What Is an FPC?
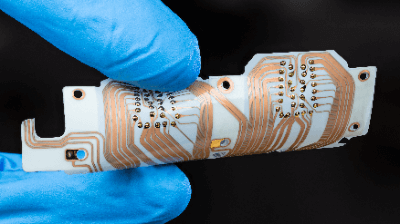 An FPC is a flexible printed circuit board. It is characterized by its paper-thinness and softness. Since it is lighter, smaller, and more economical than ordinary substrates, it has come to be widely used in recent years.
An FPC is a flexible printed circuit board. It is characterized by its paper-thinness and softness. Since it is lighter, smaller, and more economical than ordinary substrates, it has come to be widely used in recent years.
An FPC is also called flexible substrate, an acronym for Flexible Printed Circuits.
Uses of FPCs
FPCs are widely used in electrical appliances and consumer products. A typical application is smartphones. In most cases, FPCs are used in the control boards of smartphones. Because of their small size and lightweight, FPCs are useful for products that are carried daily.
In-home appliances, FPCs are used in LCD TVs. Since electronic control boards can be made smaller, they are economically advantageous. Other products include keyboards and printers, which have a wide range of uses. In addition, they are also used in heavy industry. In recent years, it has become a must-have component in the space development and aviation industries.
Principle of FPCs
The mechanism of an FPC is the same as that of a printed circuit board, but the biggest difference is that the base material is a film. Circuits are printed on insulating polyimide or polyester film with copper or other metals as wiring. Both the film and copper foil are about 12 µm to 50 µm, so they can remain quite thin even when laminated together.
FPCs are fabricated in the following manner.
- A thin copper foil is attached to a base film with an adhesive, such as epoxy resin.
- Dry film is coated on this base material for etching.
- UV light is irradiated to transfer the circuit diagram onto the dry film.
- The required portion of the circuit diagram remains on the dry film, and etching completes the circuit pattern on the copper foil.
- The dry film is peeled off, and an insulator film is applied to the entire surface for plating.
The above process completes lightweight and durable FPCs. there are two types of FPCs: single-sided FPCs and double-sided FPCs. While double-sided FPCs are less durable than single-sided FPCs, the advantage of double-sided FPCs is that they can be designed with higher density. In double-sided FPCs, the process of single-sided FPCs is repeated.
In recent years, FPC substrates with a flex-rigid structure and multilayered FPC substrates, in which a rigid substrate is sandwiched between FPCs, have also been developed. As a base material, polyimide is more heat-resistant and durable than polyester.
Other Information on FPCs
1. Characteristics of FPC
FPCs have three characteristics: high flexibility, lightweight, and high cost.
- High flexibility
Plastic films such as polyimide are used as the material for FPCs. Plastic films are used for moving parts of electronic devices because of their flexibility and bendability. - Light in Weight
FPCs are made of plastic and are lightweight. This is a necessity in the space and aviation industries, where weight restrictions are strict. - Expensive
FPCs tend to be more expensive than rigid boards, which are regular printed circuit boards.
2. Points to note when using FPCs
There are two major points to note when using FPCs.
- Difference in Bending Resistance
FPCs are characterized by high flexibility, but their flex resistance differs among manufacturers and products. - Mechanical Weakness
FPCs are light and thin films, making them mechanically weak. When mounting components, a plate called a reinforcing plate must be attached to the electronic components.
FPCs must be used in consideration of the above points.
3. Increase in the Size of the FPC Market
According to a study by Credence Research, the global FPC market is increasing year by year; it is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.6% from 2018 to 2027, and the global market size for flexible electronics is expected to grow to approximately 4.5 trillion yen by 2027.
The growing market is related to the rising demand for FPCs in the automotive, consumer electronics, and aerospace industries.