What Is Methyl Iodide?
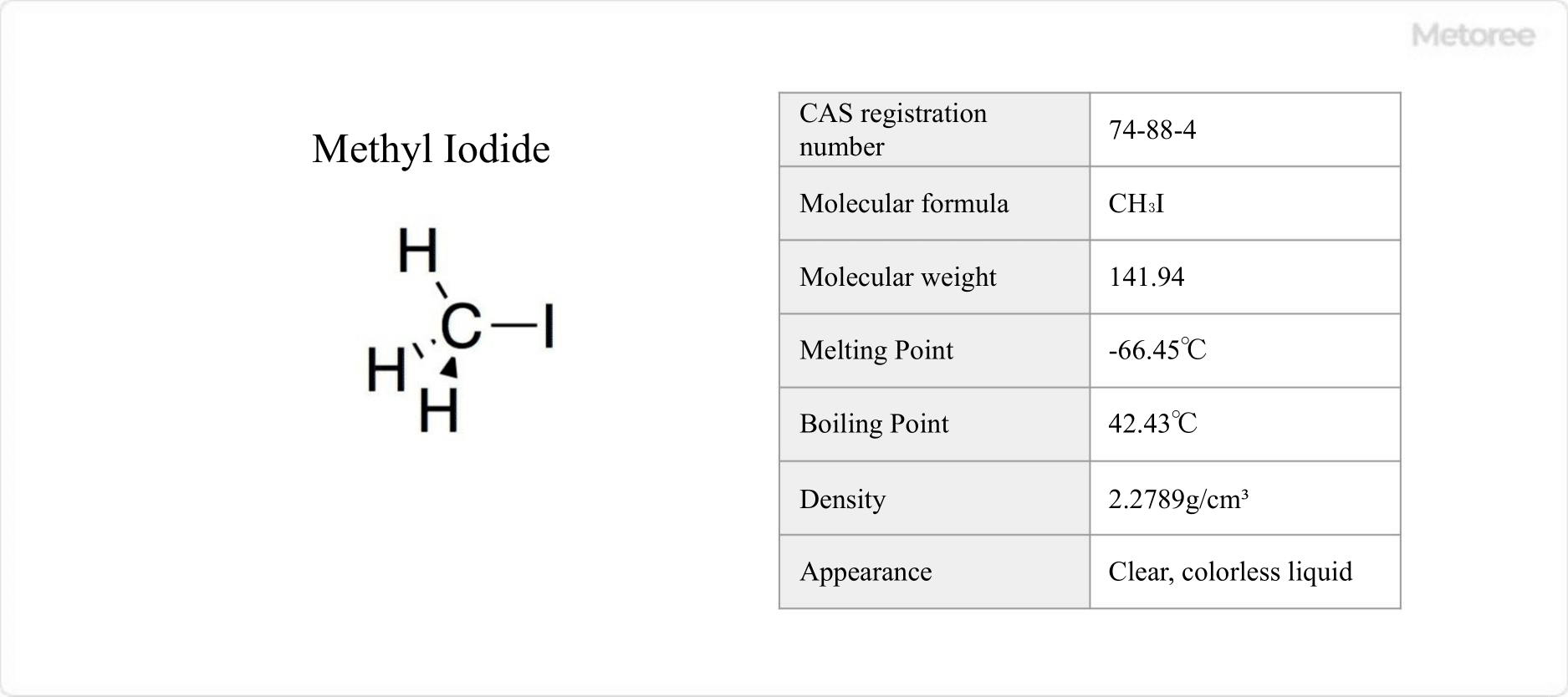
Figure 1. Basic Information on Methyl Iodide
Methyl iodide, a monoiodide of methane, is known for its CAS number 74-88-4 and MITI number 2-42. Classified as a “deleterious substance” under various laws, it is recognized for its mutagenic properties and requires careful handling due to its designation under safety laws with a controlled concentration of 2 ppm.
Uses of Methyl Iodide
Primarily used as a fumigant and in controlling bacterial and fungal diseases in agriculture, methyl iodide’s applications extend to medical treatments for iodine deficiency and as a scintillation detector in radiation detection. Its role in livestock feed highlights its importance as an essential nutrient.
1. Medical Care
It addresses iodine deficiency, preventing goiter and hypothyroidism, and acts as a thyroid-blocking agent during nuclear incidents.
2. Scintillation Detection
Methyl iodide serves as a scintillator material, fluorescing upon radiation exposure to detect gamma rays.
3. Animal Nutrition
As a crucial feed supplement, it supports thyroid function and health in livestock.
Properties of Methyl Iodide
This colorless to brown liquid is noted for its high toxicity and characteristic odor, with a melting point of -66.45°C and a boiling point of 42.43°C. It shows excellent solubility in organic solvents and water, but decomposes in light, requiring storage in dark, sealed containers.
Other Information on Methyl Iodide
1. Reactions With Methyl Iodide
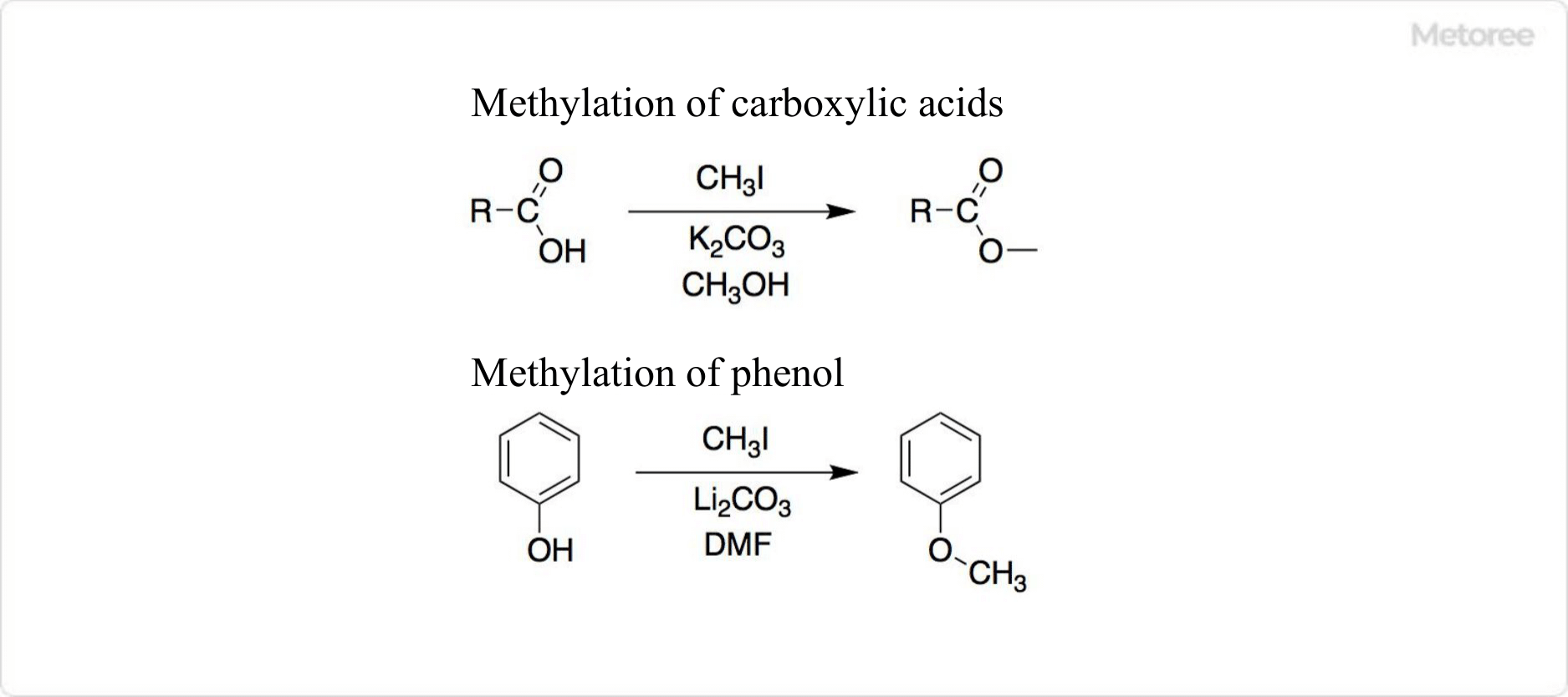
Figure 2. Reaction Using Methyl Iodide
As a precursor in Grignard reactions and a methylating agent in SN2 reactions, methyl iodide’s versatility is showcased in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
2. Methyl Iodide as a Methylating Agent
Despite its comparative expense, methyl iodide’s ease of handling and superior methylation capacity make it a preferred choice over other halides in organic synthesis.
3. Synthesis of Methyl Iodide
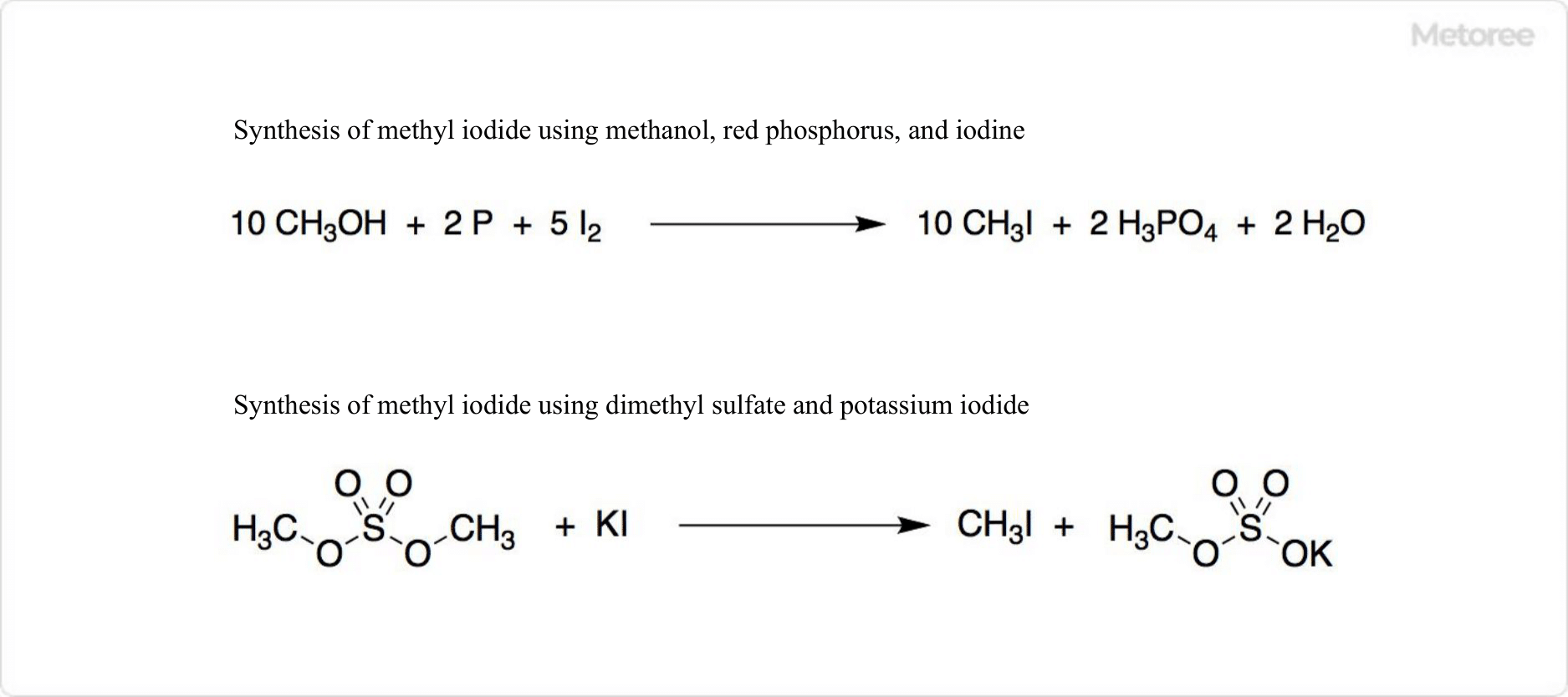
Figure 3. Synthesis of Methyl Iodide
Produced through the reaction of methanol with iodine and red phosphorus, methyl iodide can be purified by column chromatography using silica gel or alumina or synthesized in high yield through the reaction of potassium iodide with dimethyl sulfate and calcium carbonate.