What Is Heat Dissipation Material?
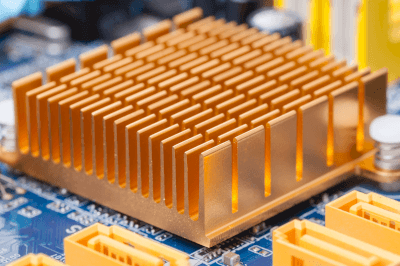 A heat dissipation material is a material used to facilitate the escape of heat from components that require temperature control.
A heat dissipation material is a material used to facilitate the escape of heat from components that require temperature control.
Heat dissipating materials are used in gel, compound, filler, adhesive, and sheet forms for various products.
The heat generated in electronic components not only slows down the operation of electronic products but also causes malfunctions and failures.
Heat dissipation material has been developed with an emphasis on how to facilitate efficient heat dissipation, especially in recent years with the emergence of high-performance electrical products that handle large amounts of data.
Applications of Heat Dissipation Material
Heat dissipation material is mainly used inside electrical products.
These products are used in a wide range of fields, including IT, industrial equipment, home electronics, automobiles, and power devices.
Applications include CPUs on motherboards, where heat is generated when electricity is applied and the temperature rises rapidly, resulting in high temperatures.
In particular, the amount of heat generated varies depending on the characteristics of the product, the time it is used, and its combination with other components.
Therefore, the amount of heat generated is calculated in advance by simulation, and the higher the amount of heat generated, the higher the Heat Dissipation Material to be used.
Principle of Heat Dissipation Material
Heat dissipation material is a material closely related to the physical properties of thermal energy.
Thermal energy is converted by physical actions, such as the flow of electricity, to energy that raises the temperature of an object.
Therefore, to lower the temperature of an object, thermal energy must be transferred outward, which means that heat must be released to the outside world, the so-called air layer.
However, since the air layer has low thermal conductivity, it is not easy to release heat from a hot object. Heat dissipation material plays this role.
Heat dissipation material is a material with high thermal conductivity. When applied or adhered to a high-temperature component, such as a CPU, the heat is transferred to the heat dissipation material.
Heat dissipation material is in contact with the air layer, so the heat accumulated in the heat dissipation material is dissipated into the air layer.
Heat dissipation material is shaped to have a large contact area with the air to facilitate heat transfer to the air layer.
This process is used to lower the temperature of electronic components to prevent them from malfunctioning.