What Is a Robotic Arm?
A robotic arm is an industrial robot that resembles the movement of a human hand.
The robot is mainly composed of a manipulator section consisting of six rotational axes and links, a hand section for grasping cargo, and a controller section for controlling the robot and checking its current status.
When introducing a robot, a safety fence must be provided for the safety of workers. However, for robots called cooperative robots, safety fences are not always necessary as long as risk assessments are conducted and the robot is operated at an appropriate risk level.
Uses of Robotic Arms
Robotic arms are classified into serial links and parallel links according to the connection method of the links. Serial link robots have links that are connected in a straight line, while parallel link robots have links that are connected in parallel.
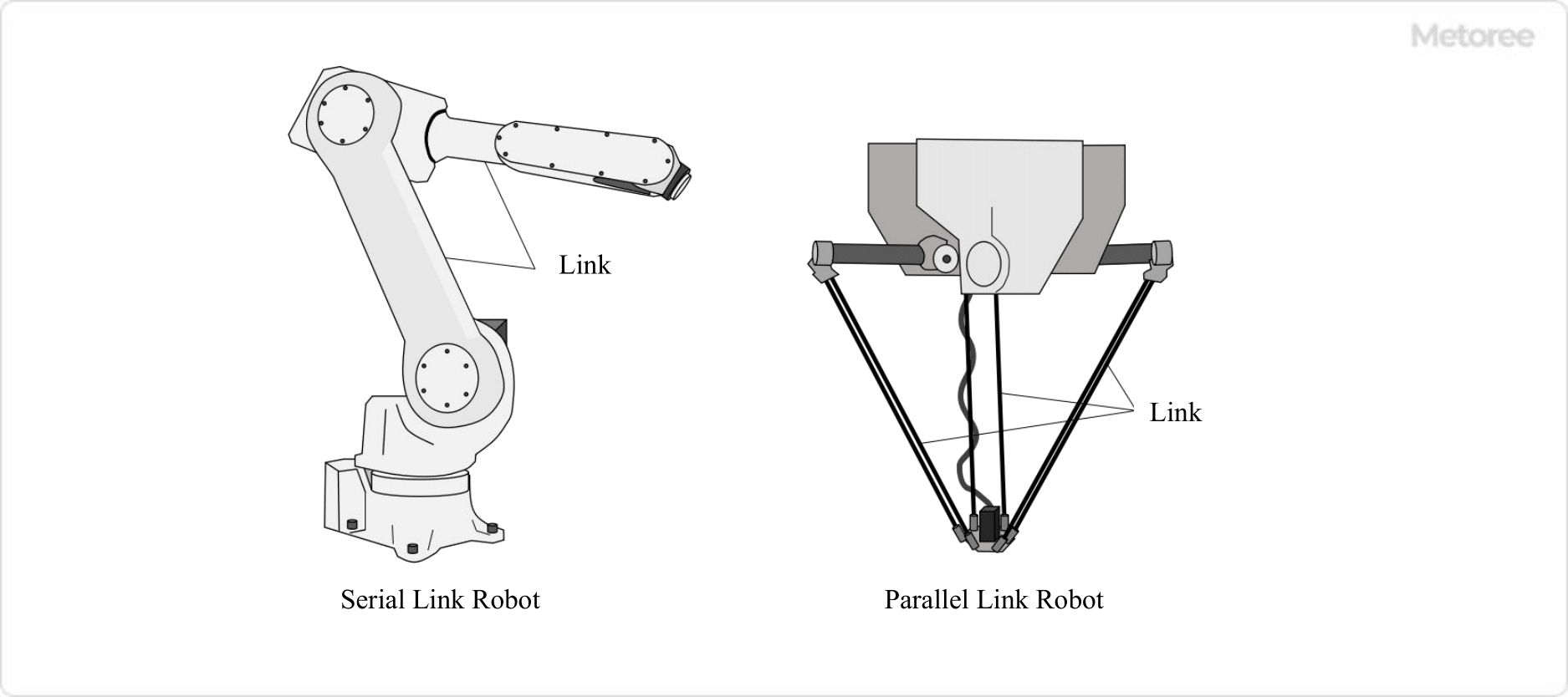
Figure 1. Serial Link Robot and Parallel Link Robot
A serial link robot is a robot in which one link is followed by the next link in a series. It is characterized by a wide range of motion and the ability to approach and work from diagonal directions, like a human hand. Taking advantage of their high degree of freedom of movement, serial link robots are used in the following applications.
1. Welding
This is the process of joining automobile bodies and other components by melting the metal of the parts. Welding can be performed by a robot to ensure accurate welding with little variation, which is expected to improve quality.
2. Assembly
This work involves assembling parts that have been incorporated into other parts, tightening screws, etc. Vertically articulated robots perform this work by hand. Vertically articulated robots can also handle tasks that are performed by human hands, allowing them to reproduce the skills of skilled craftsmen accurately.
3. Painting
This work involves applying color to automobile bodies and other objects using a spray gun attached to the end of a vertically articulated robot.
Parallel link robots are robots with parallel links coming out from the base, and the hand tips are attached to the ends of the links. Parallel link robots are characterized by their fast movement and are used for the following applications:
1. Box Packing
Packing food products (e.g., individually wrapped snacks) into plastic trays that flow on a conveyor belt.
2. Inspection
Using a camera suspended from the ceiling, the quality of parts is determined as OK/NG, and the parts are either passed on to the next process or not.
Principle of Robotic Arms
An industrial robot is composed of three elements: a manipulator that operates, a robot controller that moves and controls the manipulator, and a teaching pendant that teaches the manipulator the operation.
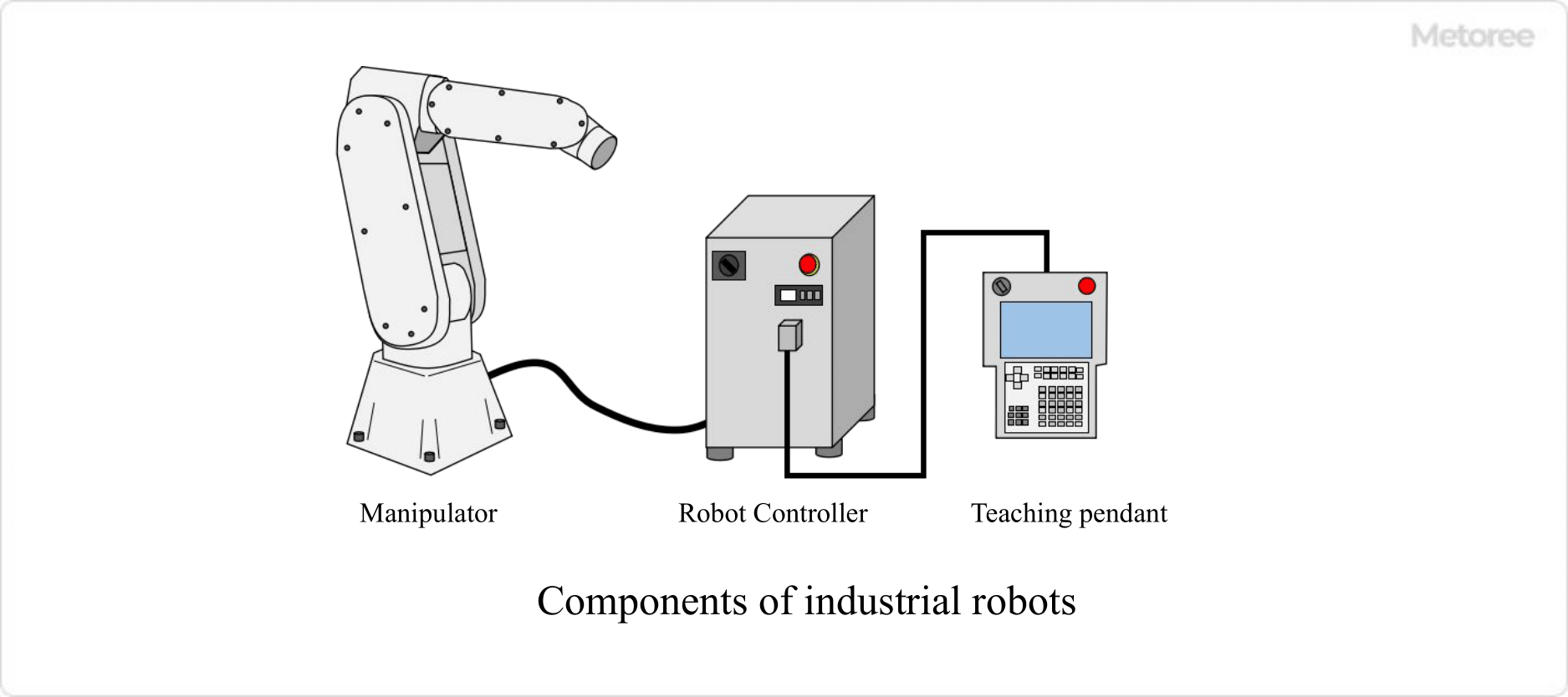
Figure 2. Components of an industrial robot
Serial link manipulators consist of a link and a rotary axis. There are six rotary axes, each of which is driven by an AC servo motor. Each of these six axes performs the following movements:
- Swivel: Swivels the entire body
- Lower Arm: Moves the lower arm to move the body back and forth
- Upper Arm: Moves the arm up and down
- Wrist Swivel: Rotates the arm
- Wrist Bend: Bends the wrist
- Wrist Rotation: Rotates the wrist
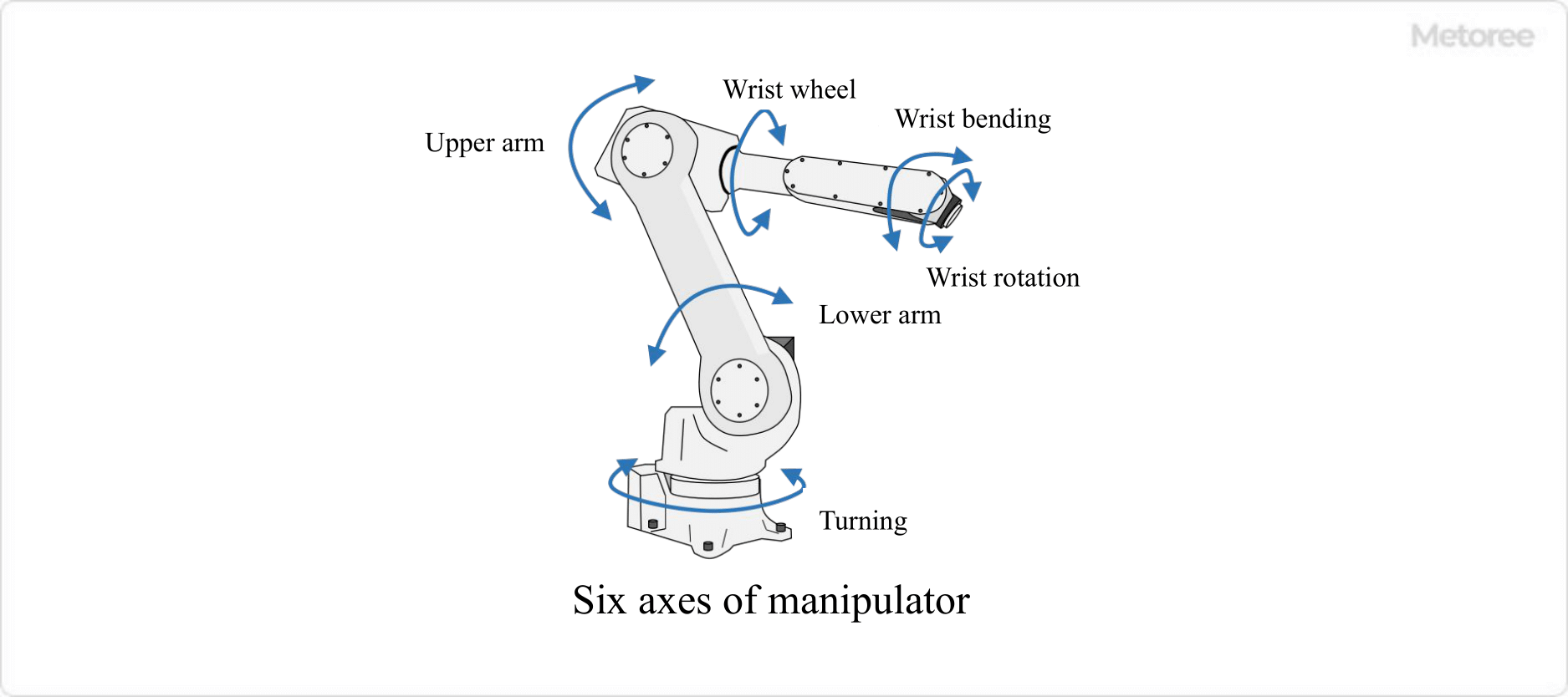
Figure 3. The six axes of the manipulator
Other Information About the Robot Arm
1. Programming of Robotic Arms
When the robot performs a movement, the robot controller is given the position coordinates (X, Y, Z) and the rotation coordinates (Rx, Ry, Rz) of the manipulator’s hand tip. The motors of each axis move to match the position and rotation angle of the manipulator’s hand, allowing the robot to perform the desired motion.
Teaching Position to the Robot With a Teaching Pendant
A teaching pendant is an input device that stores (teaches) positions to the robot. The robot can be moved directly using a keyboard or touch panel, and its posture can be taught and reproduced by the robot.
Conventional teaching pendants for industrial robots require some familiarity with their operation. In recent years, a technique called direct teaching has emerged that allows even novice operators to teach robots easily.
Programming Coordinates With a Personal Computer
This is a method in which the coordinates of the robot are specified by programming on a personal computer.
Until now, coding-type programming, such as C language, has been mainstream, but coding requires proficiency in programming itself, and debugging the program takes a lot of time.
In recent years, an increasing number of robot manufacturers have offered simulator-type programming tools. This programming tool projects a robot model on a PC and allows the user to manipulate the robot on the PC to teach the coordinates. The feature of this tool is that the movements of the robot can be visually understood, and the robot’s movements can be taught without requiring coding expertise.
Recognizing Coordinates by Image Recognition
A camera takes pictures from the top, determines where the robot should move next, and automatically calculates the coordinates. This method is used for bulk picking. Picking in bulk is the process of grabbing parts randomly stacked in boxes and placing them on a conveyor belt for the next process or packing them in boxes.
Image recognition is effective for tasks where the coordinates of the robot’s movement change each time, but it is important to note that the cost of building the system is high.
2. Role of Industrial Robotic Arms
Industrial robotic arms are becoming increasingly popular in various industries, such as factories, manufacturing sites, and distribution centers. The advantage of introducing a robotic arm is that it can work in place of humans without taking a day off, even at night or on holidays. For these users, the robotic arm is expected to contribute to labor-saving to solve manpower shortages, and to improve productivity.
It is said that many of the mistakes that occur at production sites are human errors, and human work can lead to variations in quality and reduced efficiency. The introduction of an industrial robotic arm can reduce human error and maintain a consistent quality of work and products. In addition, since production history data is kept, analysis for quality improvement and prompt feedback in response to complaints can be realized.
Furthermore, robots can be used to handle hazardous materials, work in high places, transport heavy objects, and perform other heavy work that requires precision, which could lead to injury risks and potential accidents, thereby ensuring the safety of workers and improving the working environment.