What Is a Hexagon-Slotted Nut?
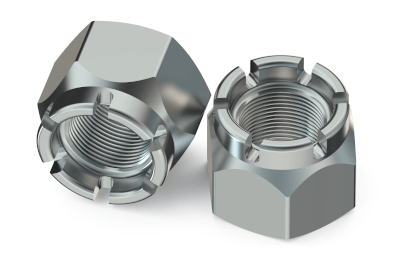
Hexagon-slotted and castle nuts are nuts with grooves cut into one end on all six sides. These grooves allow for the insertion of a split pin into a drilled hole in both the thread and the nut groove to prevent loosening.
They are sometimes referred to as “castle nuts” because their shape, including the grooves, resembles that of an old Western-style castle. Castle nut features a small surface area around the six grooved sides, facilitating a tight and compact wrap of the split pin around the nut.
Uses of Hexagon-Slotted Nuts
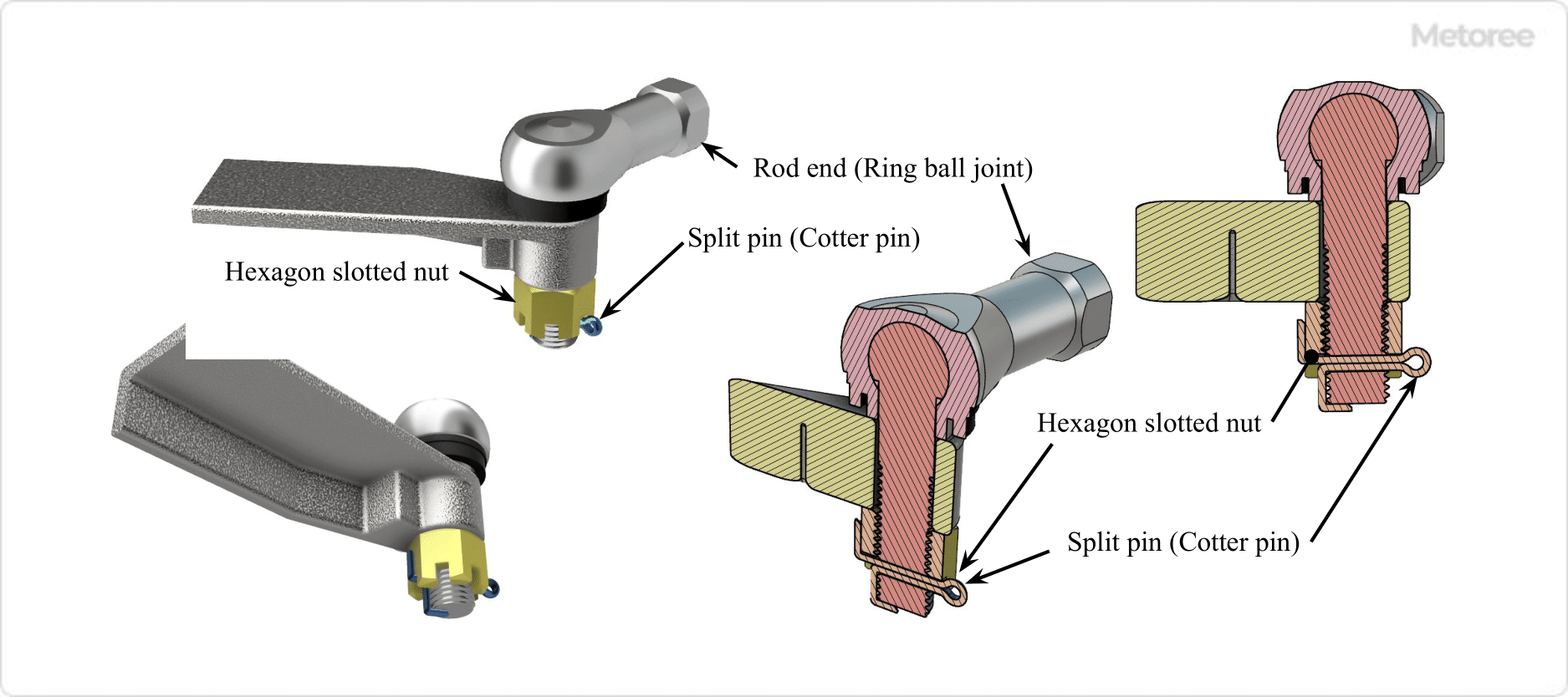
Figure 1: Application of Hexagon Slotted Nuts
Hexagon-slotted nuts are used to prevent loosening and nut dropout by inserting a split pin or similar device into the nut groove and threaded hole. Although various nuts are now widely available, hexagon-slotted nuts were frequently used for their reliable prevention of loosening.
However, because their installation requires drilling on the thread side, they are costly and can damage the thread. Nowadays, their use is limited to situations such as high-temperature environments or when the nut mustn’t fall off, even if loosened.
Hexagon-slotted nuts can be reused during disassembly and reassembly, but the split pin should not be reused; it must be replaced with a new one.
Principle of Hexagon-slotted Nuts
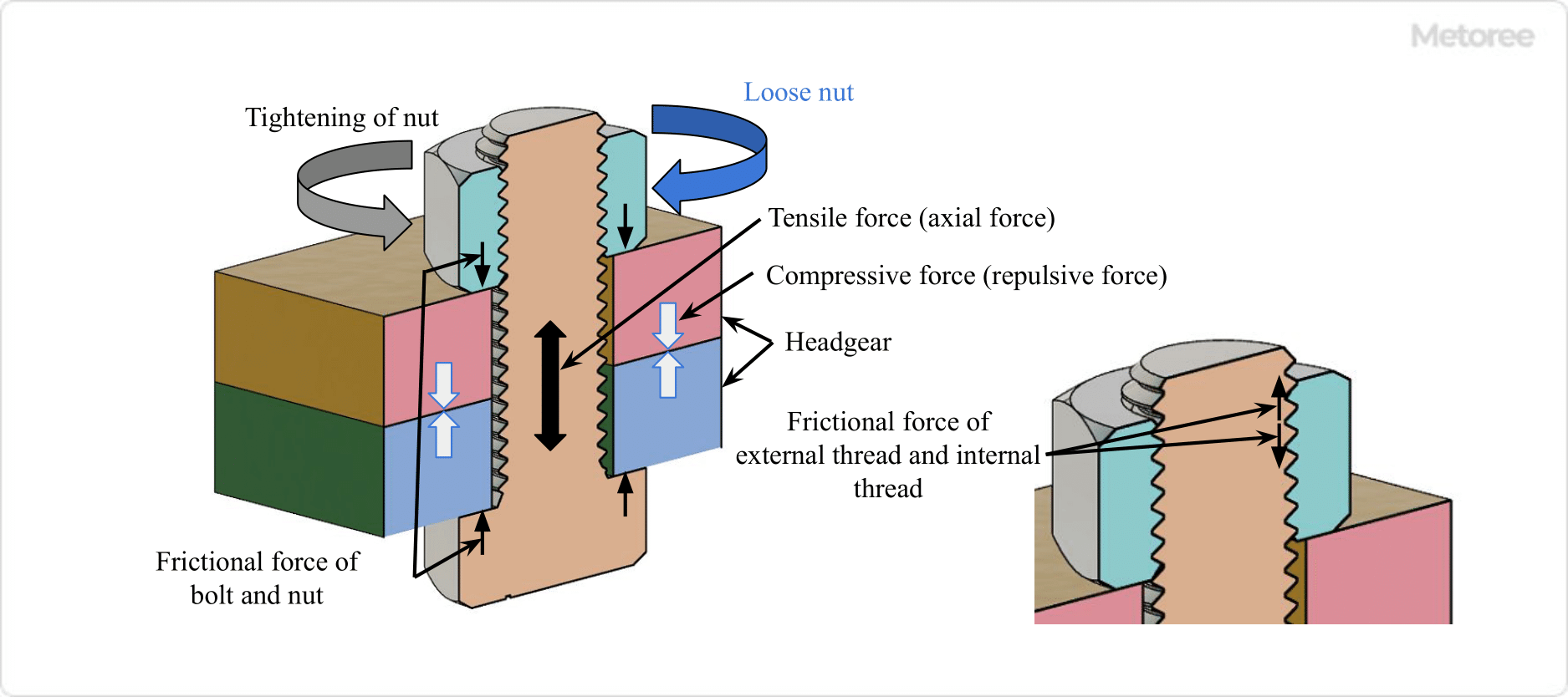
Figure 2: Principle of Screw Tightening and Loosening
The principle of screw tightening and loosening involves applying a compressive force to the fastened object and a tensile force to the bolt shaft, which is repelled by the object. This tensile force generates a frictional force between the bolt/nut’s seating surface and the fastened object, securing the screw in place.
In this state, three frictional forces work together:
- The frictional force between the male and female threads
- The frictional force between the fastened object
- The frictional force between the bolt/nut seat and the fastened object
Screw loosening occurs when these frictional forces are reduced due to various factors, such as distortion or indentation of the seating surface, vibration-reducing axial force, or lubrication reducing friction between threads.
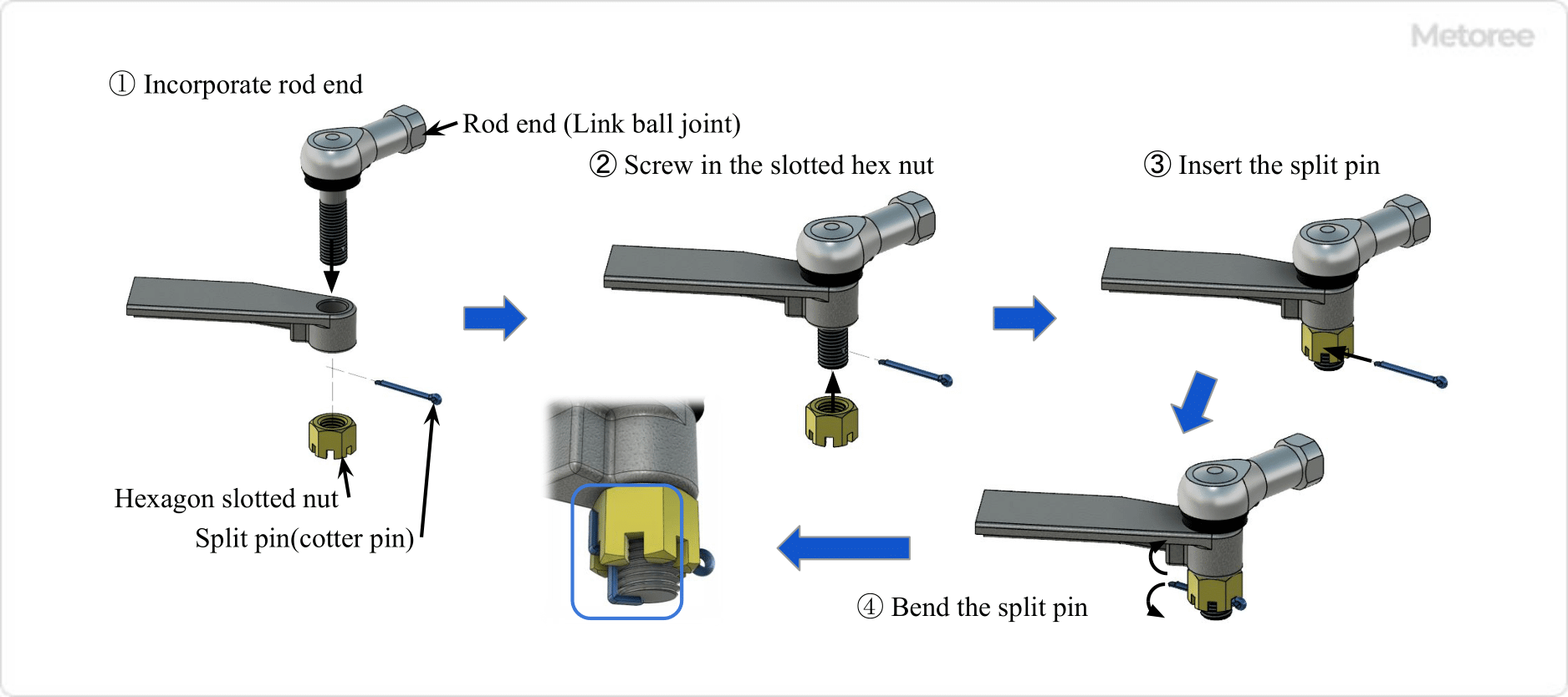
Figure 3: Installation of Hexagon Slotted Nut and Split Pin
The hexagon-slotted nut compensates for the reduction in initial axial force but does not prevent slippage of the seating surface or loosening due to the nut’s return rotation. Installation involves inserting a split pin into the bolt groove and threaded hole, bending the split pin tips into the groove along the nut side and the threaded side and end, ensuring the nut stays in place without loosening.
Types of Hexagon Slotted Nuts
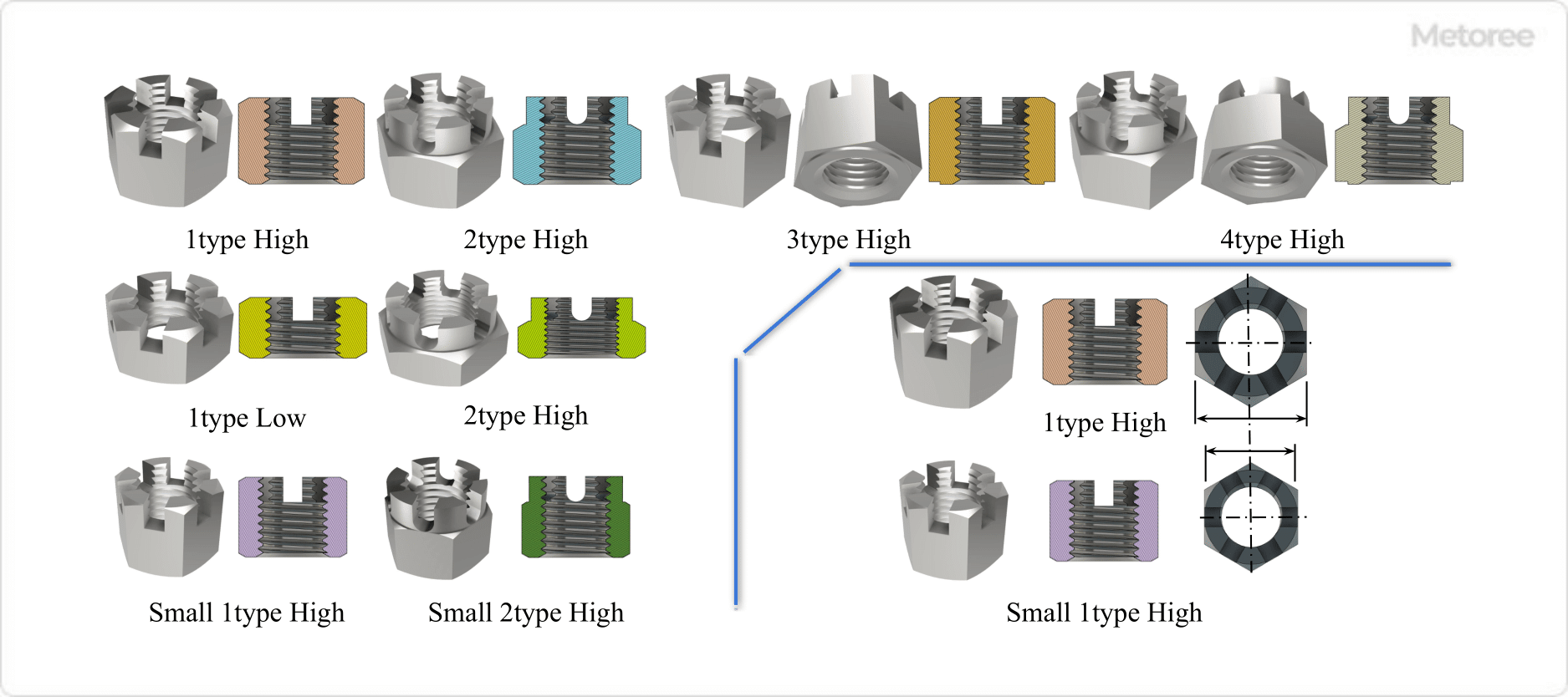
Figure 4: Types of Hexagon Slotted Nuts
The types of hexagon-slotted nuts are generally specified in various standards. Figure 4 illustrates each type and shape.
1. Type 1 High/Low
The hexagonal part has an infeed groove, and the nut height is high, suitable for small nominal diameters. This type is chosen when there are restrictions on nut height.
2. Type 2 High Type and Low Type
The high type features a groove from the hexagonal portion to the upper part, intended for large nominal diameters..
3. Type 3 and 4
Type 3 has a Class 1 seat, and Type 4 has a Class 2 seat, differentiating them by their seating surface specifications.
Other Information on Hexagon Slotted Nuts
1. Standards for Hexagon Slotted Nuts
- ANSI/ASME B18.2.2 nuts for general applications: machine screw nuts, hex, square, hex flange, and coupling nuts (inch series)
2. Material of Hexagon Slotted Nuts
Hexagon-slotted nut materials are specified according to various standards. Some types and nominal diameters are to be determined by agreement between the delivery parties.