What Is Horizontal Milling Machinery?
A milling machine is a machine in which a blade called a milling cutter is installed on a spindle and rotated to process an object fixed to the machine.
A milling machine with the spindle mounted in a direction transverse to the ground is called a Horizontal Milling Machinery or Horizontal Type Milling Machine. They can be further classified not only by the direction in which the spindle is mounted but also by differences in operation, such as whether the table is moved or the spindle is moved.
While vertical milling machines are generally used in most cases, horizontal milling machinery is suitable for machining grooves, holes, and cutting, and can perform side machining that is not possible with other milling machines.
Cutting tools attached to the spindle can be roughly classified into bores and shanks as defined by JIS standards, and the type of machining that can be performed on a milling machine can be changed by changing the cutting edge.
Uses of Horizontal Milling Machinery
Horizontal milling machinery uses flat milling machines, side milling machines, corner milling machines, etc. Flat milling machines are not often used for plane milling because flat milling is not efficient.
Horizontal milling machinery is often used for milling grooves, steps, and sides. Machining can be varied by changing the shape of the uniform cutting edges on both sides.
Square milling cutters have angled cutting edges on the circumference and can machine v-shaped grooves by cutting in two places at the same time.
The shank type is a rod-shaped tool such as an end mill, and the cutting edge on the tip is used to cut a hole or groove.
Principle of Horizontal Milling Machinery
In a milling machine, the object is fixed to the machine and a blade called a milling cutter is attached to the spindle, which is installed horizontally to the ground, in accordance with the processing.
In machining with a milling machine, the reference is taken to be a surface, and the cutter is brought into slight contact with the object, and the part that has been slightly shaved is set as the zero point, and the entire surface is shaved for machining.
Horizontal milling machinery differs from vertical milling machinery in that it has its spindle facing sideways to the ground to change the direction and transmission of force, and in addition to machining deep holes, which is not possible with vertical milling machinery, only horizontal milling machinery can perform side machining.
Also, with horizontal milling machinery derived from horizontal machining Centers, there are machining centers that can rotate the table 360° under NC control, enabling machining on four sides by rotating the table.
The advantage of the horizontal machining center is that the backside can be machined without removing the workpiece from the table.
Other Information on Horizontal Milling Machinery
1. Characteristics of Horizontal Milling Machinery
Horizontal milling machinery has a feature that chips released during machining do not easily accumulate on the workpiece or fixed jig because the spindle is machined horizontally to the workpiece.
If too many chips accumulate on the workpiece, various disadvantages may occur, such as reduced visibility, scratches on the jig and workpiece, damage to the cutting tool, and the generation of composed cutting edges, which must be cleaned regularly or blown away with a blower.
Horizontal milling machinery is used for applications that require continuous machining for a relatively long period, such as mold carving, taking advantage of its feature that chips do not accumulate easily.
The automatic pallet changing function enables continuous unmanned operation without setup changes.
2. Cautions for Horizontal Milling Machinery
If you are accustomed to handling a vertical milling machine, it is easy to get confused about the X/Y direction.
Also, due to the horizontal nature of the cutting tool mounting, if a heavy cutting tool with a long holder is mounted, it will deflect under gravity, resulting in a loss of accuracy and rigidity. Therefore, it is necessary to chuck knives with a holder length as short as possible compared to vertical milling machines.
It is also necessary to adjust the coolant direction and pressure, paying attention to the fact that gravity makes it difficult for the coolant jet from the spindle to reach the cutting edge, which is a weakness unique to the horizontal type.
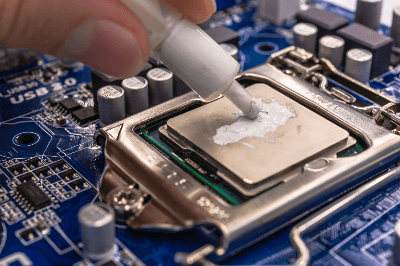 Thermal grease is a highly thermally conductive grease used to help dissipate heat from components and electronic devices that generate high heat.
Thermal grease is a highly thermally conductive grease used to help dissipate heat from components and electronic devices that generate high heat.