What Is a Survey Meter?
Survey Meter is a portable and simple radiation measuring instrument used to measure the dose rate in the air or the amount of radioactivity (surface contamination) on workers’ clothing in facilities where radiation or radioisotopes are handled.
Radiation includes, in order of penetrating power, neutrons, gamma rays, X-rays, beta (beta) rays, alpha (alpha) rays, and charged particle rays. The order of penetrating power depends not only on the type of radiation but also on its energy. The choice of the measuring instrument depends on the purpose, such as measuring the type and amount of radioactive materials or measuring the radiation dose.
Uses of Survey Meter
1. Monitoring of Air Dose Rates
Monitoring posts are installed in the vicinity of nuclear facilities and at designated points in each prefecture. Monitoring posts measure the amount of radioactive dust by measuring β-rays from radioactive dust adhering to air dose rate meters and dust monitors in order to monitor the leakage of radioactive materials (dust, etc.).
Scintillation survey meters with high sensitivity to γ-rays are most suitable for measurement in areas with low dose rates, such as urban areas. Measurement of radiation dose is legally required for radiation workers, and personal dosimeters such as film badges and TLD dosimeters (thermoluminescence dosimeters) are mainly used.
2. Surface Contamination Monitoring
Surface contamination is often measured using GM counter tube survey meters, which measure β-rays, scintillator survey meters, which measure α-rays, and proportional counter tube survey meters, which measure both α- and β-rays.
The standard values for radioactive contamination in food are extremely small, and a combination of a high-sensitivity germanium semiconductor detector or scintillation detector and an analyzer is used.
Principle of Survey Meter
The basic atoms of a survey meter differ depending on the model (GM coefficient tube, ionization chamber, or scintillation type) and the type of radiation (especially neutron radiation).
1. Ionization of Gas
As shown in Figure 1, a cylindrical detector is filled with an inert gas such as helium or argon, and a high DC voltage is applied between the central anode and the surrounding cathode. γ (X) rays can be ionized via electrons generated inside the detector by reaction with the cathode material, while α and β rays can ionize gas directly. The number of pulses from the discharge triggered by ionization can be used to measure the air dose rate, and the effective dose rate of about 0.1 μSv/h to 10 Sv/h can be obtained from the number of pulses counted in one minute.
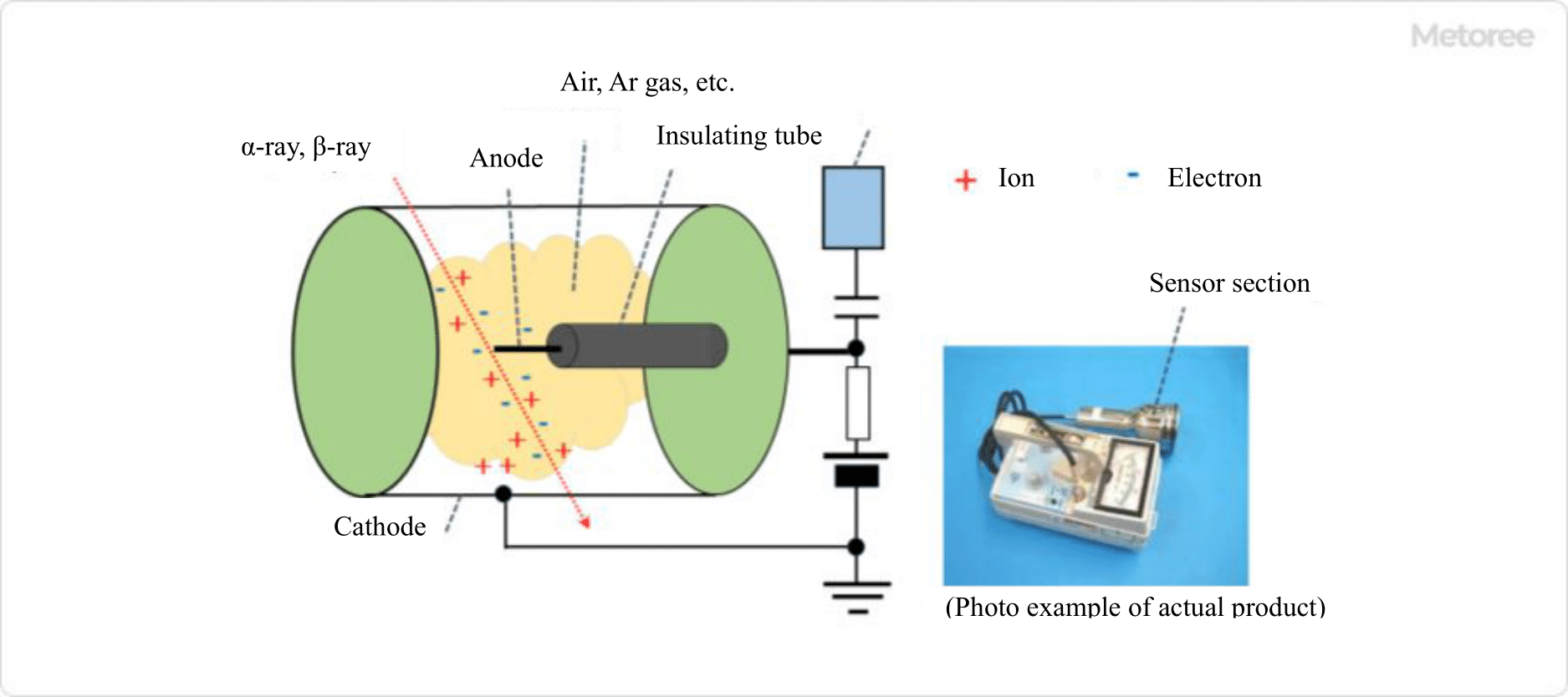
Figure 1. Basic structure and measurement principle of a GM-tube survey meter
An ionization chamber detector has the same structure as a GM-tube survey meter, with the detector filled with air or argon. When radiation strikes the detector, the air is ionized into cations and electrons, and the ionization chamber survey meter displays the minute current that flows between the electrodes. Ionization chamber survey meters are suitable for measuring β- and γ-rays and low-energy X-rays, and can measure effective dose rates in the range of 1 μSv/h to 5 Sv/h, depending on the model.
2. Scintillation by Excitation
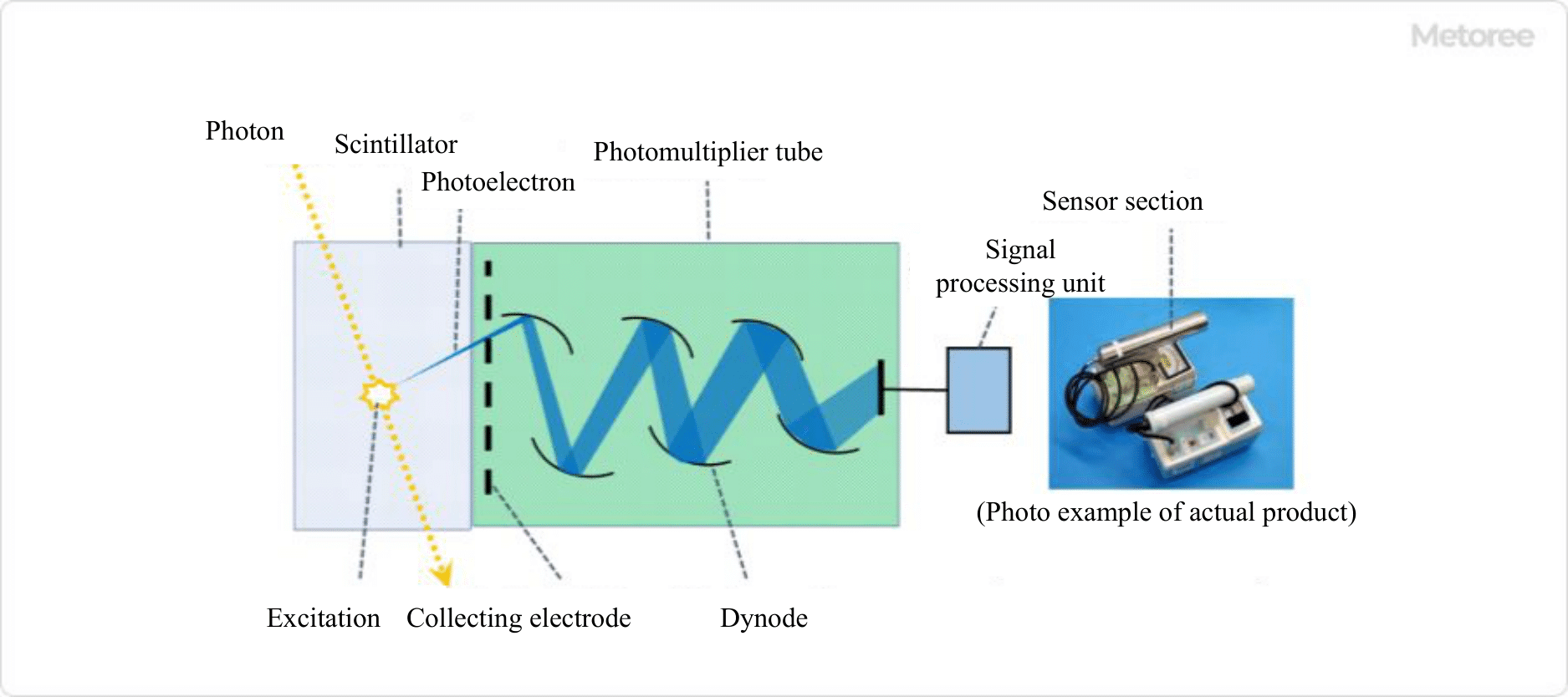
Figure 2. Basic structure and measurement principle of a scintillation survey meter
A scintillation survey meter consists of a scintillator and a photomultiplier tube as shown in Figure 2. When radiation strikes the scintillator, the crystalline material of the scintillator is excited by the photoelectric effect and other effects.
The photomultiplier tube converts the faint light generated when the scintillator returns to the ground state into an electric current, amplifies it, and counts the resulting pulsed current. Scintillators for γ (X) rays are highly sensitive and suitable for low-level radiation measurements in general environments.
3. Detection of Neutrons by Nuclear Reaction
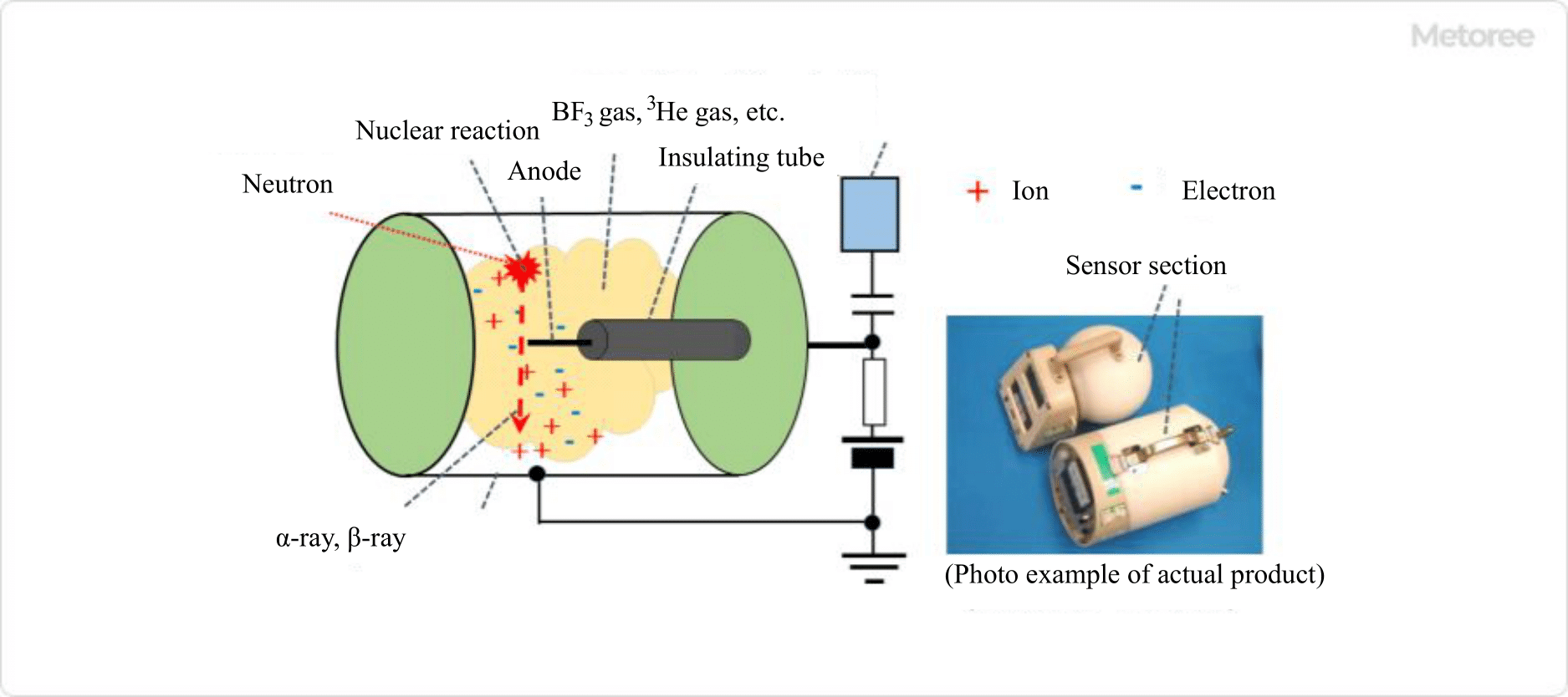
Figure 3. Basic structure and principle of a survey meter for neutrons
As a neutron survey meter, BF3 or 3He gas is filled into a detector consisting of a cathode and anode as shown in Figure 3, and α-rays and protons (p) produced by the nuclear reaction of 10B(n,α)9Li and 3He(n,p)3H are measured using the same principle as in an ionization chamber. Neutron energy ranges from thermal neutrons (0.025eV) to fast neutrons (10MeV). The effective dose rate is considered to be in the range of 0.01 μSv/h to 0.01 mSv/h.
Some detectors are spherical, usually called Bonner balls. By using multiple spheres of different sizes, the neutron energy spectrum (intensity distribution) can be obtained.
4. Personal Radiation Dosimeter
Integral dosimeters, such as film badges and TLD dosimeters, are used as personal radiation dosimeters. Film badges are based on the photosensitivity of photographic film to radiation and consist of a plastic case containing various filters and a small piece of film.
TLD dosimeters utilize the fluorescent properties of certain crystalline materials, such as CaSO4, which emit fluorescence in response to the amount of radiation received.
Other Information on Survey Meter
1. Radiation Units
- Gy (Gray)
A unit of absorbed dose. 1 Gy is equal to 1 kg of a substance absorbing 1 J (joule) of energy.
- Sv (Sievert)
A unit of equivalent dose or effective dose. Equivalent dose is the dose absorbed by each organ of the human body multiplied by the weight of each type of radiation (radiation weighting factor). The effective dose is the sum of the equivalent dose for each organ multiplied by the organ sensitivity weights (tissue weighting factors) for all organs. When referring to radiation dose, effective dose is generally used.
- Bq (Becquerel)
The unit of measurement for the amount of radioisotopes. When a radioisotope decays once per second, that is 1 Bq.
2. Radiation Exposure Control for Radiation Workers
Radiation workers are required to ensure that their radiation dose does not exceed 100 mSv for five years and 50 mSv for one year. For women and pregnant women, lower limits are set by law. For the general public, the standard is 1 mSv or less per year of effective dose.
To obtain correct measurement results in environmental monitoring, periodic calibration (correction of deviations in indicated values), daily inspections, and bag-ground measurements should be performed to provide a guide in case of abnormalities or malfunctions. Cases of accidents involving radiation workers leading to serious fatalities have been reported in many countries around the world. Accidents at nuclear facilities and other facilities are caused by structural defects and deviations from worker procedures, and there is a need for safety management of facilities and adherence to worker procedures.
3. Radiation Facilities
High-energy ion accelerators used for particle physics research can also be used as a high-energy neutron source by injecting protons into targets such as W (tungsten) or Li (lithium). LINAC (linear electron accelerator), etc., are used for tire hardening and treatment.
Alpha-ray sources such as 241Am (americium) are used to evaluate alpha-ray soft errors (reversal of 1, 0 data) in semiconductor devices. γ-ray irradiation equipment using 60Co (cobalt), which is used for sterilization, prevention of potato germination, and various irradiation effect studies, requires radiation exposure control for workers and researchers.
The above research and testing facilities are usually classified as “controlled areas” under the “Law Concerning Regulation of Radioactive Isotopes, etc.”, and radiation exposure and surface contamination of objects, workers, and researchers, as well as the carrying in and out of radioisotopes, are strictly controlled.
4. Nuclear Fuel Handling Facilities
Low-energy neutrons are used in experimental reactors such as those at Kyoto University, MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), and the Halden reactor in Norway to treat brain tumors. In this process, living organisms and surrounding equipment may be activated.
On the other hand, commercial nuclear reactors in normal operation are required to have a periodic inspection of the reactor building and equipment approximately once a year. During the inspection, the reactor is shut down and there are no neutron rays. On the other hand, in an operating reactor core, radioactive isotopes such as 60Co are produced by the activation of structural materials and other materials.
Radioactive materials dissolve in the reactor coolant and are absorbed by the inner surface of the reactor cooling system piping, causing external radiation exposure to workers. When disassembling and repairing equipment, surface contamination must also be taken into consideration, so a survey meter is a must-have item during work.





 A Servo Drive is a amplifier device that controls a
A Servo Drive is a amplifier device that controls a  Silica Sand is a quartz grain.
Silica Sand is a quartz grain.