What Is a HEPA Filter?
A HEPA filter is a device that collects micron-sized particles in the air with high efficiency. HEPA is an abbreviation for “High Efficiency Particulate Air”
As an ultra-high performance filter, it is used at the final stage of sorting through a filter for coarse dust. There is a high need for HEPA tilters to clean the air in industrial applications that maintain environmental sanitation or require clean rooms.
Uses for HEPA Filters
One application of HEPA filters is to maintain a clean environment in clean rooms. When air conditioning equipment is used in a clean room, HEPA filters are attached to the air conditioning equipment to prevent particulates from entering the clean room.
HEPA filters can also be used in fan units incorporated into manufacturing equipment to purify the air. In some cases, HEPA filters are installed in the exhaust systems of workplaces that handle dust. Also, HEPA filters are required to be installed if the substances handled fall under specified chemical substances, so it is important to check the regulations that apply to the substances handled.
Increasingly, HEPA filters are being installed in air purifiers not only for the manufacturing industry but also for general household use.
Pollen, which causes hay fever, is 10 to 30 μm in diameter, and microorganisms such as mold and mites are 5 μm or larger in diameter, so HEPA filters can collect more than 99.97% of these substances.
Principle of HEPA Filters
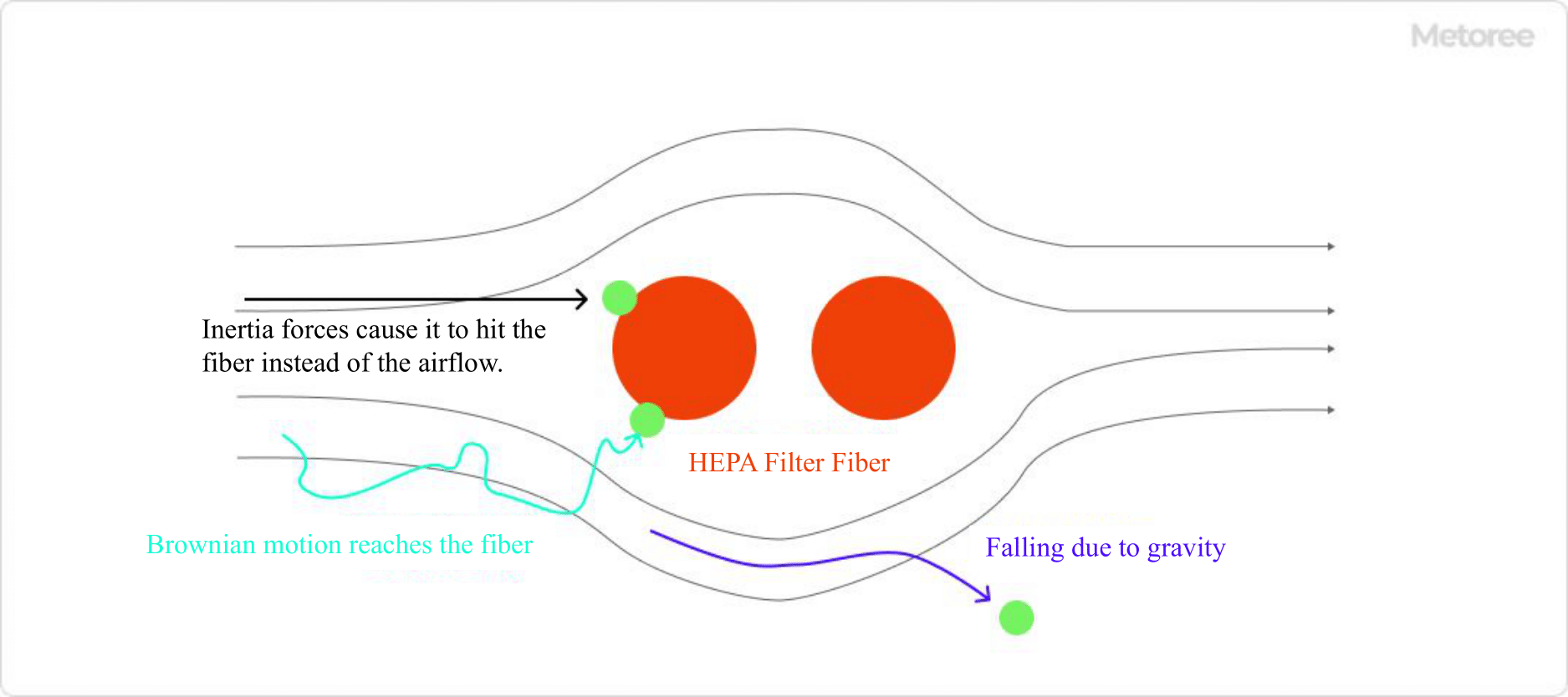
Figure 1. HEPA filter collection principle
HEPA Filters are made of filter paper made of fine glass fibers with a diameter of 1 to 10 µm, which are shaped into a corrugated pattern and mounted in a sturdy frame. The glass fibers are intricately intertwined within the filter, and the fine particles contained in the passing gas are adsorbed.
Typical target particle diameters are 1 μm or less. For larger particles, an air filter is used instead of a HEPA filter. The adsorption process of fine particles can occur through contact between fibers and fine particles, or through Brownian motion after collision. 0.1 µm to 0.2 µm particles are less efficiently collected by HEPA filters.
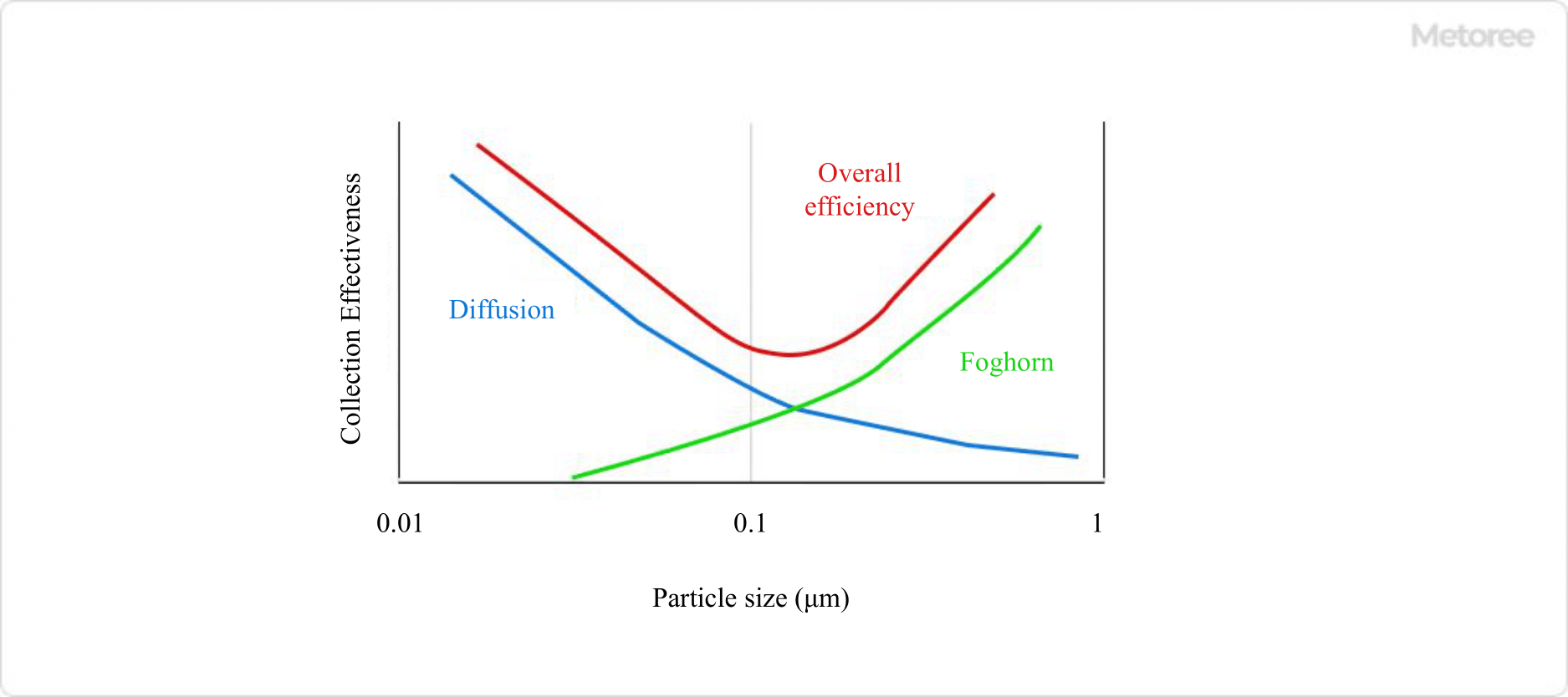
Figure 2. Collection efficiency of HEPA filters
Because small particles are strongly affected by static electricity, electrostatic HEPA filters are also available that use electrostatic forces to attract fine particles. This can increase the collection efficiency of fine particles.
Other Information on HEPA Filters
Efficient Use of HEPA Filters
Because HEPA filters are very fine-grained, they become clogged after prolonged use, and their collection efficiency gradually declines. As the collection efficiency decreases, the pressure drop increases and the filter may be damaged because it cannot withstand the pressure difference between the front and back of the filter.
The following are ways to prolong the life of a HEPA filter without replacing it:
1. Install a pre-filter
HEPA Filters can collect very fine particles, but because of their fine grain, they are prone to clogging when larger particles reach the filter. Therefore, installing a coarser pre-filter before the HEPA filter can extend its life.
2. Avoid oil mist
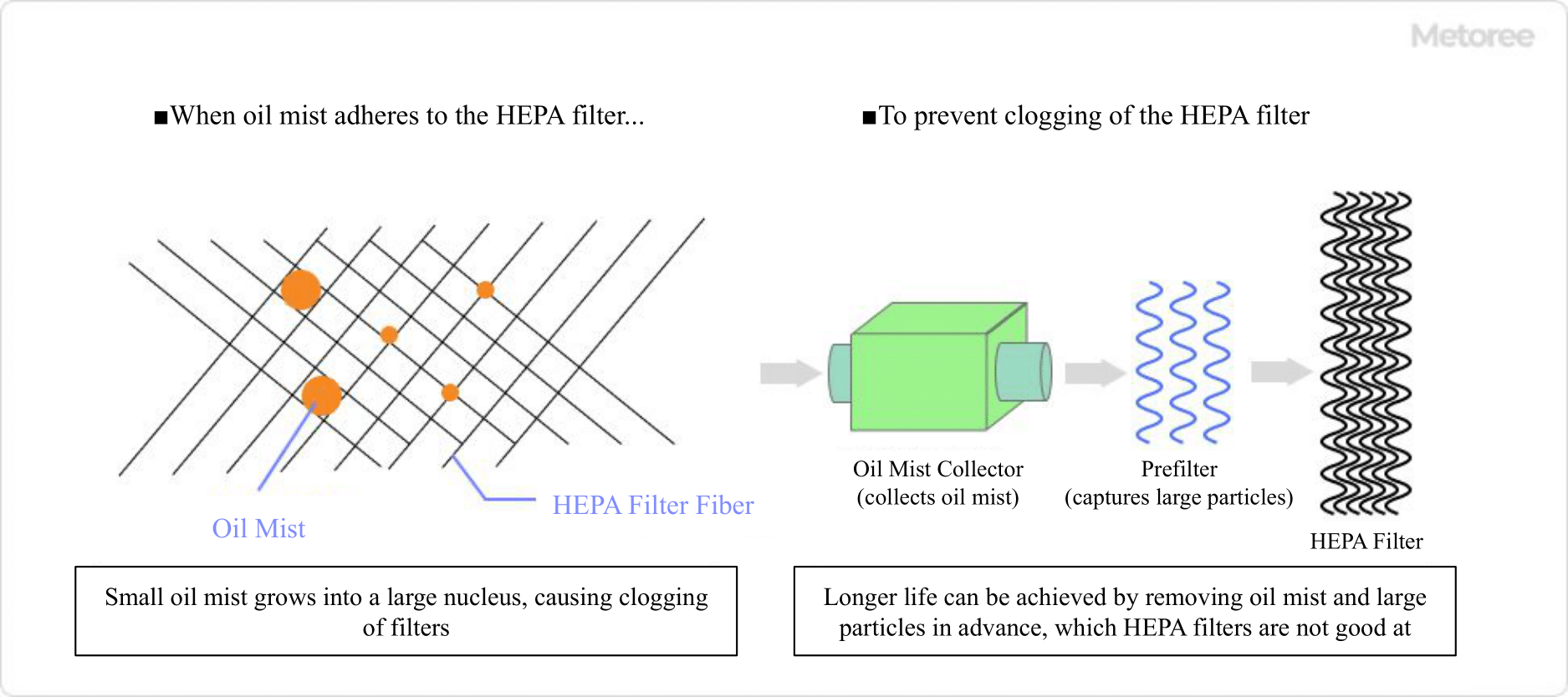
Figure 3. Longer service life of HEPA filters
When oil mist reaches the HEPA filter, it forms a film that can cause clogging. When using HEPA filters in areas where oil mist is generated, remove the oil mist with a dedicated device such as a mist collector.