What Are FRP Resins?

FRP Resins are fiber reinforced plastics (FRP), which are made by mixing matrix resins such as epoxy resins with reinforcing materials such as glass fibers.
FRP Resins are widely used as lightweight and strong materials for aircraft and other transportation equipment parts, construction materials, sporting goods, and even in the space industry for rocket and satellite parts.
The physical properties of FRP Resins vary depending on the matrix resin and reinforcing material used. Therefore, it is important to select the most suitable FRP Resins for each application.
Uses of FRP Resins
FRP Resins are used in aircraft and other transportation equipment parts, chemical storage tanks, construction materials, sports equipment, and even rocket and satellite parts.
FRP Resins are called by different names depending on the reinforcing material added, and each has different characteristics. FRP Resins containing glass fibers are GFRP.
GFRP has a greater specific strength than metal materials, is a lighter material, and is non-conductive due to the presence of glass.
On the other hand, CFRP, which contains carbon fibers, is stronger and harder than GFRP, but conducts electricity.
However, all FRP Resins share the same properties of being light and strong.
Structure of FRP Resins
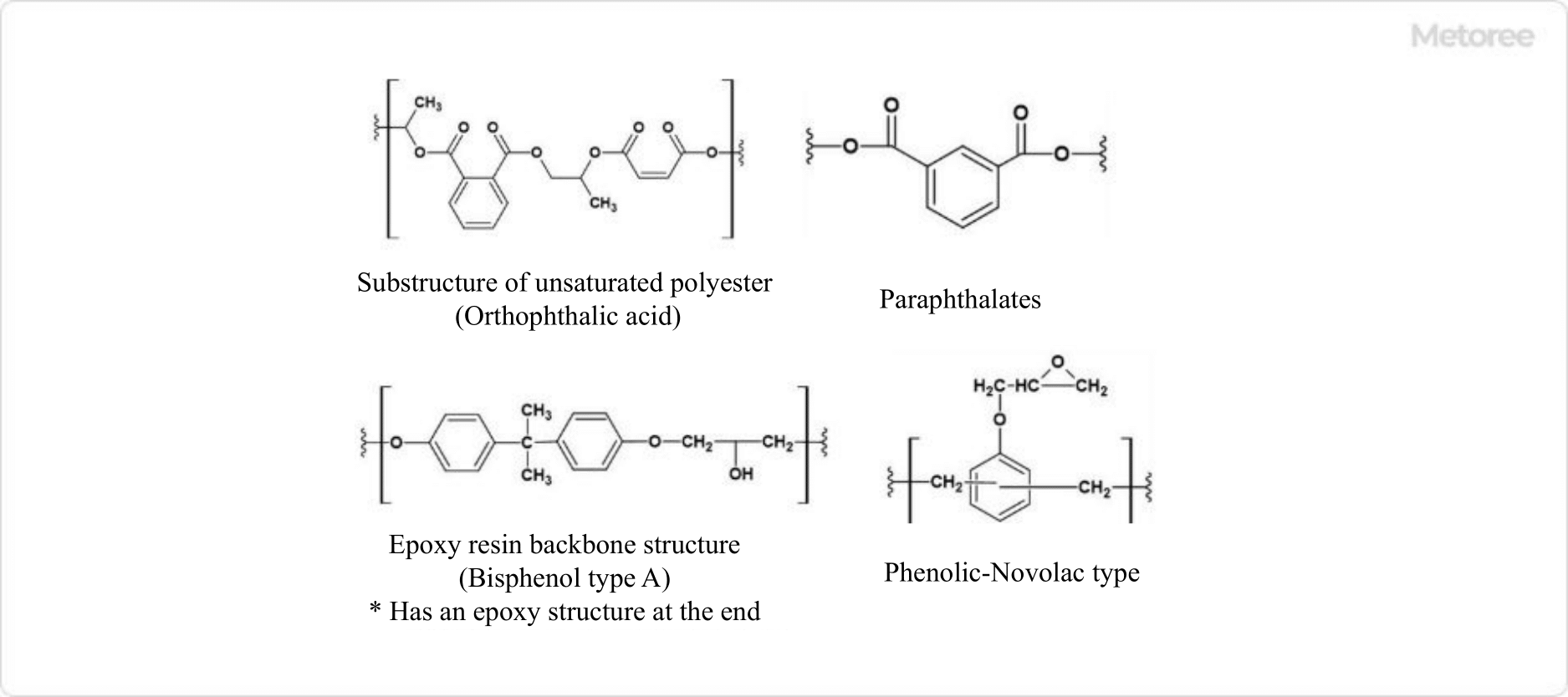
Figure 1. Structure of FRP resin
FRP Resins are composed of matrix resins and reinforcing materials. Unsaturated polyester resins, epoxy resins, and vinylester resins are used as matrix resins.
Unsaturated polyester resins have the advantages of easy molding and excellent water resistance. Flame resistance can also be added by adding halogens.
Epoxy resins have excellent acid and alkali resistance and chemical resistance but are difficult to mold. Vinylester resins are easy to mold and have excellent mechanical strength. Bis-A resins are inferior in solvent resistance but superior in acid and alkali resistance, and Novolac resins are inferior in oxidation resistance but superior in solvent and heat resistance.
Types of FRP Resins
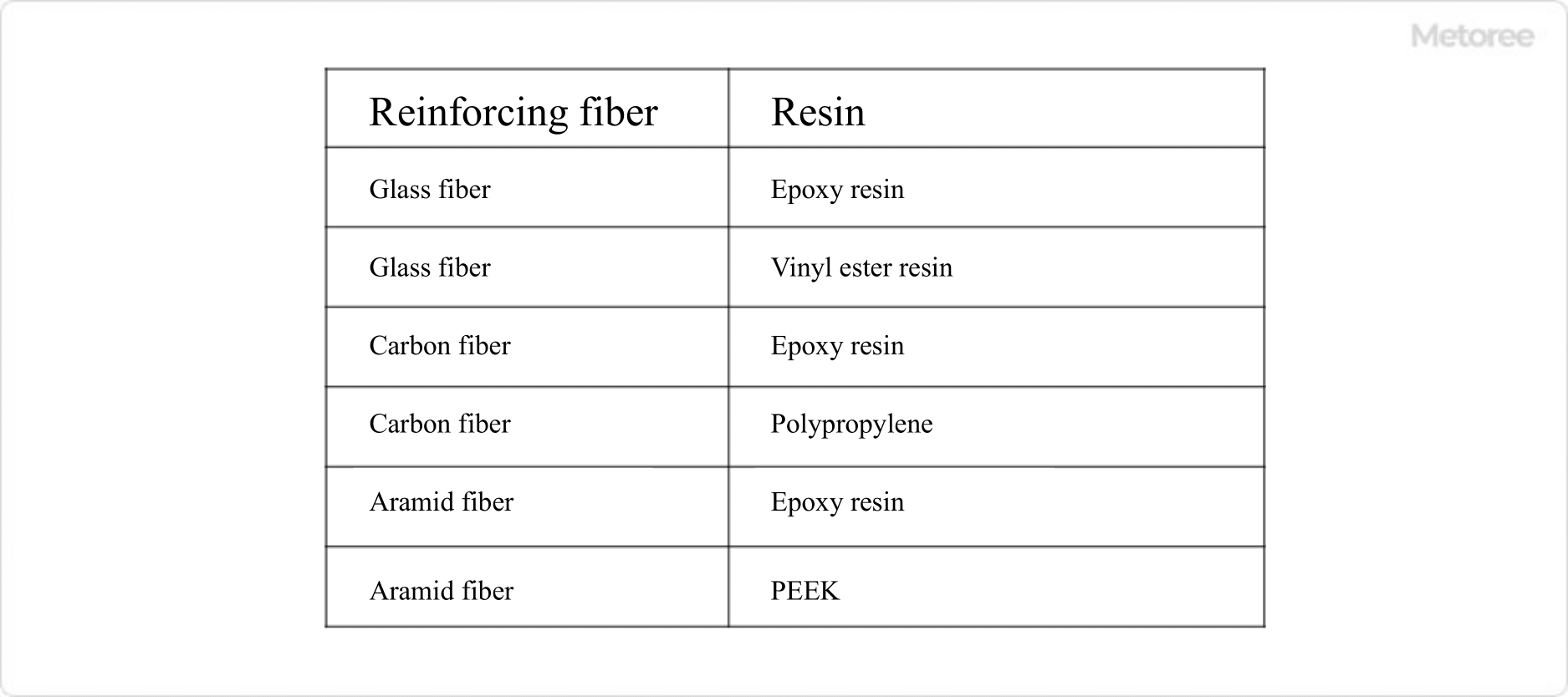
Figure 2. Types of FRP resins
Glass fiber, carbon fiber, and aramid fiber are used as reinforcing agents in FRP Resins. GFRP made with glass fibers has a higher specific strength than metal, is non-conductive, and is relatively inexpensive.
On the other hand, CFRP made of carbon fiber is stronger, lighter, harder, and more conductive than GFRP. AFRP made with aramid fibers is lighter and stronger, but less workable.
Because of their different chemical structures, the corrosion resistance of each type of reinforcement varies greatly. The properties of GFRP also change with the grade of glass fiber used.
E-glass, the most commonly used for FRP Resins, contains very little alkali metal and has excellent water resistance, but when in contact with strong acids, components such as Al and Ca leach out, causing cracking.
Carbon fiber, on the other hand, is affected by strong oxidizing chemicals, but can be used in most environments without problems. Aramid fibers have amide bonds that cause hydrolysis when in contact with alkaline chemicals, and they are easily degraded by ultraviolet rays.
Other Information on FRP Resins
Processability of FRP Resins
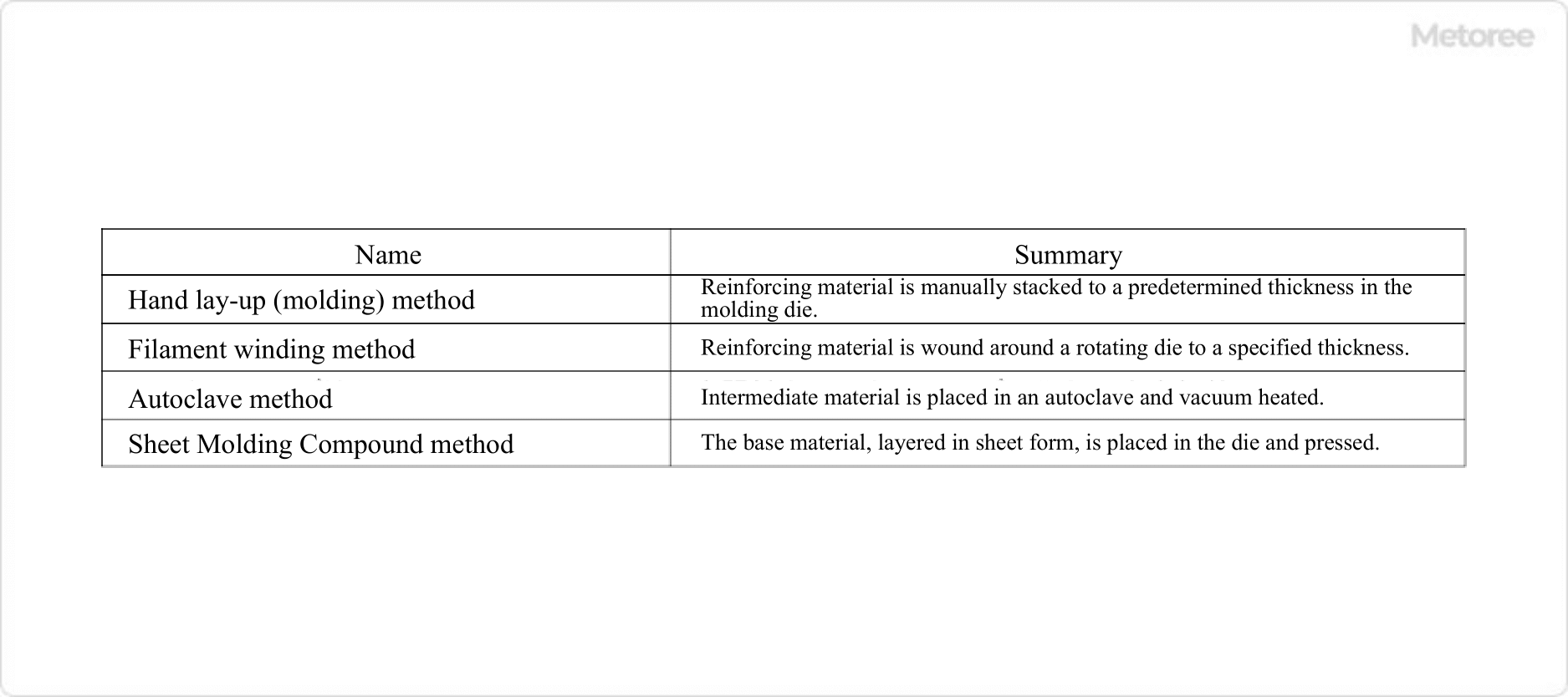
Figure 3. Processability of FRP resin
Carbon Fiber FRP Resins (CFRP) are formed by infiltrating liquid thermosetting epoxy resin into carbon fibers, cutting out semi-cured sheets, and pressurizing and thermosetting them in an autoclave. However, the above method requires matrix resin to permeate the fibers, making it difficult to apply to thermoplastic resins with high viscosity.
On the other hand, molding methods for CFRP using thermoplastic resin are still being studied, for example, press molding. In this method, carbon fiber containing thermoplastic resin is heated, transported, and pressed in a die, then cooled and cut for processing.
However, this method still has issues, such as the need for a method to cut CFRP with high strength cleanly and without blade wear.