What Is Diacetone Alcohol?
Diacetone alcohol is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H12O2. It combines ketone and alcohol functional groups, resembling condensed acetone in its molecular structure. Its CAS number is 123-42-2.
Uses of Diacetone Alcohol
Diacetone alcohol serves as a solvent for fats, oils, resins, and nitrocellulose, and is used in printing inks, coating resins, metalworking fluids, lubricants, and cleaning agents. It is a high-boiling point solvent with low vapor pressure, ideal for reducing the viscosity of heavy organic liquids and minimizing temperature effects on viscosity.
It is also utilized in the production of cellulose ester lacquers, printing inks, alkyd and vinyl resin coatings, epoxy resins, water hardening agents, photographic films, anti-icing agents, artificial silks, and leathers. Additionally, diacetone alcohol is a precursor for various organic compounds such as methyl isobutyl ketone (solvents and paints), methyl isobutyl carbinol (electronic materials), and hexylene glycol (penetrating agents and detergents).
Properties of Diacetone Alcohol
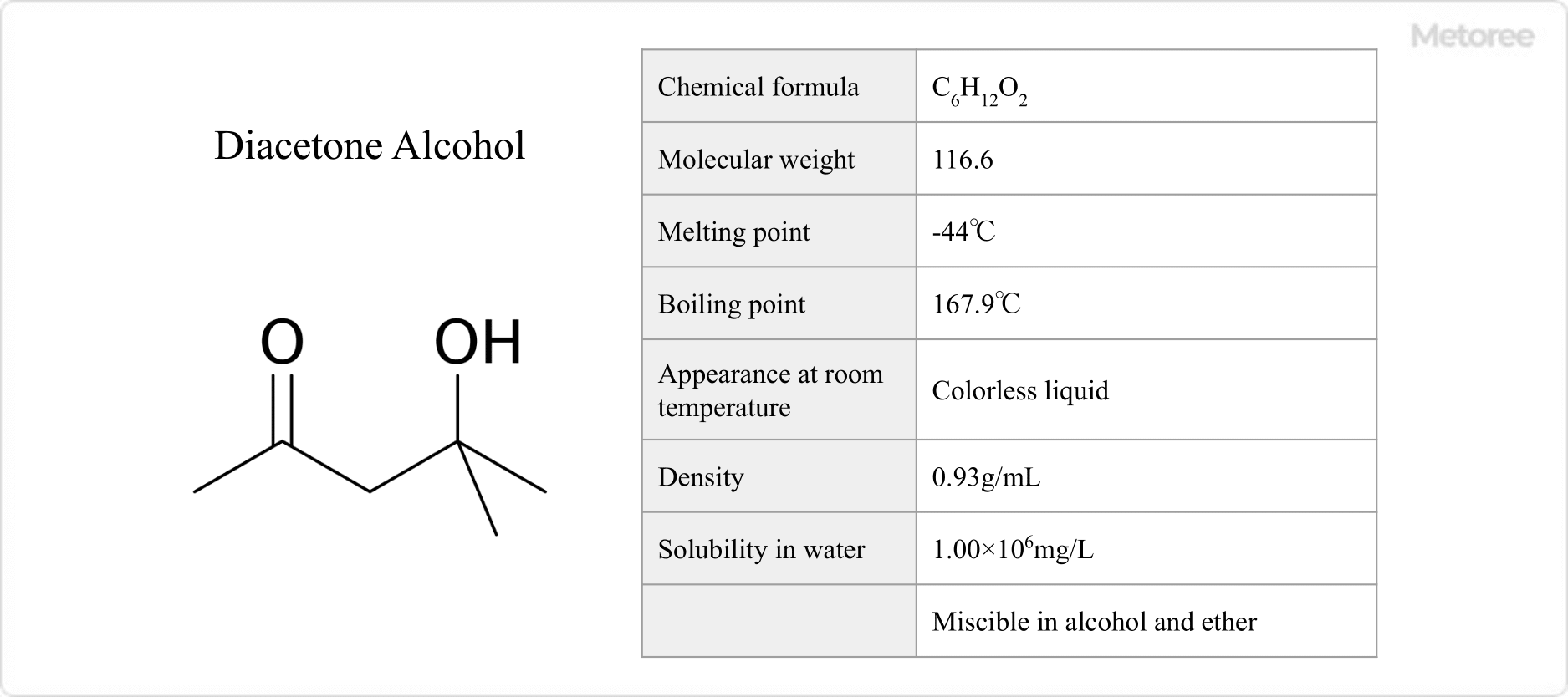
Figure 1. Basic Information on Diacetone Alcohol
Diacetone alcohol has a molecular weight of 116.16, melts at -44°C, and boils at 167.9°C. This colorless, virtually odorless liquid is generally stable under normal handling conditions. It is soluble in water at 1.00 x 106 mg/L and miscible with alcohols and ethers. Its density is 0.93 g/mL, with a flash point of 66°C and a spontaneous combustion temperature of 603°C.
Types of Diacetone Alcohol
Diacetone alcohol is marketed both as a research reagent and an industrial chemical.
1. Reagent Products for Research and Development
For research and development, diacetone alcohol is offered in various quantities, including 500 mL and 15 kg, tailored for laboratory use. These products are easily stored at room temperature and provide a cost-effective option for researchers.
2. Industrial Chemicals
As an industrial chemical, diacetone alcohol is primarily used as a solvent in applications such as paints, gravure inks, adhesives, insecticides, and photographic film production. It is available in 16 kg oil cans, 196 kg drums, and 1,000 L containers.
Other Information on Diacetone Alcohol
1. Synthesis of Diacetone Alcohol
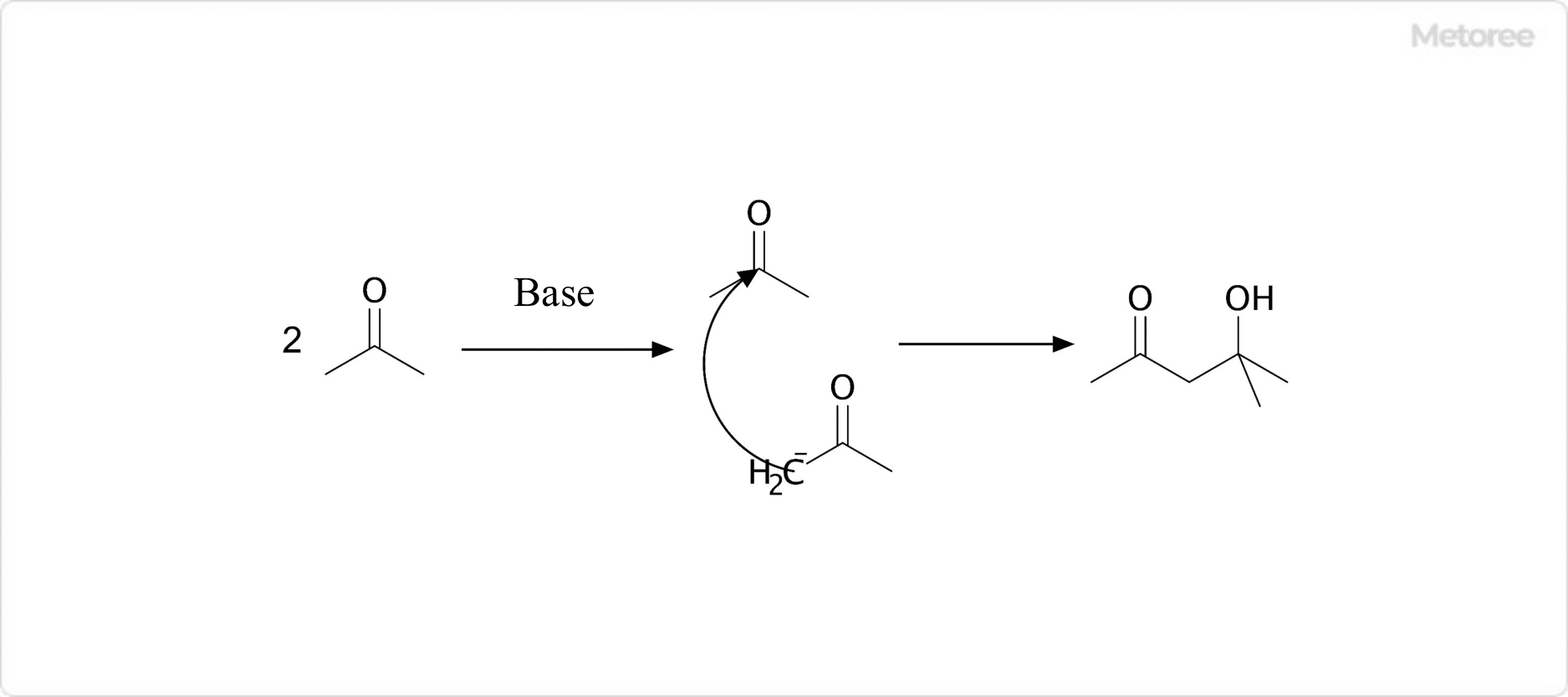
Figure 2. Synthesis of Diacetone Alcohol
Diacetone alcohol is produced industrially by the dimerization of acetone through aldol condensation, using a base such as barium hydroxide as a catalyst.
2. Chemical Reaction of Diacetone Alcohol
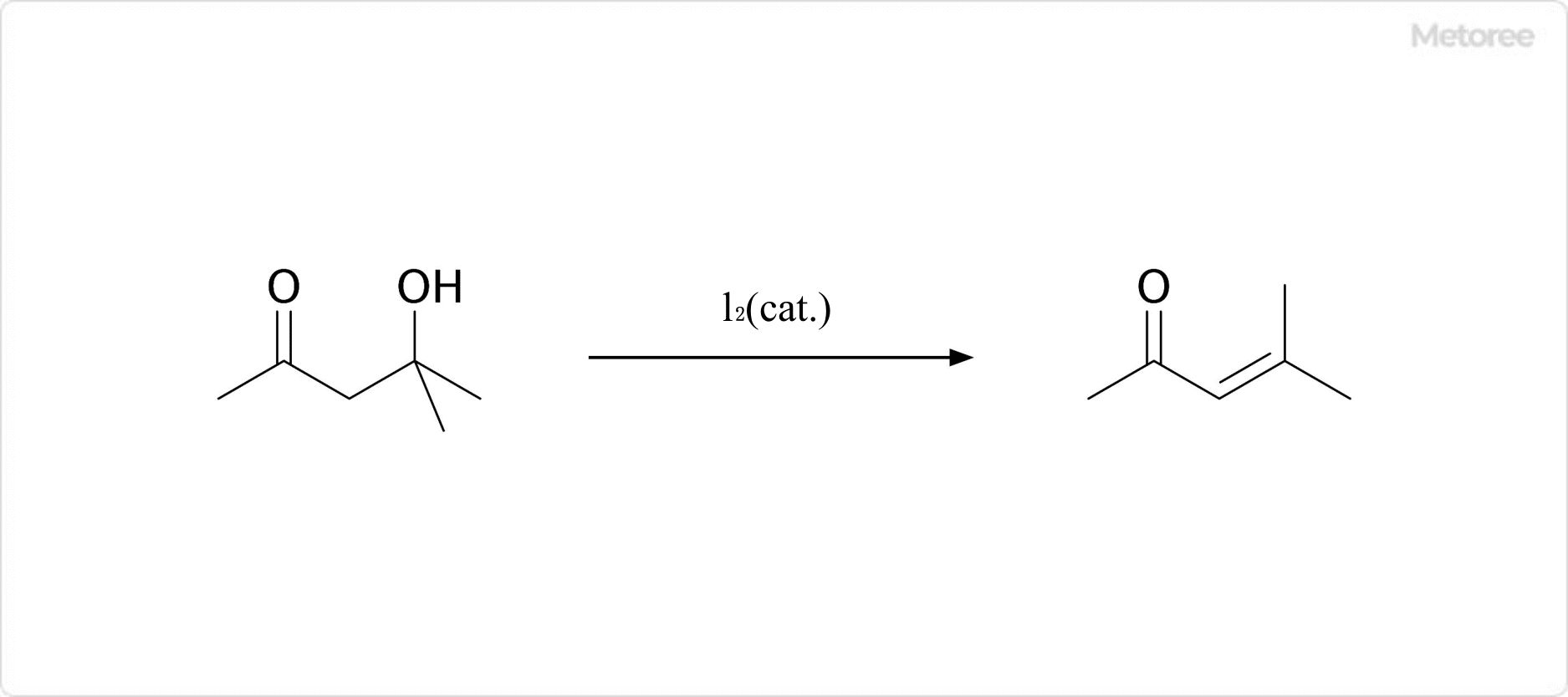
Figure 3. Dehydration Reaction of Diacetone Alcohol
Upon heating, combustion, or contact with acids, bases, or amines, diacetone alcohol decomposes into acetone and mesityl oxide. It reacts violently with oxidizing agents, potentially forming flammable or explosive gases. Hazardous by-products include acetone, methyl alcohol, and hydrogen.
3. Diacetone Alcohol Hazard and Regulatory Information
Diacetone alcohol is classified under GHS as a flammable liquid, skin, and eye irritant, toxic to reproduction, and potentially harmful to specific organs. It is regulated under various laws, requiring careful handling and compliance with safety and environmental regulations.