What Is Glass Paint?
Glass Paint is a coating made of quartz glass dissolved in a solvent.
Since it is liquid at room temperature, it can be painted and cured at room temperature. It can be applied to a wide variety of materials.
Uses of Glass Paint
Glass Paint is often used to paint the exterior walls and roofs of houses because of its durability and weather resistance, as well as its ability to be applied at room temperature. Glass Paint is also used to coat the interior walls and water surfaces of homes because of its ability to coat many materials, including wood, concrete, mortar, and metal.
Principle of Glass Paint
Glass Paint is made by dissolving quartz glass in a solvent. Curing occurs through accelerated hydrolysis and dehydration-condensation of the glass-forming components in this glass paint.
That is, the organopolysiloxane groups bonded to the same main chain as the glass are hydrolyzed and converted to hydroxy groups. The changed hydroxy groups then react with the remaining organopolysiloxane groups to dealcoholize and cure.
Types of Glass Paint
Glass Paint generally refers to completely inorganic glass paint. However, it may also include organic Glass Paint.
1. Fully Inorganic Glass Paint
Fully Inorganic Glass Paint is a type of glass paint with a very high quartz glass content of 99.7%. Fully inorganic glass paint does not contain any organic matter and has properties equivalent to those of glass. It is semi-permanently durable and nonflammable, with no deterioration over time or flammability concerns. It also has excellent water repellency, water permeability, chemical resistance, and antifouling properties due to its glass properties.
If this coating is used for coating exterior walls and roofs of buildings, weather resistance, heat resistance, water permeability, stain resistance, and mildew resistance can be ensured. In addition, it forms a thin film with very high transparency, creating a luxurious appearance.
Furthermore, this paint uses alcohol instead of organic solvents for dilution, which has the advantage of being less harmful to the human body and the environment. However, the disadvantage is that it is more expensive than regular paints and takes longer to install, making the construction cost more expensive.
2. Organic Glass Paint
Organic Glass Paint is made from inorganic materials and petrochemicals. Although it is a glass paint, it is a mixture of organic materials, which oxidize and degrade the coating film.
It does not have the characteristics of all-organic glass paint, and is positioned as a less expensive version of glass paint.
Other Information on Glass Paint
1. Disadvantages of Glass Paint
Glass Paint is suitable for painting exterior walls, but it is not suitable for exterior walls with sealing. The service life of sealing is estimated to be 7 to 10 years. Therefore, maintenance is required for exterior walls with sealing in accordance with the service life of the sealing.
On the other hand, glass paint is said to last approximately 20 years. In other words, if glass paint is applied on top of a sealed exterior wall, maintenance of the sealing is required while the glass paint is still durable. As a result, the disadvantage is that the glass paint, which is expensive in both price and construction, must be repainted before it can be fully utilized.
An additional disadvantage is that glass paint’s characteristics make it difficult to apply multiple coats. Therefore, it is important to use glass paint after considering the number of future repaints.
2. Finish of Glass Paint
Glass Paint can also be used for woodworking. Glass Paint is a liquid form of quartz glass dissolved in a solvent, which penetrates into the wood fibers and hardens. This has the advantage of allowing the paint to retain the taste and texture of the wood surface.
Another advantage is that wood can be painted with the same texture both indoors and outdoors. By allowing it to penetrate, wood can be protected from corrosion and mold arising from the inside. It can also be deposited on the surface to protect it from water, scratches, and mites.

 A cover roof is a type of roof renovation method.
A cover roof is a type of roof renovation method.
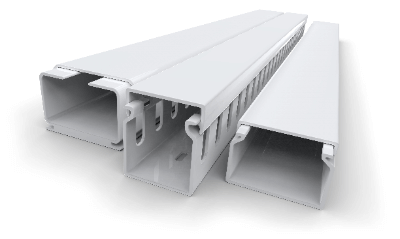 A cutting duct is a component that allows electric wires to pass through its interior to improve the appearance and prevent electric shock.
A cutting duct is a component that allows electric wires to pass through its interior to improve the appearance and prevent electric shock. An Omni wheel is a wheel that can move in any direction. It consists of a main rotating part on the body and a passive rotating part of rollers placed on the outer circle of the body.
An Omni wheel is a wheel that can move in any direction. It consists of a main rotating part on the body and a passive rotating part of rollers placed on the outer circle of the body.
 An elastomer is a generic term for a polymer compound with elasticity. There are two types of elastomer:
An elastomer is a generic term for a polymer compound with elasticity. There are two types of elastomer:  Emulsion Paint is a paint in which the disadvantages of conventional oil-based and water-based paints are improved by the emulsion technique.
Emulsion Paint is a paint in which the disadvantages of conventional oil-based and water-based paints are improved by the emulsion technique.