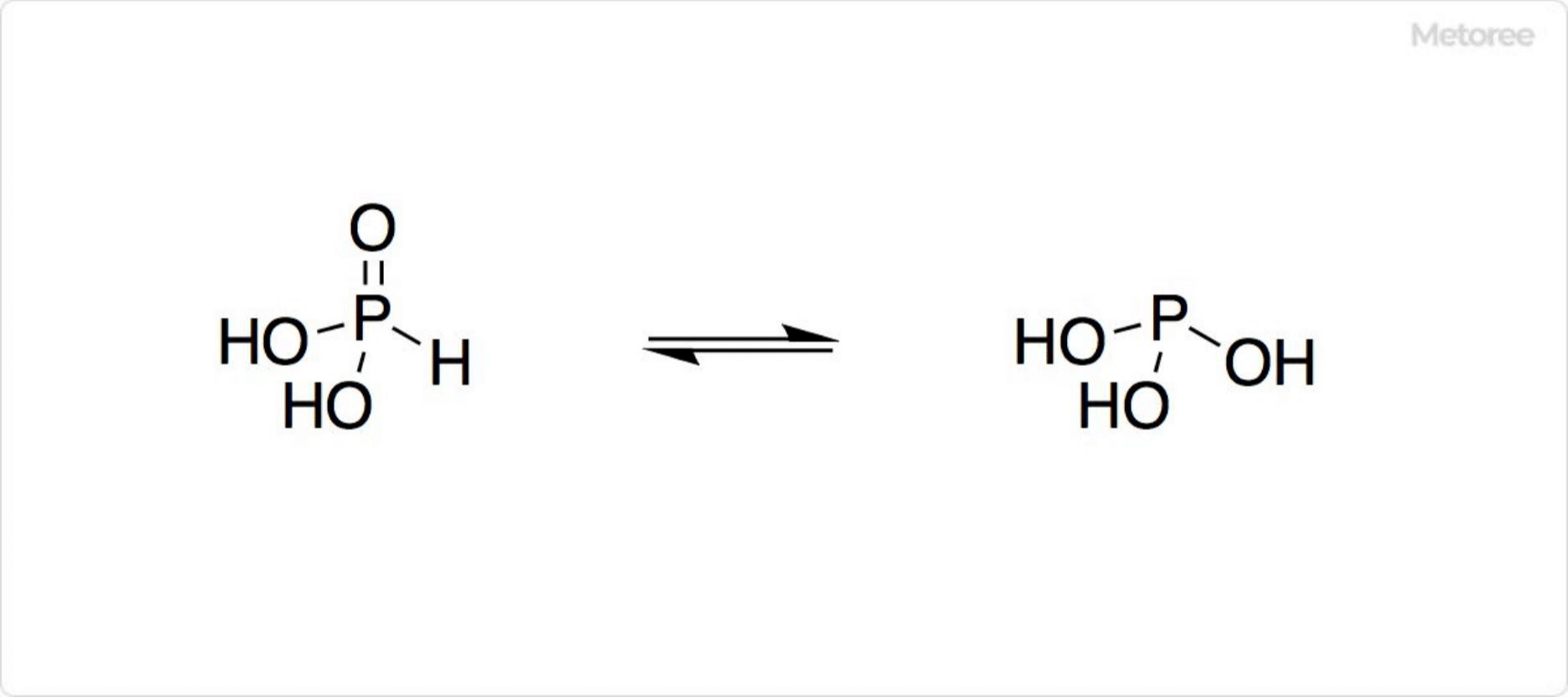
Figure 2. Structure of Phosphonic Acid
The formula of phosphonic acid is HP(=O)(OH)2. The presence of the P-H bond is confirmed by physical measurements, indicating the formation of only mono- and di-substituted salts, with no trisubstituted salts being produced. The molecule is tetrahedral in shape.
Phosphonic acid exists in tautomeric equilibrium with phosphorous acid. In this equilibrium, phosphonic acid predominates.
In organophosphorus chemistry, phosphonic acid broadly refers to compounds containing a phosphorus-hydrogen bond and a phosphoryl group, including various organic derivatives such as alkyl phosphonic acids.
Other Information on Phosphonic Acid
1. Synthesis of Organic Phosphonic Acid
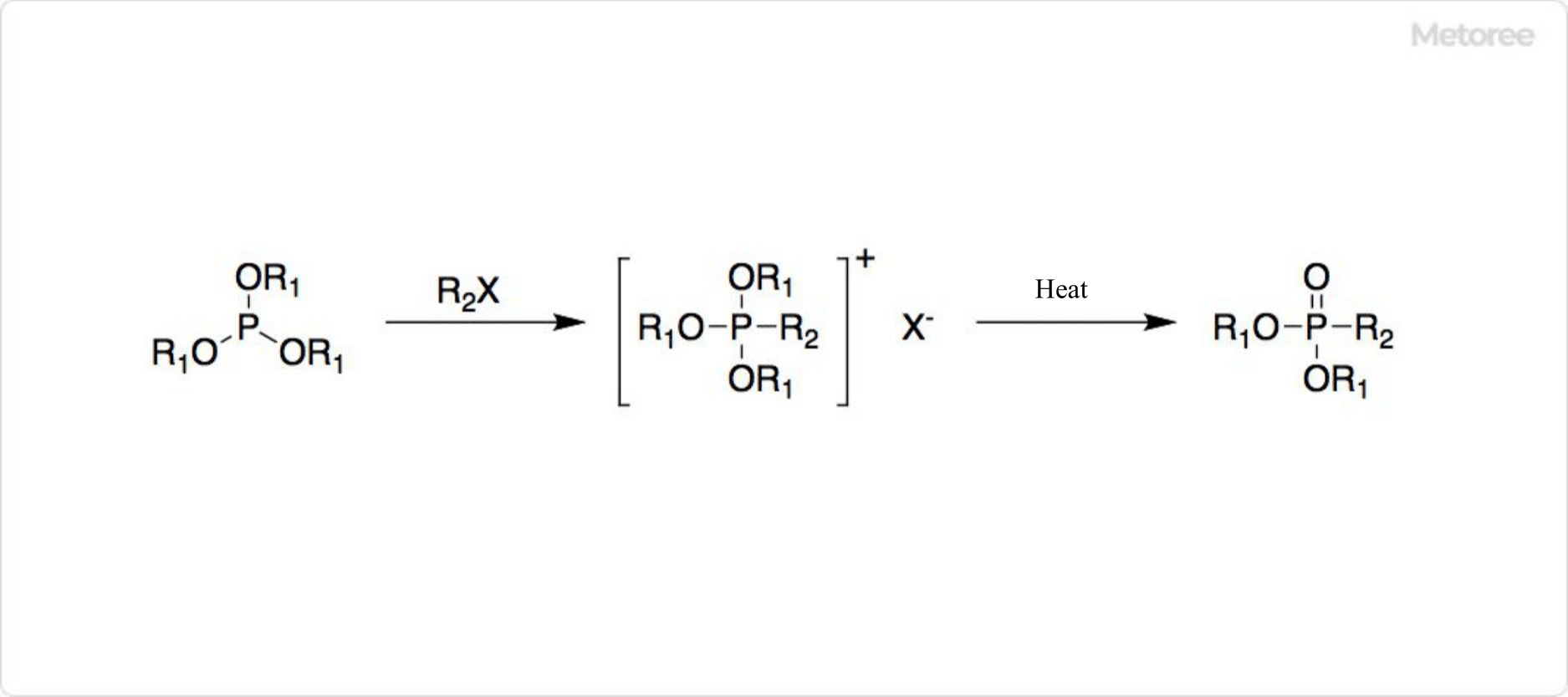
Figure 3. Synthesis of Organic Phosphonic Acid
Organic phosphonic acids are derivatives in which a hydrogen atom on the phosphorus atom is substituted with an alkyl group. Examples include methylphosphonic acid (CH3P(O)(OH)2) and phenylphosphonic acid (C6H5P(O)(OH)2).
Trialkyl phosphite esters undergo isomerization, transferring an alkyl group from the oxygen to the phosphorus atom, producing alkylphosphonic acid dialkyl esters through the Michaelis-Arbuzov Reaction.
2. Reaction of Phosphonic Acid
Phosphonic acid’s reactivity, especially that of the P-H bond, is leveraged for synthesis. Aminophosphonates, obtained through the Kabachnik-Fields or Pudovik reactions, serve as valuable chelating agents. Industrially, nitrilotris (methylene phosphonic acid) is synthesized.
Alkylation of phosphonic acid with an acrylic acid derivative via Michael addition produces a phosphonic acid bearing a carboxy group.