What Is Carbon Fiber?
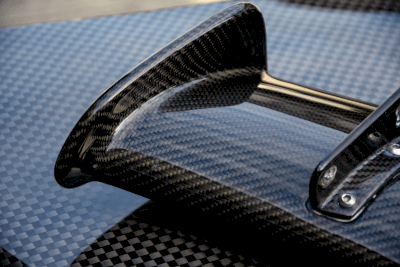 Carbon fiber is a light and strong fiber composed mostly of carbon.
Carbon fiber is a light and strong fiber composed mostly of carbon.
Carbon fiber is made by flame-proofing an organic compound in fibrous form, followed by a high-temperature heat treatment (sintering) at 1,800°F or higher to remove hydrogen and nitrogen atoms from the raw organic compound, resulting in a carbon atom content of 90% or higher.
Applications of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is used in many fields as a substitute for metal materials, taking advantage of its ability to reduce weight while maintaining strength. In addition, its flexibility, electronic conductivity, corrosion resistance, and flame resistance make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Carbon fiber is rarely used on its own; instead, it is generally used as a composite material combined with materials such as resins, ceramics, and metals. Specifically, carbon fiber is used in aircraft, rockets, and satellites, which require lightweight and high strength. It is also used in surgical orthotics such as artificial limbs, and nursing care equipment such as wheelchairs and nursing care beds, because of its lightness and ease of handling.
Particularly in the automotive industry, carbon fiber can contribute to lower fuel consumption by reducing the weight of vehicles. For this reason, carbon fiber has attracted attention and has been used in racing vehicles since the early days of its development. Carbon fiber also has applications in the sporting goods field, such as golf shafts, fishing rods, reels, bicycle frames, tennis rackets, skis, and snowboards, due to its high strength and elastic modulus.
In the future, carbon fiber is also expected to be used in the construction and civil engineering fields, for example, by attaching carbon fiber sheets to concrete structures to reinforce their earthquake resistance and as a substitute material for cables and steel frames in suspension bridges.
Types of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is classified into two types based on raw materials: PAN-based carbon fiber and pitch-based carbon fiber. Currently, PAN-based carbon fiber is the mainstream, accounting for 90% of the global production of carbon fiber.
1. PAN-Based Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber made from PAN (polyacrylonitrile) fiber has extremely high strength and modulus and is widely used in industrial fields that require high reliability, such as the space industry, and in more familiar applications, such as leisure goods and sports.
The most common use of carbon fiber is in the industrial field. In the automotive field, it is used in hoods, spoilers, gasoline tanks, and many other parts. It is also used as a substitute material for metal parts, such as leaf springs and gears.
2. Pitch-Based Carbon Fiber
Pitch-based carbon fiber has the feature of adjustable modulus of elasticity. For this reason, it is used in parts that do not require high elasticity and, conversely, in products that do require high elasticity. Pitch-based carbon fiber is further classified into mesophase pitch fiber and isotropic pitch fiber.
Mesophase pitch is a high-performance carbon fiber (HPCF) with high strength and high modulus. Isotropic pitch, on the other hand, has randomly oriented molecules and is optically isotropic.
The resultant isotropic pitch fiber exhibits lower mechanical properties, such as strength and elastic modulus, compared to mesophase pitch fiber. However, it performs similarly in other aspects and is a general-purpose carbon fiber (GPCF) with a lower elastic modulus.
Other Information on Carbon Fiber
How Carbon Fiber is Produced
Carbon fiber can be produced from either PAN-based carbon fiber or pitch-based carbon fiber, depending on the raw material.
- Flame-Proofing: Fibers are oxidized by heating at a temperature of 400~500°F in air to prevent melting in the subsequent process.
- Carbon Fiber: Heating at 1500-2900°F in an inert atmosphere removes hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen from the fiber.
- Graphitization: Graphitization of carbon by heating to 4,500~5,400℃ in an inert atmosphere to improve the modulus of elasticity.
1. PAN Carbon Fiber
PAN-based carbon fiber is made from acrylic fiber (PAN fiber). In the flame retardant process, the acrylic fiber molecules are heated at 400-500°F in air to form a cyclic structure. In the carbonization process, the heat of 1,850°F or higher is applied in an inert gas to change the molecular structure of a crystalline carbon structure.
Carbon fiber with high strength and high elastic modulus is produced at the end of the carbonization process. However, graphitization, in which a heat of 3,650°F or higher is applied, produces graphite fiber with slightly lower strength but high elastic modulus.
2. Pitch-Based Carbon Fiber
Coal and petroleum pitches, which remain after distillation of tar obtained by dry distillation of coal and petroleum, are converted into fiber and sintered. Long fibers are made from the pitch in a melt-spinning process before the flame retardant process, and the precursor fiber is obtained by stabilizing the fibers. The precursor fiber is flame retarded, carbonized, and graphitized in the same manner as PAN carbon fiber to produce pitch-based carbon fiber.