What Is Oil-Based Paint?

Oil-based paints are paints that use organic solvents, such as thinner, and often include dry or non-drying oils instead of synthetic resins. This category also includes acrylic paints used in artwork. They are distinct from water-based paints, where water evaporates during drying, as opposed to the organic solvents in oil-based paints.
Uses of Oil-Based Paints
Oil-based paints are known for their durability and finish quality, making them suitable for roofing, exterior walls, car bodies, ships, and indoor areas requiring high durability like flooring. They are also used on metals and other materials that are not compatible with water-based paints due to their high adhesion and versatility.
Differences Between Oil-Based and Water-Based Paints
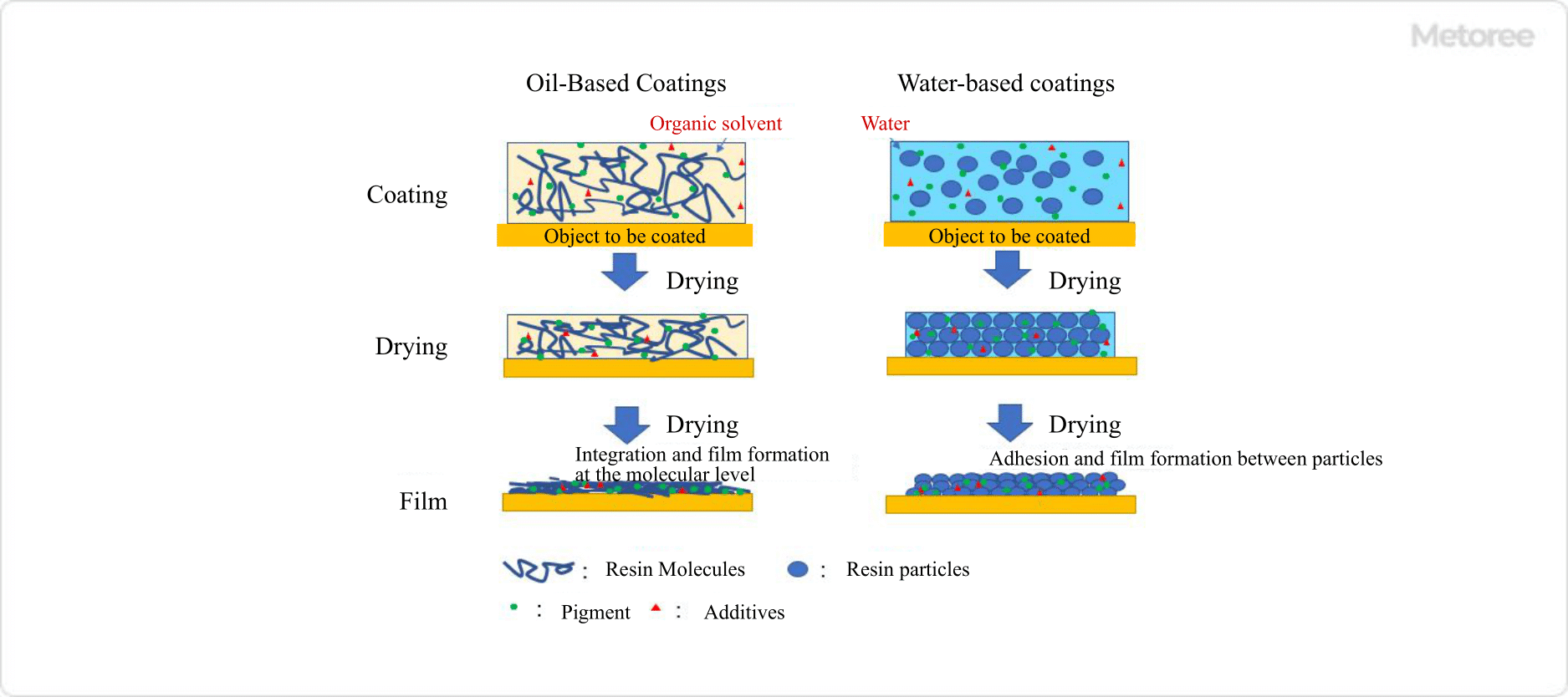
Figure 1. Difference between oil-based and water-based paints
Oil-based paints have stronger coating films, better adhesion, durability, and weather resistance than water-based paints, but they also have a stronger odor and are more expensive.
Types of Oil-Based Paints
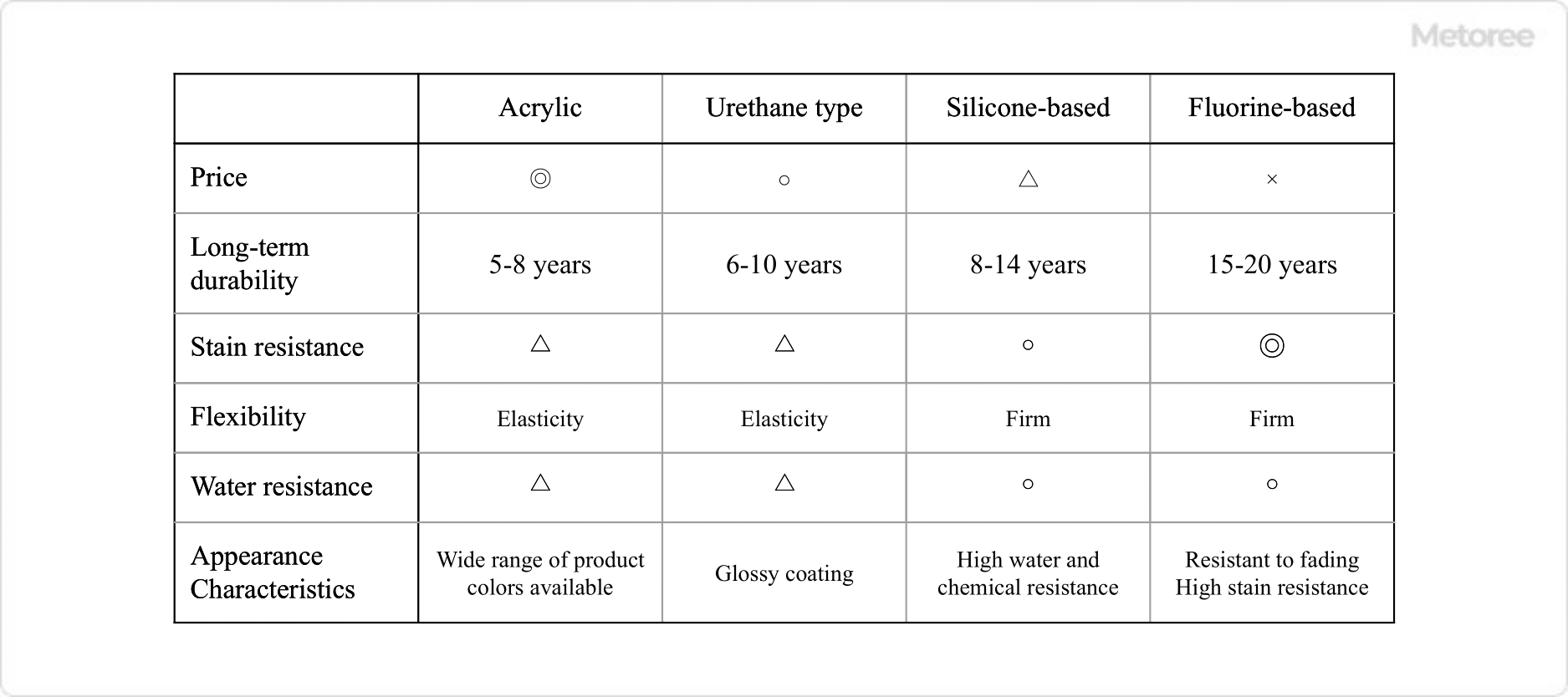
Figure 2. Comparison of paint properties between different resins
Oil-based paints include four main types of resins: acrylic, urethane, silicone, and fluorine, each offering distinct advantages in terms of color, gloss, durability, and weather resistance.
Other Information on Oil-Based Paints
Classification of Solvents
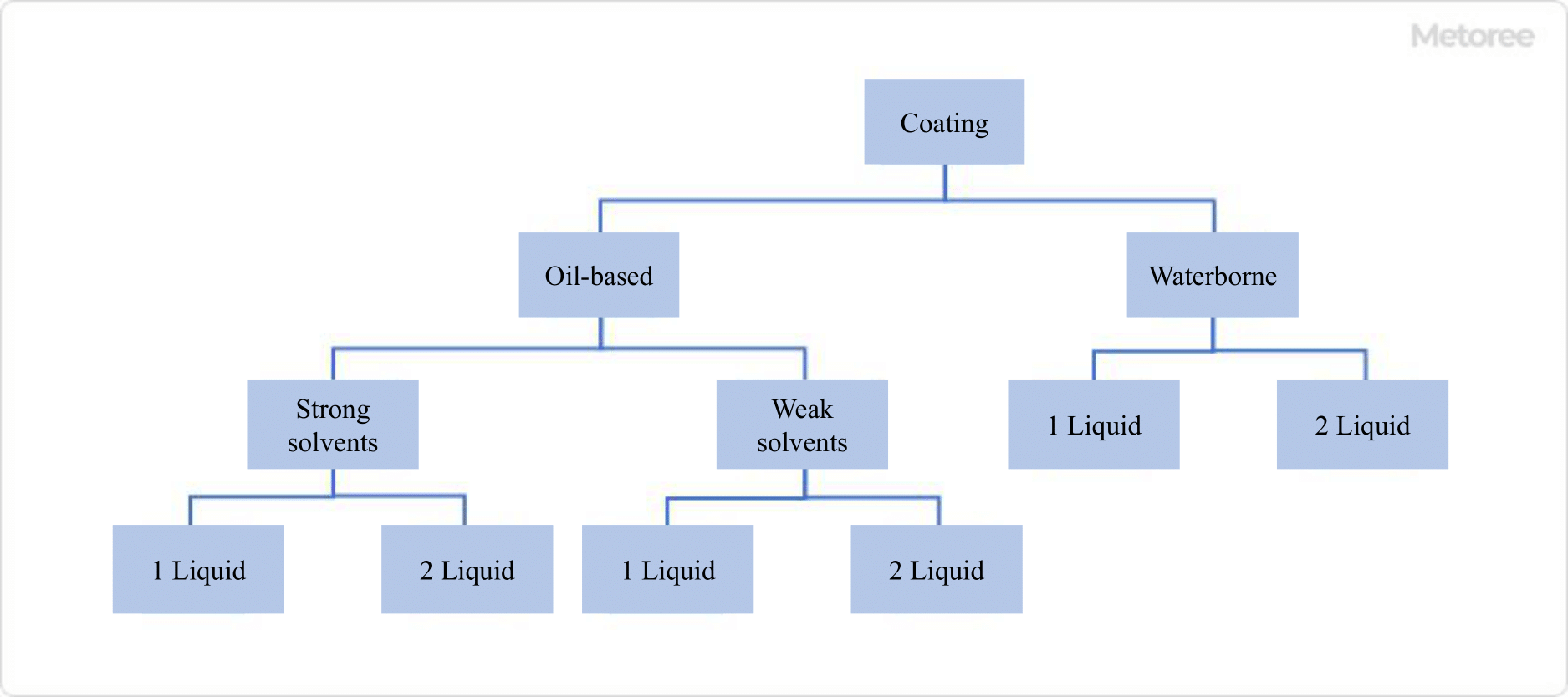
Figure 3. Classification of paints
Oil-based paints are classified into strong and weak solvent types. Strong solvents dissolve resins more effectively but may damage certain substrates, while weak solvents are less volatile and take longer to dry.
Classification by Usage
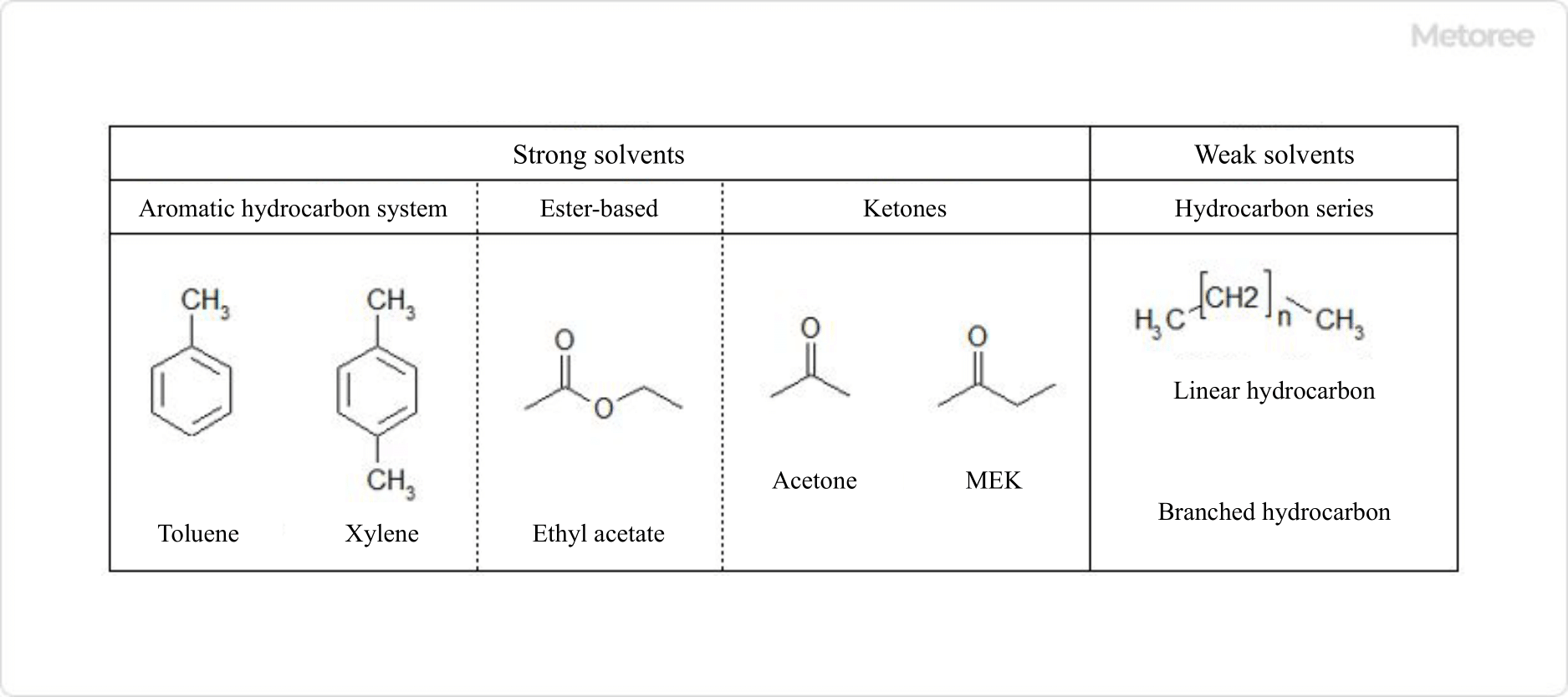
Figure 4. Types of strong and weak