What Is a Remote I/O?
A remote I/O is a device used to input, output, and operate measurement remotely. It also inputs and controls devices in factories and other facilities through a network. Because it is used over a network, there is no need for wiring or other complicated wiring settings, and it is effective in reducing noise caused by transporting data over long distances. Remote I/O is widely used in various factories today, where factory automation using IoT, etc. is progressing in order to reduce labor costs and improve production efficiency.
Uses of Remote I/Os
Remote I/Os are used on the factory floor where various factory automations are implemented. They are used to manage in a control room, etc., measurement devices such as temperature, pressure, humidity, current, voltage, etc., collectively that need to be measured and controlled in a factory and that support network communication.
There are many products on the market that support network lines for various measurement devices, and they should be selected appropriately according to the network used by the measurement devices in use.
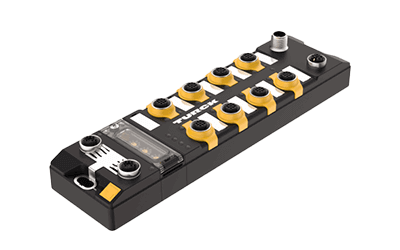
Configuration of Remote I/Os
A remote I/O consists of a network communication section, a processing unit, and a connection section connected by a single cable. In the connection section, many of the products come with terminals for various connections, allowing you to connect sensors, switches, LEDs, and other control wiring. Some products support more than 60 connections. Remote I/Os can also be connected in parallel. When the number of connections required is insufficient for one remote I/O, or when introducing new electronic components that require new wiring, it is relatively easy to expand by adding additional remote I/Os in parallel. The network communication section connects to a PLC, DCS, or other remote I/O in the control panel via a network.
Principle of Remote I/Os
Remote I/Os, also called distributed I/Os, pass input signals to and from PCs, PLCs, and other master devices in a factory via communication.
1. PLC
PLC, from which remote I/Os pass signals to and from, stands for programmable logic controller, and is a controller used to control equipment and facilities. In manufacturing plants, PLCs control the operation of various devices, such as conveyor belts and sensors.
2. Network
For the networks used by remote I/Os, there are many products on the market that are compatible with the various industrial networks offered by the manufacturers that market PLCs.
Typical industrial networks include EtherNet/IP, EtherCAT, PROFINET, CC-Link, and HLS. Processing equipment handles a variety of communications. Some products use CPUs for high-speed processing, while others provide inexpensive products without CPUs or other components.
Other Remote I/O Information
1. Remote I/O Radio
Remote I/O, or input/output (IO) communication methods for remotely operated devices, include the wired method, in which devices are directly connected to each other with communication lines, and the wireless method, in which a transmitter/receiver is built into the device and communicates wirelessly. Here, Remote I/Os refers to the remote operation of devices using a wireless method.
There are several types of wireless radio communication methods, and Wi-Fi is the most commonly used communication method, especially used in many recent home appliances. However, when Remote I/Os are actually used wirelessly, they are often used in industrial applications such as factories, buildings, and special buildings, etc. In order to cope with the demand for high reliability, there are many cases where each manufacturer uses its own frequency band in the vicinity of 1G. The reliability of the communication method by using the right materials at the right time is the know-how of each company.
2. Remote I/O Ethernet
The remote I/O ethernet refers to the use of a communication standard called Ethernet for remote input/output of electrical and electronic equipment, known as Remote I/Os. Ethernet is a communication protocol standard from the physical layer to the data link layer in the OSI model, which organizes the functions required for communication between information devices. As a data link layer protocol, its main role is to transfer data reliably within the same network.
Specifically, the role of Ethernet is to transfer data from one Ethernet interface to another Ethernet interface in the same network. And to send data out of an Ethernet interface, each “0” and “1” bit is converted from an electrical signal to a physical signal, and the physical signal received through the Ethernet interface is converted back to an electrical “0” and “1” signal. As a physical protocol, the Ethernet standard also standardizes its physical signal conversion and use of cable media.
3. HLS
HLS is a “one master to multiple slaves” network that can control a batch of digital I/Os at high speed. 63 slave ICs can be connected to one master IC, and a maximum of 2016 I/Os can be controlled.
The HLS master IC has a built-in memory for I/O control registers and communication control registers corresponding to each slave IC.