What Is Plasma Cutting Equipment?
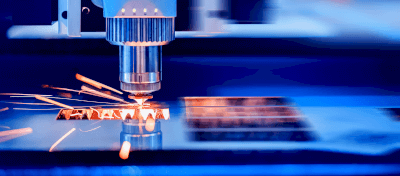
Plasma cutting equipment utilizes plasma from an arc discharge for cutting, offering shorter cutting times and higher efficiency compared to traditional laser and gas cutting methods. Capable of cutting materials up to 100 mm thick at low costs, plasma cutting is versatile, allowing for the cutting of metals like stainless steel and complex curves.
Uses of Plasma Cutting Equipment
Primarily used for metal cutting in shipyards and steel bridge construction, plasma cutting excels with materials that resist oxidation, such as stainless steel and aluminum alloys. It supports a wide range of material thicknesses, making it ideal for cutting thick materials that lasers struggle with.
Principle of Plasma Cutting Equipment
Plasma cutting generates an arc discharge between the workpiece and an electrode, melting the material with arc heat. A surrounding airflow then expels the molten material, facilitating the cut.
Types of Plasma Cutting Equipment
Types vary based on the plasma gas used, including argon and hydrogen for stainless steel and nonferrous metals, oxygen for carbon steel, compressed air for cost efficiency, and nitrogen, though its use has declined due to environmental concerns.
Features of Plasma Cutting Equipment
While laser cutting is faster for materials 1-6 mm thick, plasma cutting is advantageous for thicker materials, handling up to 150 mm. It can process nearly all conductive materials, including those not suitable for gas cutting. However, its requirement for a high-voltage power supply limits its outdoor use.
Other Information on Plasma Cutting Equipment
What Is Plasma?
Plasma, the fourth state of matter, forms at high temperatures when gases ionize into electrons and positive ions. It is essential for plasma cutting, leveraging its conductive properties to efficiently process metals.