What Is an Air Tank?
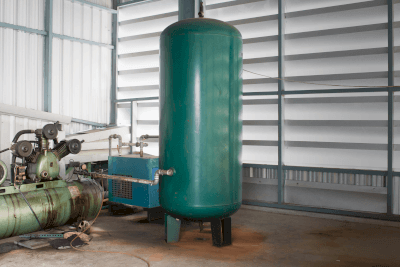
Air tanks are pressure vessels used to store compressed air.
They are sometimes also called an accumulator. Mainly connected downstream (secondary side) of an air compressor, an air tank serves to equalize pressure fluctuations of compressed air supplied from the compressor. They are also used to prevent rapid depressurization when a large amount of compressed air is used instantaneously.
The effect of the air tank is to protect and extend the life of the air compressor. Since the air tank acts as a buffer for air delivery, the air compressor no longer needs to be started and stopped frequently.
In addition, even if the compressor is shut down in the event of a power failure or other emergency, the air tank will provide a constant supply of compressed air, reducing the risk of accidents that could cause pneumatically driven equipment to lose power instantly.
Uses of Air Tanks
Air tanks are used in pneumatic lines in various types of machinery and equipment. Their main purpose is to equalize pressure and protect air compressors when large volumes of compressed air are used. Air tanks are also essential when there are conditions where the air consumption of pneumatic equipment is higher than the air discharge of the compressor.
For safety purposes, an air tank may be used even when the air volume is insufficient. This is because air cylinders, which operate by air, lose their output when the compressed air supply is cut off, so they are more likely to operate unexpectedly in the event of a power failure. If this puts workers at risk, an air tank can be installed so that compressed air is supplied to the cylinder for a certain period, even if the compressor stops running.
As a result, the cylinder does not suddenly lose power, creating a situation that can be addressed in the moment. Air tanks are also often used in trucks and other large vehicles. Trucks use compressed air in their brakes, suspension, and transmissions, and Air tanks store the compressed air that drives these devices.
Principles of Air Tanks
Air tanks hold compressed air and maintain the pressure above a certain level, stabilizing the air pressure used and protecting the air compressor. Air tanks must have sufficient capacity to do their job.
In addition to upstream and downstream connections, the air tank is equipped with a pressure gauge, safety valve, and pressure switch. If the internal pressure exceeds the pressure, the container can withstand, the air is exhausted to the outside to reduce the pressure for safety.
In addition, since the air compressor takes in air from the installation environment and compresses it, moisture in the air will condense in the piping and air tank to some extent. This moisture must be removed because it can cause tank corrosion. Air tanks are therefore equipped with a drain valve to drain it out.
Today, a good deal of equipment is equipped with an automatic drain valve (drain trap). Since the condensate may contain oil from the compressor or components of environmental origin, it cannot be discharged directly from the plant to the sewage system. Therefore, a condensate purifier may be connected.
How to Select Air Tanks
When selecting an air tank, the first step is to determine the capacity. The required capacity can be calculated or determined empirically from the output of the compressor to be used.
When calculating, the required capacity is set based on the air consumption of the pneumatic equipment, the required pressure, and, in the case of intermittent use, the time of use, while also taking into consideration the compressor’s ability to compensate for air. On the other hand, if the figure is calculated empirically, it is based on the assumption that the compressor is properly selected for the amount of air used, and that a compressor with a large output requires a larger tank.
However, it should be based on examples of similar usage: the more pneumatic devices consuming compressed air, such as air cylinders and air guns, that are used simultaneously for one compressor, the larger the required air tank capacity. If you are unsure about the selection, it is recommended that you consult with an experienced contractor rather than doing it yourself.
Other Information on Air Tanks
Air Tank Management
Air tanks hold high-pressure air inside and can be a pressure hazard, so proper management is important. In particular, strength (i.e., no damage caused by something hitting the tank) and proper operation of safety valves and pressure switches are important to ensure safety.
In terms of laws and regulations, depending on the air pressure, content volume, and dimensions, a pressure vessel may be classified by regulations. In this case, periodic voluntary inspections, etc., must be conducted at the business site, etc.
 As the name suggests, a compressor engine is a type of
As the name suggests, a compressor engine is a type of