What Is a Terminal Relay?
 A terminal relay is an input/output signal processing device that integrates multiple relays and terminal blocks.
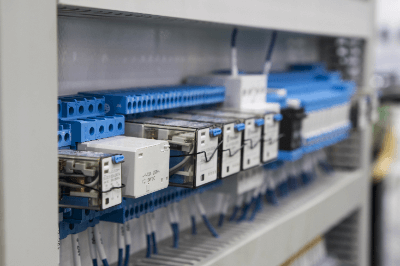
A terminal relay is an input/output signal processing device that integrates multiple relays and terminal blocks.
It is used as an interface device to relay I/O of programmable controllers and solenoid valves. The main structure of a terminal relay, which plays the role of I/O interface device, is a terminal block on a pedestal with a built-in printed circuit board, and multiple independent single-pole type small relays can be mounted on this pedestal according to the application, as a compact relay structure while excelling in maintainability, This contributes to downsizing of equipment and reduced wiring.
Uses of Terminal Relays
Terminal relays are mainly used in industrial applications.
The following are examples of terminal relay applications:
- For internal signal communication in presses and processing machines
- For relaying signals between large pumps and fans and control equipment
- For relaying signals from slurry processing equipment
Generally, microcomputers, PLCs, and other control devices are used to control large industrial equipment in complex ways. While these control devices are capable of complex internal processing, the allowable output signal current is often small. Conducting large currents through these devices may have adverse effects, such as accelerating failure frequency.
Therefore, if you wish to control equipment with large load currents or inrush currents, such as solenoid valves, isolate the outputs of the control equipment by means of relays. However, installing multiple power relays and other relays side by side occupies space and complicates control wiring.
Terminal Relays are a device that combines a terminal block and relay into a single unit, allowing a lineup of small, single-pole relays. Therefore, space and wiring savings can be achieved.
Principle of Terminal Relays
Terminal relays are composed of terminal block components and relay components.
1. Terminal Block Component
The terminal block component consists of a relay socket and a terminal block. The part that conducts electricity is made of copper or iron screws, and the casing is made of hard synthetic resin. Many products are fixed by tightening the external wiring, which is processed with round terminals, etc., with iron screws.
Generally, most products have sockets that can accommodate four relays, with two inputs and two output terminals per relay. 16-point products are also available. Terminal Relay is sometimes referred to as a relay terminal.
2. Relay
A relay is a component that insulates and relays signals. Terminal relays are generally small, single-pole relays. It is often installed by inserting it into a terminal block component with a pin on the back side. Relay specifications are often printed on the casing on the relay surface, and products with various power supply specifications and signal types are sold.
How to Select a Terminal Relay
When selecting a terminal relay, the following considerations should be taken into account:
1. Number of Output Points
The number of output points is the number of points that can be output by the terminal relay. Most general-purpose products have 4 output points, but there are products with 16 or 32 output points for connection to PLCs. In the case of a system that controls many devices, the more output points, the less wiring is required.
2. Input Specifications
The input specification is the type of signal input to the coil portion of the relay. 100 VAC, 24 VDC, and other specifications are available. Select the input specification according to the output specification of the control equipment.
3. Output Specification
Output specifications are the specifications of the signals output by the relay. Factors such as signal type and rated energizing current are included.
Signal types are mainly classified into contact and non-contact. With contacts, the signal is transmitted by mechanically operating a metal section with an electromagnetic coil. It tends to have a large allowable current and has the advantage of being heat resistant. However, it has the disadvantage that the contact parts gradually wear out due to opening and closing operations.
The non-contact method uses semiconductors or solid-state relays to transmit electrical signals. Since there is no physical drive, it can withstand high open/close frequencies and high speed open/close operations. However, they are susceptible to heat and have drawbacks, such as semiconductor components that can fail if currents exceeding their rated currents flow through them.
The rated current rating is the amount of current that can be conducted. The larger the current value, the more capable it is of controlling large loads, but the larger the relay often becomes. Generally, when used as terminal relays, most products have a current-carrying capacity of 1 to 5 A.