What Is a Hex Nipple?
A hex nipple is a type of threaded pipe fitting featuring a hexagonal center, facilitating the use of a wrench for tightening, with male threads on both ends. This fitting is commonly utilized in general piping systems for water, oil, steam, air, and gas, enabling the connection of pipe fittings and equipment with male threads. The term “nipple” is defined as a pipe fitting with male threads cut at both ends of a straight shaft.
The center portion of a nipple does not have to be strictly hexagonal. For nominal diameters larger than 3/4B (20A), both hexagonal and octagonal shapes are acceptable.
Applications of Hex Nipples
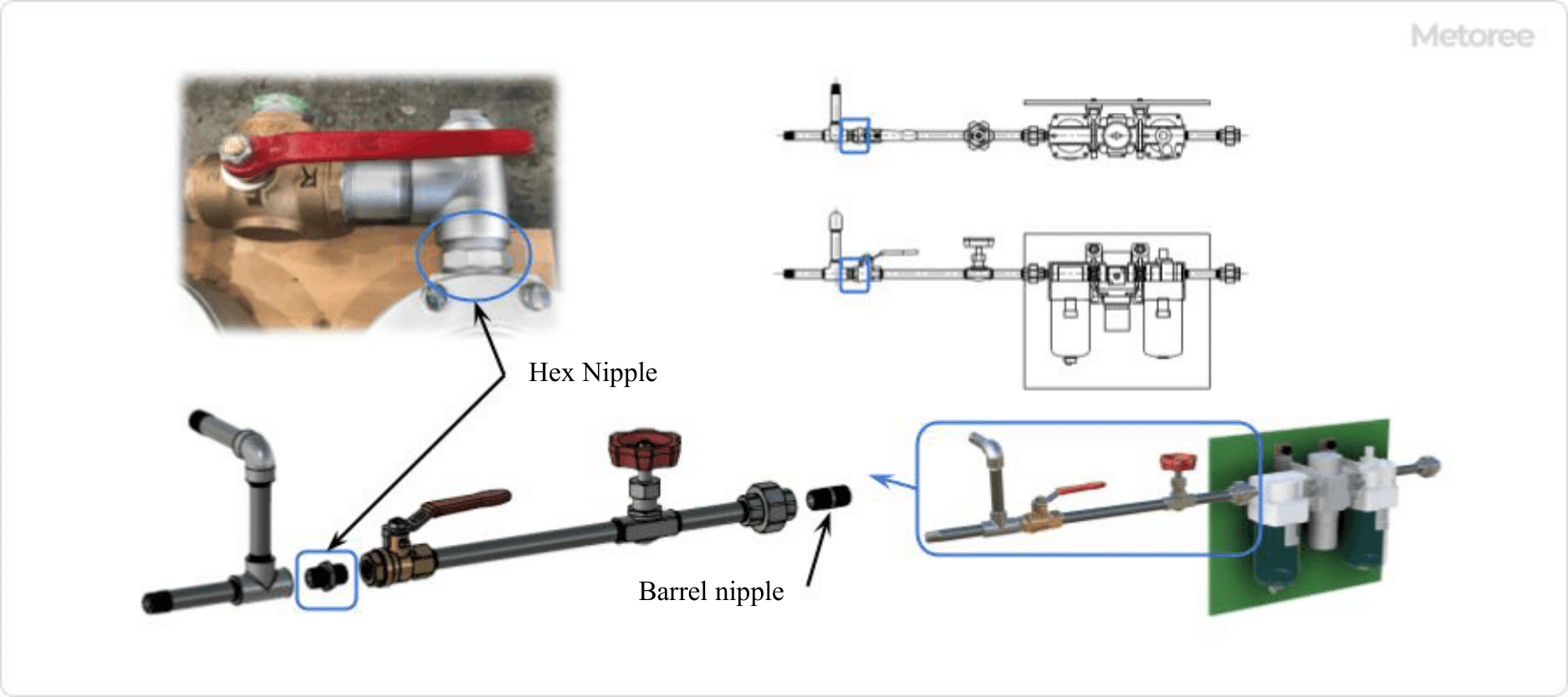
Figure 1. Example of Hex Nipple Use
Hex nipples find use across a broad spectrum of applications, from industrial to general gas piping systems. Their threaded connections offer ease of installation and disassembly. However, they are not recommended for high-pressure fluid piping due to potential leakage at the threaded connections.
The design allows for easy and secure tightening of the hex portion with a wrench or spanner, making them suitable for general-purpose piping connections.
Principle of Hex Nipples
Piping connections can be established through screwing, plugging, flanging, or welding, with hex nipples being a type of fitting joined by screwing. These fittings employ taper threads (R threads) on both ends, compatible with both tapered (R) and parallel (Rp) pipe threads, facilitating straight connections to various pipe fittings and equipment.
Types of Hex Nipples
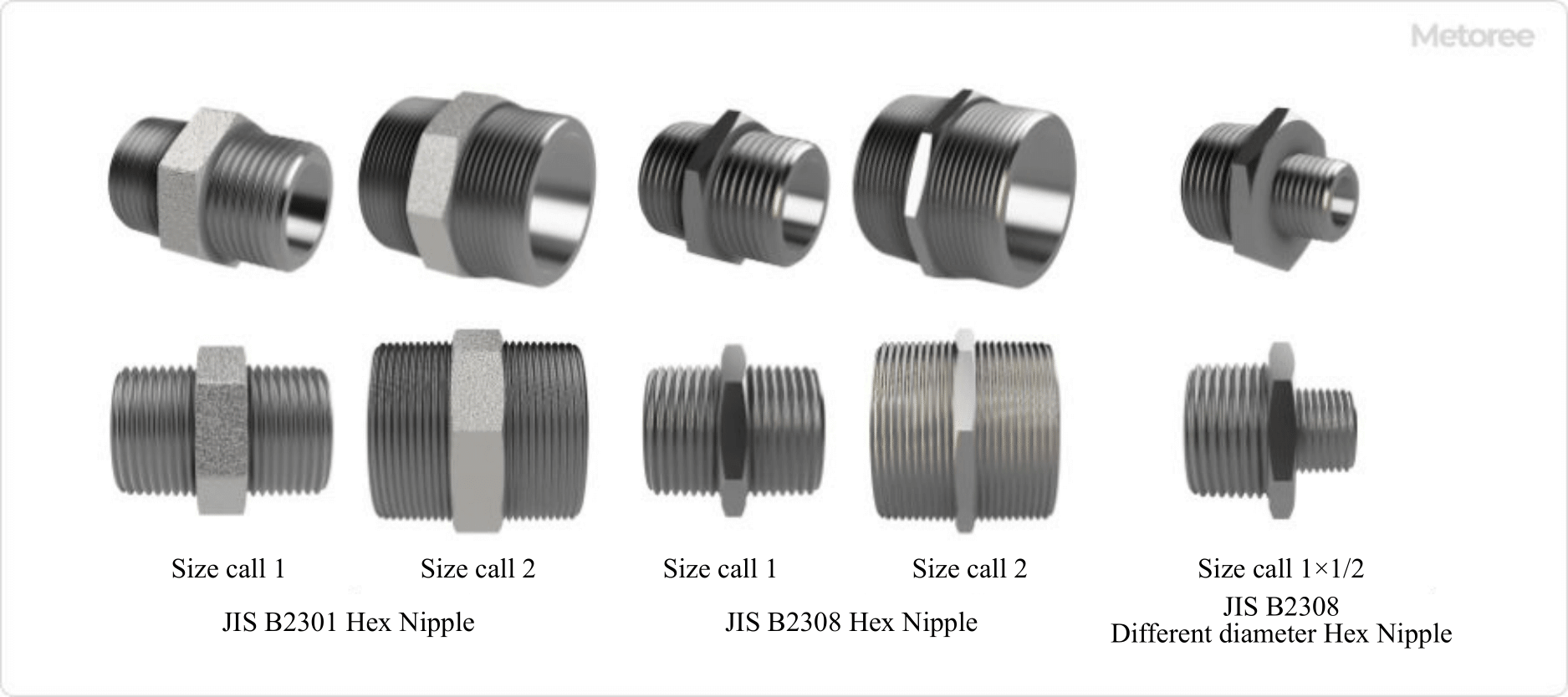
Figure 2. Types of Hex Nipples by Shape
1. Classification by Shape
Hex nipples can be hexagonal or octagonal in the center portion, depending on the nominal diameter, which, if larger than 3/4B (20A), may be octagonal.
2. Same Diameter/Different Diameter
There are two types of hex nipples: those with the same diameter threads on both ends and those with different diameters. The term “same-diameter” is typically implied for same-diameter nipples. Hex nipples with different diameters feature concentric threads.
Other Information on Hex Nipples
2. Nominal Size of Pipe Fittings
The following table shows the correspondence between pipe fitting sizes and the nominal diameter (A) or DN (ISO 6708).
| Pipe Fitting Size Nominal |
1/8
|
1/4
|
3/8
|
1/2
|
3/4
|
1
|
1-1/4
|
1-1/2
|
2
|
2-1/2
|
3
|
4
|
| Nominal Size (A), (DN) |
6
|
8
|
10
|
15
|
20
|
25
|
32
|
40
|
50
|
65
|
80
|
100
|
3. Nipples Other than Hex Nipples
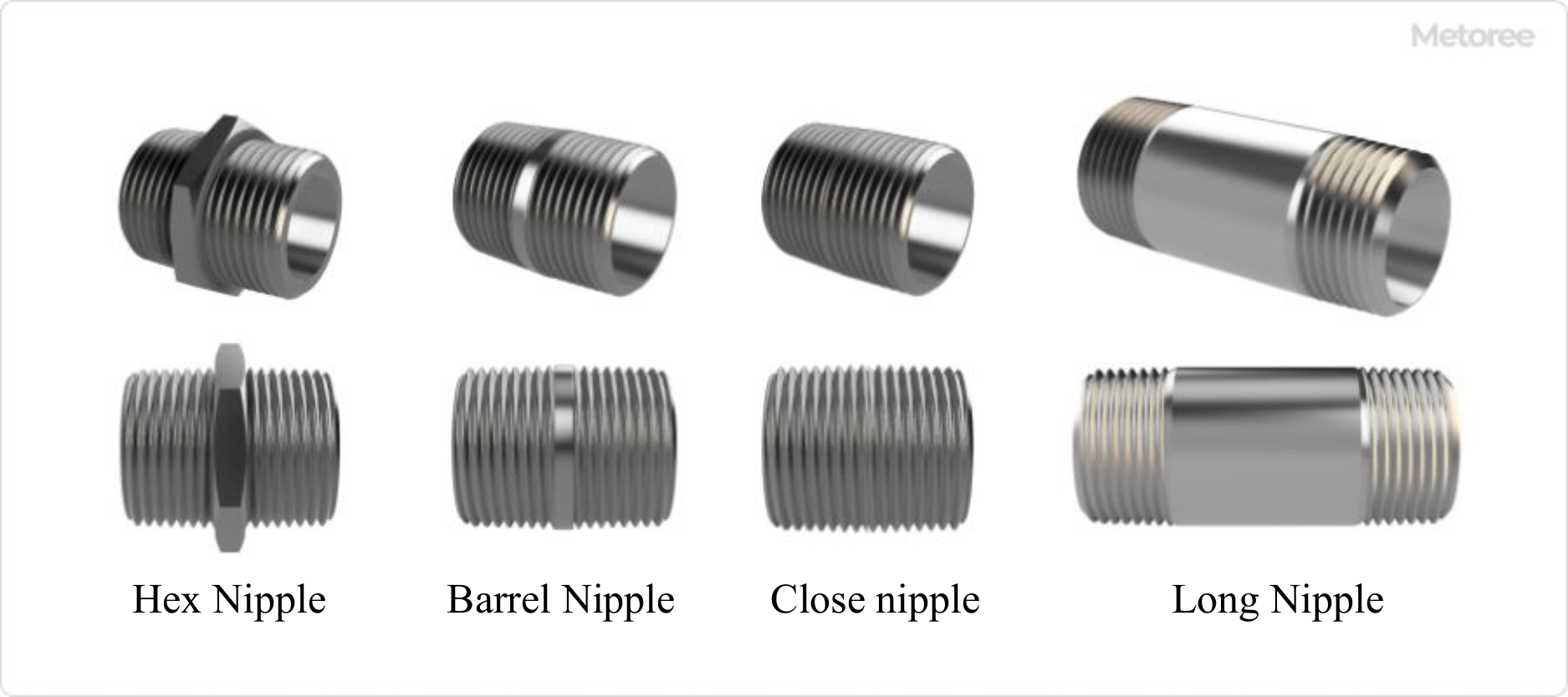
Figure 3. Hex Nipple and Other Nipple Shapes
Alongside hex nipples, other types include barrel nipples, close nipples, and long nipples, which are tightened using a pipe wrench. These variants offer different advantages in terms of the distance between connected fittings and equipment.


