What Is Cutting Oil?

Cutting Oil is used in metalworking processes such as turning and milling to “lubricate metals to reduce friction,” “cool heat generated during machining,” “control the scattering of cutting dust and cleaning,” and “prevent rusting.
Cutting Oil contributes to preventing seizures, improving dimensional accuracy, and extending tool life. Cutting Oil is applied to the point of contact between the cutting tool and the workpiece during machining, as shown in the photo above.
Uses of Cutting Oil
Cutting Oil is used to lubricate, cool, clean, and prevent rust during cutting, grinding, rolling, drawing, pressing, and other processes of metal materials. Cutting oil generally comes out of a nozzle installed in a machine tool, and is applied (poured) onto the tip of the cutting tool.
Cutting oil remains on the part after machining, so if cutting oil needs to be removed as a delivery item, clear instructions must be given at the time of the machining request. On the other hand, packing and transporting the parts with cutting oil remaining may provide advantages such as “prevention of rust, etc.” and “resistance to deterioration even if stored for a long period of time,” etc. Therefore, judgment must be made according to the characteristics of the parts.
In addition, cutting oil generally comes out of a nozzle that is mounted as part of the machine tool, but some types have a hole in the tool itself through which cutting oil comes out. The nozzle type can be used for various sizes of workpieces because the direction of the cutting oil can be adjusted by changing the position and direction of the nozzle.
The type with holes in the tool itself has stronger pressure to inject Cutting Oil, which makes it easier to pour off cutting dust.
Types of Cutting Oil
There are two main types of Cutting Oil: Insoluble Cutting Oil, which is used as lubricating oil, and Water Soluble Cutting Oil, which is a mixture of lubricating oil and additives in water. Water-soluble Cutting Oil is diluted 10~50 times during processing.
1. Insoluble Cutting Oil
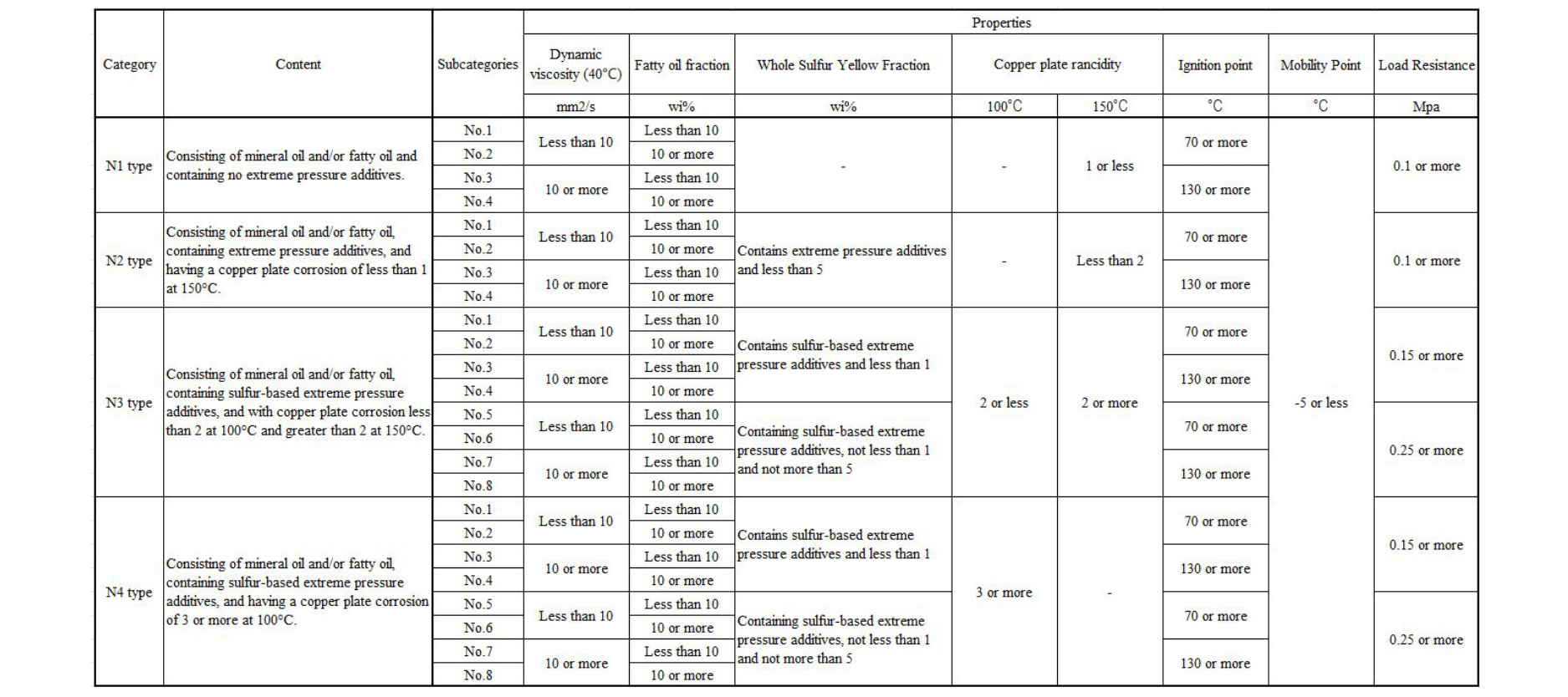
Figure 1. Types and properties of insoluble cutting oils
Insoluble Cutting Oil is mainly composed of base oil such as mineral oil to which extreme pressure additives and friction reducers are added, and has superior lubricity compared to water-soluble cutting oil. Cutting oils are classified into four types, N1 to N4, according to the JIS standard, depending on the combination of extreme pressure additives, kinematic viscosity, and sulfur content.
- N1
Does not contain extreme pressure additives and is used for machining nonferrous metals such as copper and castings, which are prone to corrosion.
- N2
Contains extreme pressure additives and is suitable for various types of steel.
- N3 and N4
In addition to extreme pressure additives, they contain sulfur content and are used when machining difficult metals or when severe machining surface accuracy is required.
2. Water-Soluble Cutting Oil
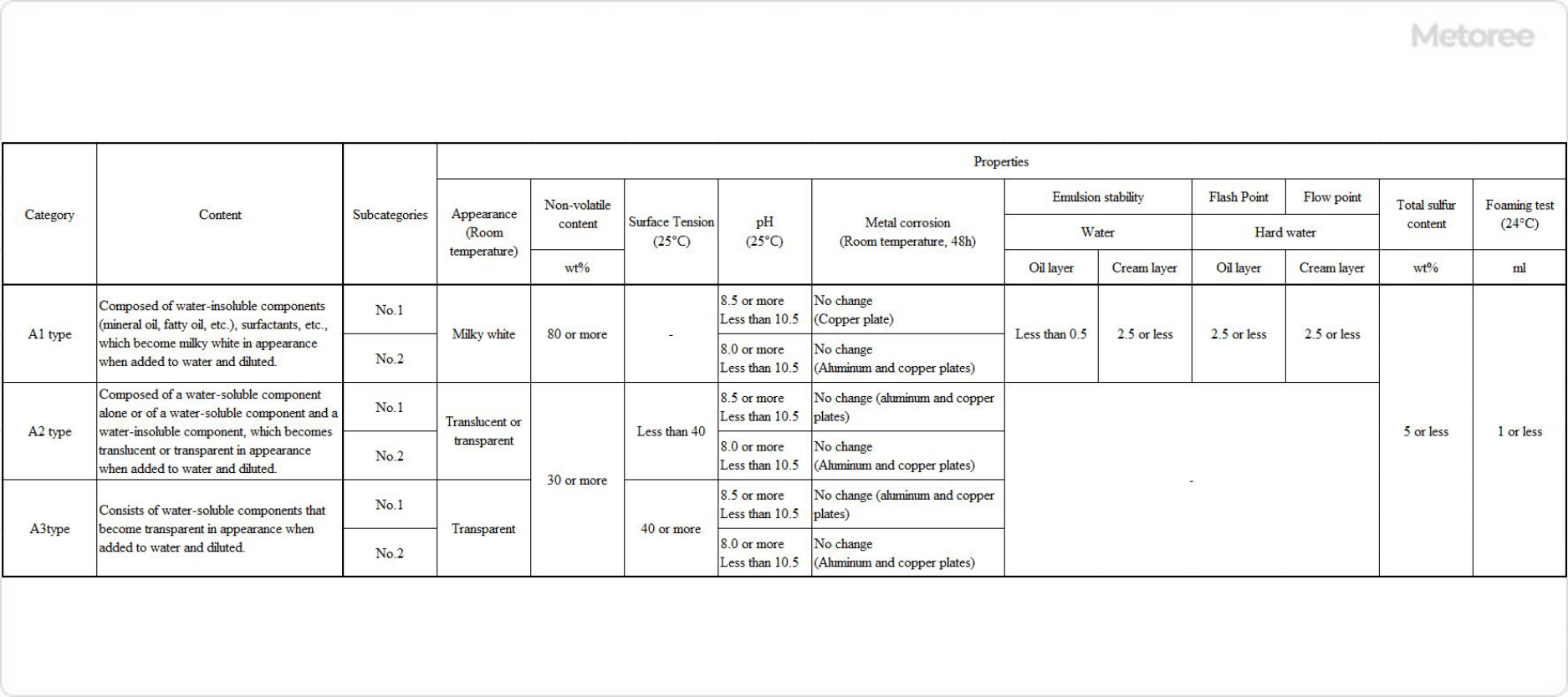
Figure 2. Types and properties of water-soluble cutting oils
Water-soluble Cutting Oil is mainly composed of a lubricating oil base and water, to which surfactants and rust inhibitors are added to impart dispersibility and solubility in water, and is also used when diluted with water at the time of use. Since water is the main ingredient, it has excellent cooling properties and can be classified into three types according to JIS standards.
- A1 (Emulsion Type)
A1 is a water-soluble Cutting Oil with good lubricity and a cloudy white color when diluted.
- A2 (soluble Type)
It has good cooling and penetrating properties and becomes slightly cloudy when diluted.
- A3 (Solution Type)
Cooling and rancidity resistance, also easily separates from other oils. Appearance remains almost the same even after dilution.
It is important to distinguish between insoluble and water-soluble Cutting Oils depending on the machining method. Insoluble Cutting Oils have better lubricity and are suitable for precision machining at low speeds, while water-soluble Cutting Oils have better cooling and chip cleaning properties and are suitable for continuous machining at high speeds.
Other Information on Cutting Oil
Additives for Cutting Oil
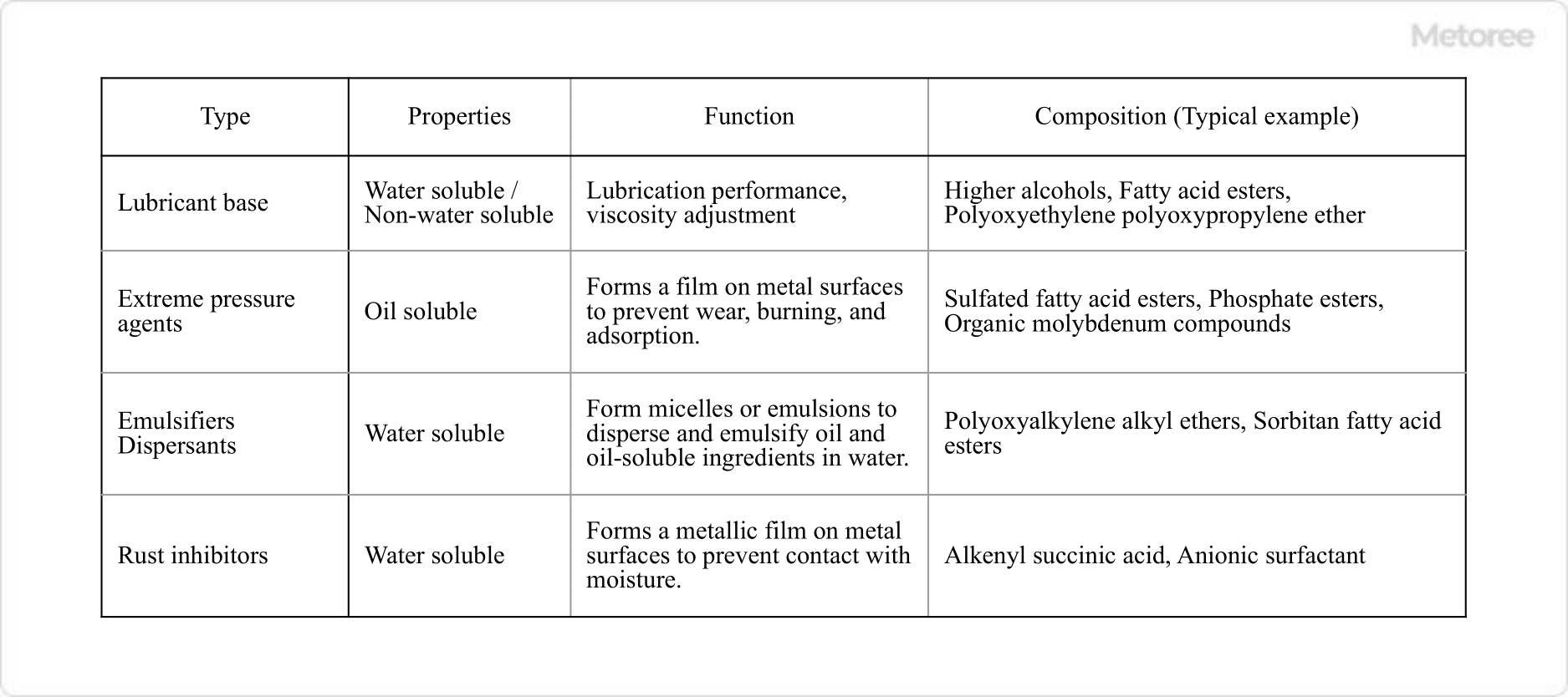
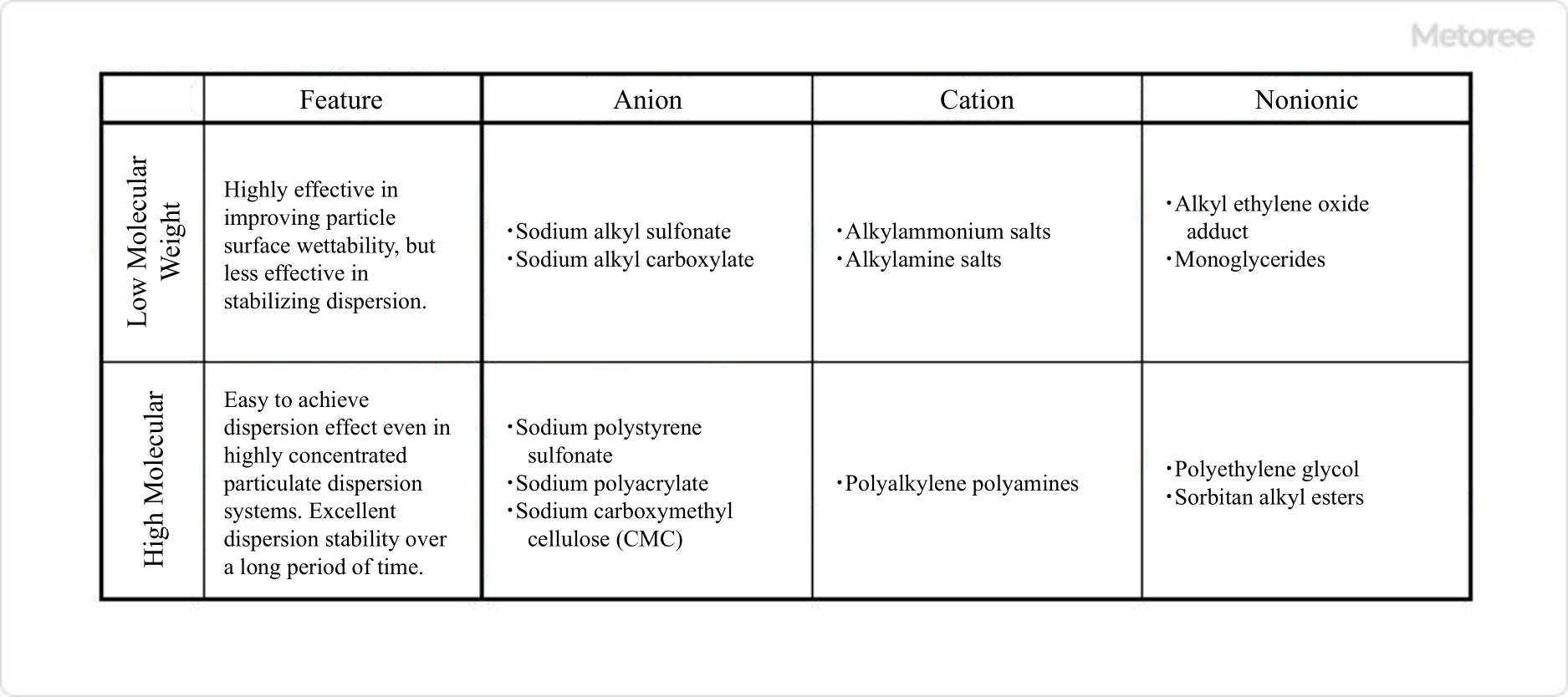
Figure 3. Types of cutting oil additives
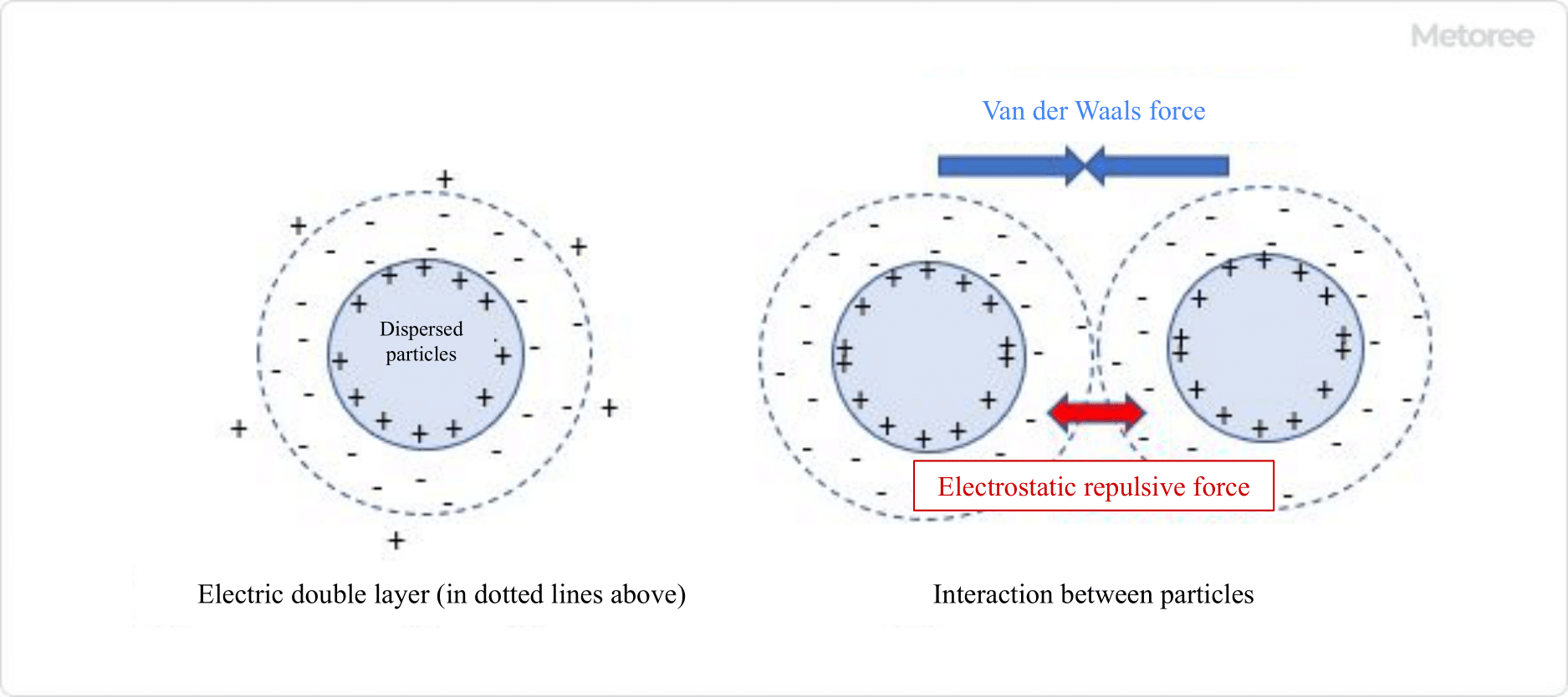
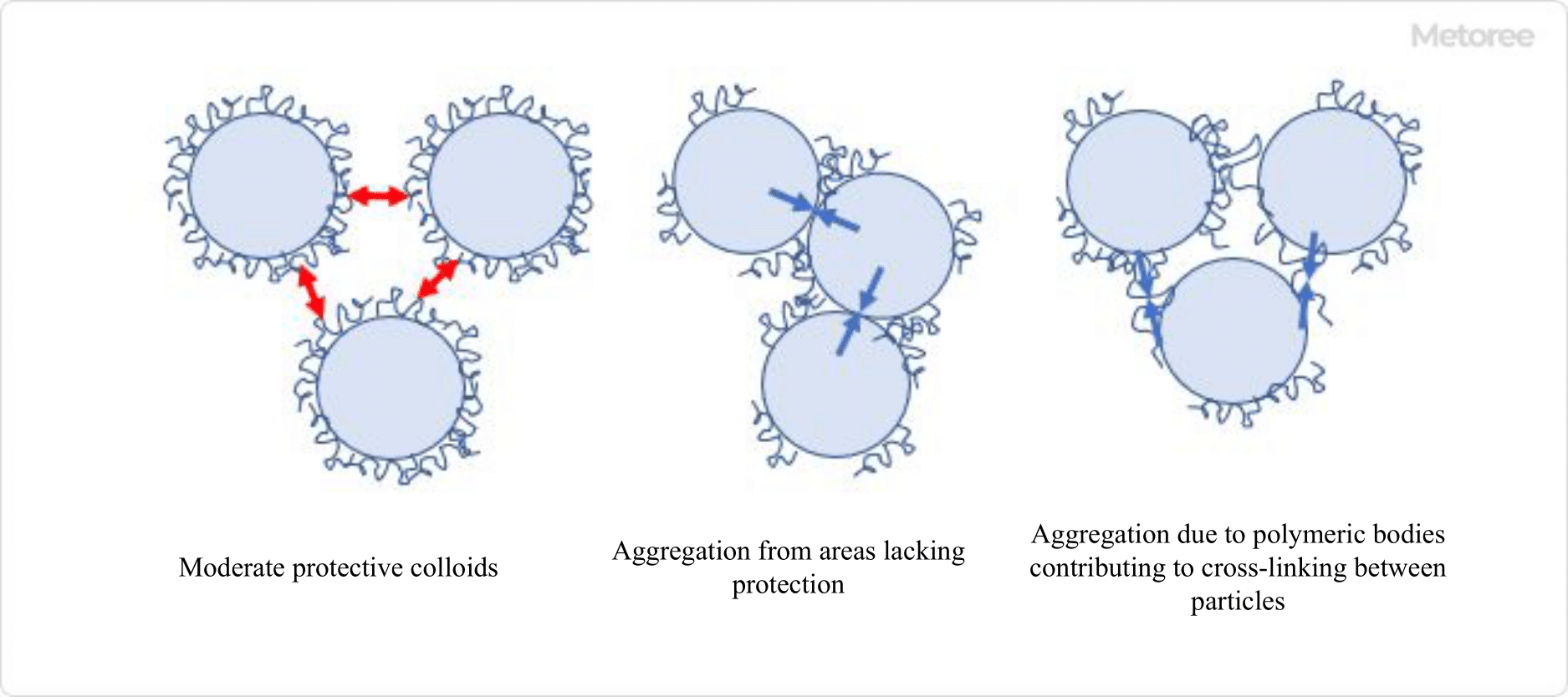
Cutting Oil additives include lubricant base materials, extreme pressure agents, emulsifiers, dispersants, and rust inhibitors. In recent years, the need for water-soluble Cutting Oil has been increasing due to the need for improved working environment, safety, and processing speed.
The disadvantage of water-soluble Cutting Oil, besides its inferiority in lubricating performance, is that it is prone to problems such as bacterial growth, rust formation, and foaming. For this reason, in addition to the additives listed in Table 3, preservatives and cationic dispersants with high antimicrobial properties are used.


 A control cabinet is a box that stores components and electrical equipment used to control industrial machinery and equipment.
A control cabinet is a box that stores components and electrical equipment used to control industrial machinery and equipment.