What Is Polycarbonate Resin?

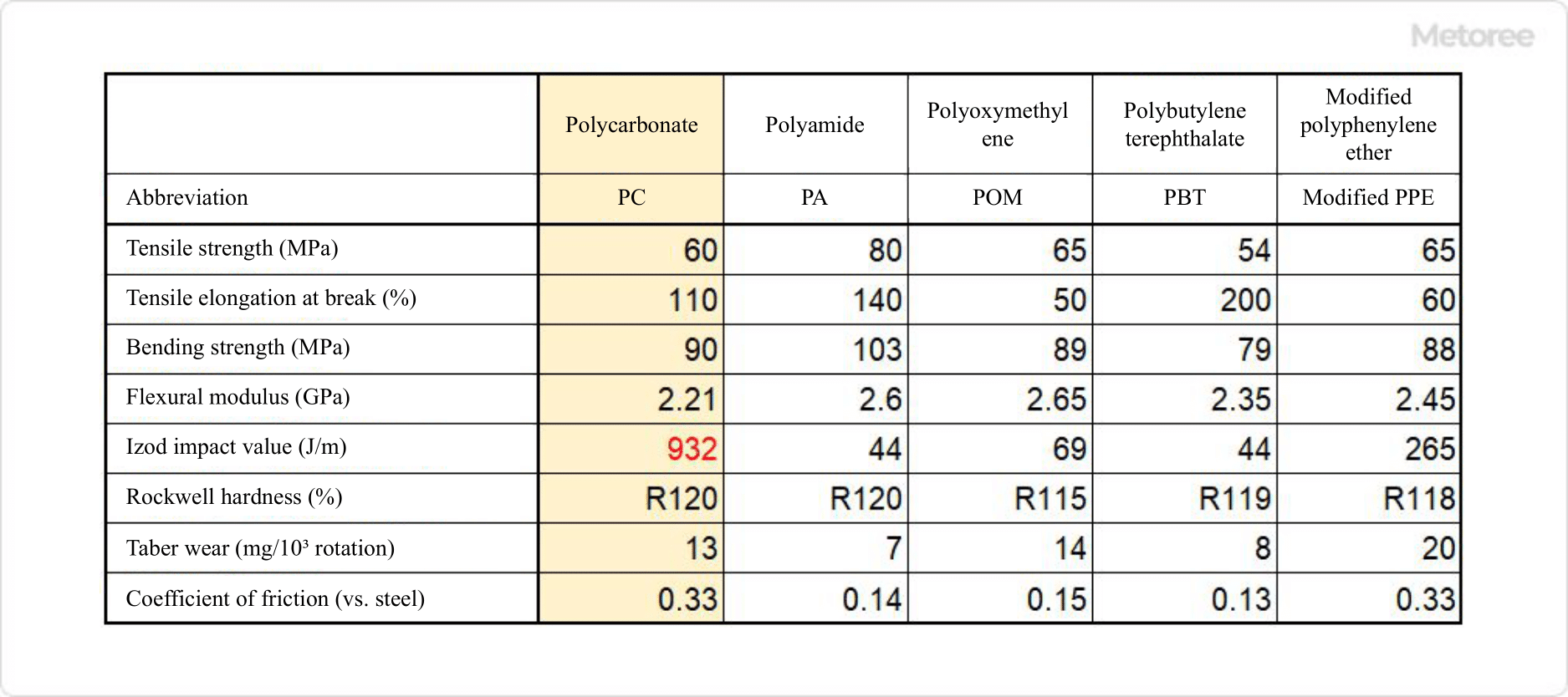
Figure 1. Five major general-purpose engineering plastics and their physical properties (Reference: Chemistry Handbook, 5th Edition)
Polycarbonate Resin is a type of engineering plastic and one of the five major general-purpose engineering plastics. Among general-purpose engineering plastics, polycarbonate resin is the only one that is colorless and transparent, and its transparency is so high that it can be compared to that of glass.
It also has the highest impact resistance of all general-purpose engineering plastics, and because it contains two benzene rings in its main chain, it is self-extinguishing, meaning that it will not spread even if set on fire.
Polycarbonate Resin is highly processable, as it is compatible with most of the basic molding techniques used for plastics. However, although cracking and breakage rarely occur, it should be noted that it is susceptible to fatigue and scratching, and that it is weak against alkalis and organic solvents.
Uses of Polycarbonate Resin
Polycarbonate Resin is used in a great many applications because of its excellent resistance to a wide variety of conditions and its ease of processing.
The following are examples of applications for Polycarbonate Resin along with its characteristics:
1. Transparency
Due to its high transparency, polycarbonate resin is used in optical applications such as eyeglass lenses, camera lenses, and CD and DVD substrates.
2. Impact Resistance
Because of its strong impact resistance, it is used for bulletproof materials, etc., and there is almost no risk of cracking when used in general environments.
3. Weather Resistance
Because it is resistant to ultraviolet rays and does not deteriorate easily, it maintains its high strength for a long period of time when used outdoors. It is used for roofing materials, solar panel surfaces, and other outdoor applications, as well as for automobile headlamp lenses, roof rails, and door handles.
In recent years, it has also been adapted to molding methods using 3D printers, and its use is expanding more and more.
4. Dimensional Stability
With its high dimensional stability, polycarbonate resin is used for smartphone cases and other applications.
Polycarbonate Resin Manufacturing Process
There are two industrial production methods for polycarbonate resin: interfacial polymerization and ester exchange. The density varies depending on the manufacturing method, and the addition of modifiers to polycarbonate resin can make it an even better resin material.
1. Interfacial Polymerization Method
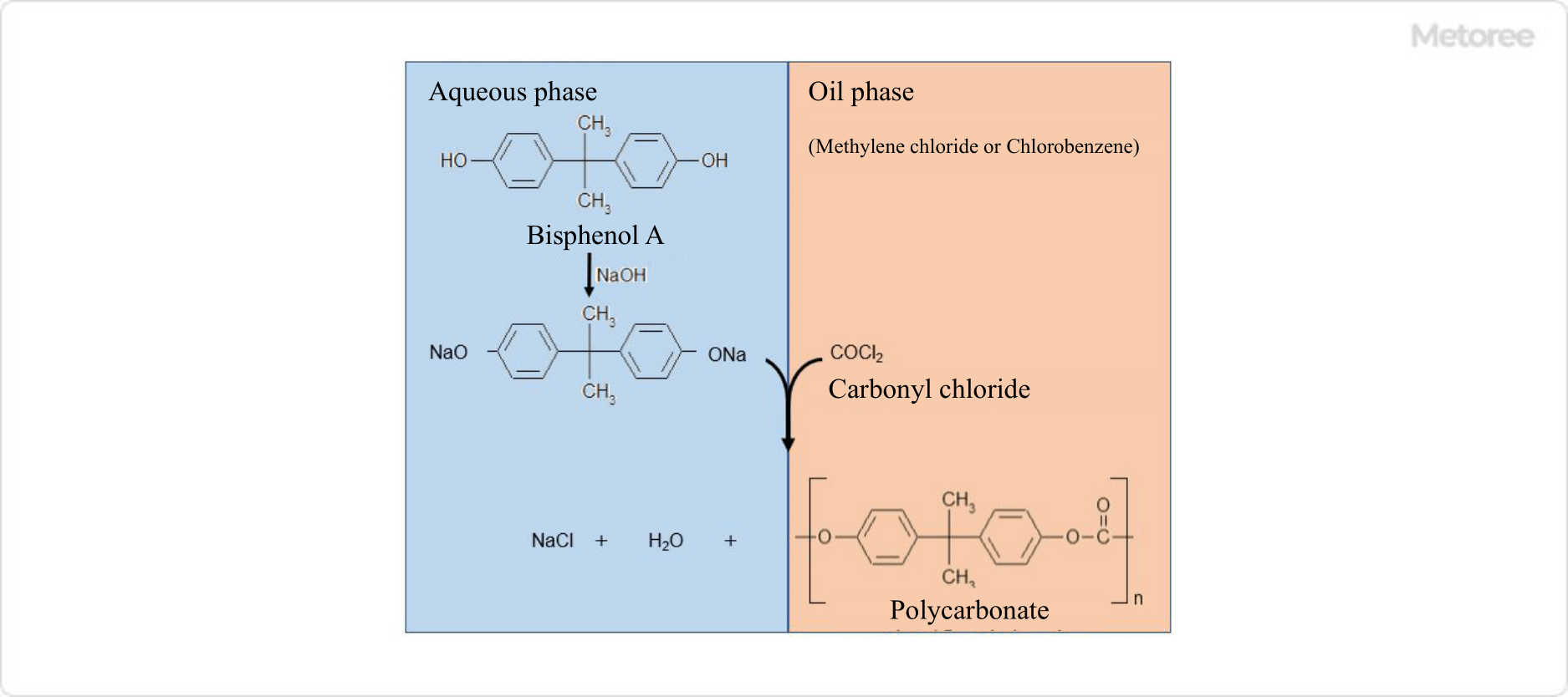
Figure 2. Reaction equation of the interfacial polymerization method
In this method, polycarbonate is produced by adding carbonyl chloride to a suspension solution of bisphenol A in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and methylene chloride or chlorobenzene, which undergoes a condensation polymerization reaction at the interface between the aqueous and oil phases.
Compared to the ester exchange method, the reaction conditions are milder, and polycarbonates of a wide range of molecular weights, from low to high, can be produced.
After polymerization, polycarbonate resin is dissolved in the oil phase, and granular polycarbonate is obtained through the separation, neutralization and purification process, polymer recovery process, and drying process.
2. Ester Exchange Method
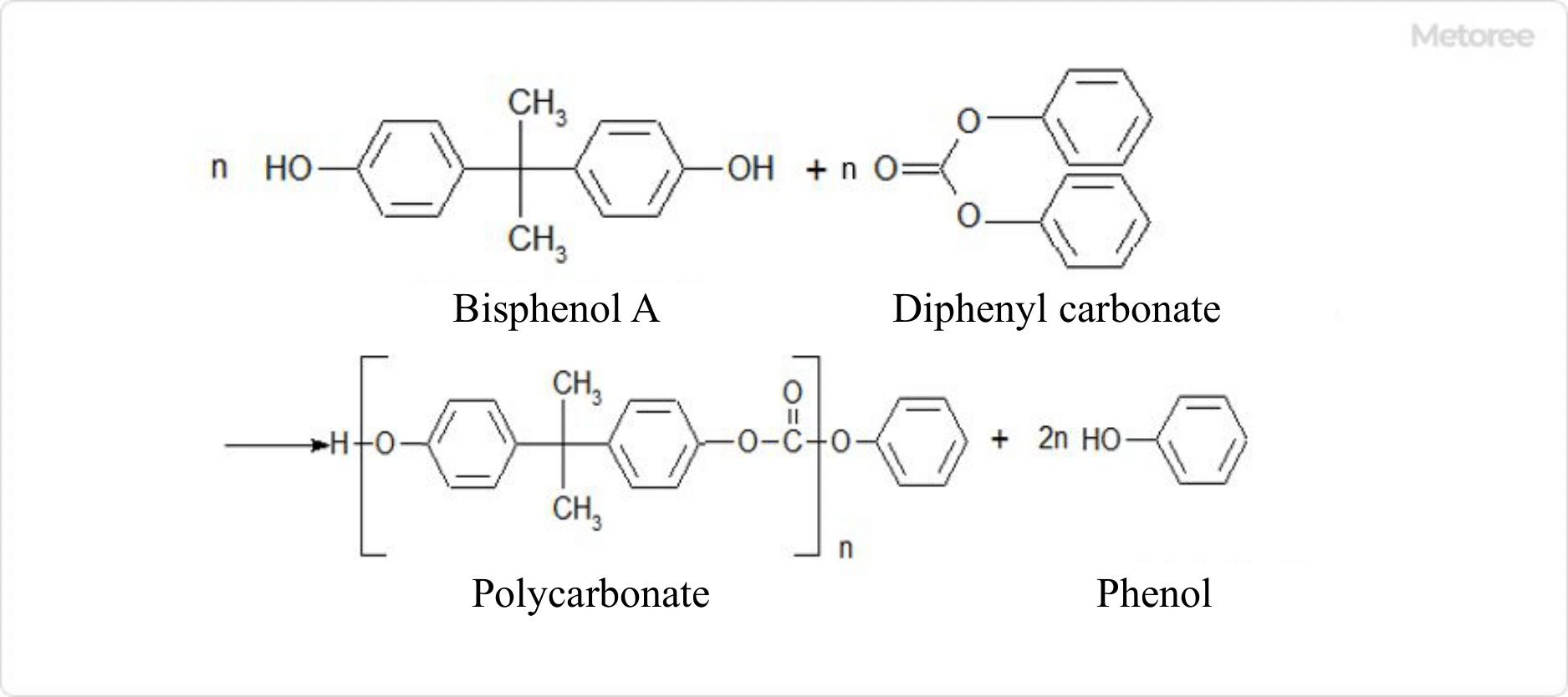
Figure 3. Reaction equation for the ester exchange method
In this method, bisphenol A and diphenylcarbonate are melt-mixed in the presence of a catalyst to produce polycarbonate through polycondensation while recovering phenol under high temperature and reduced pressure without the use of solvents. The recovered phenol is reused as a raw material for diphenylcarbonate.
The resulting polycarbonate is obtained in a molten state and can be pelletized into products, making this method of synthesis simpler than the interfacial polymerization method in terms of post-processing.
Other Information on Polycarbonate Resins
1. Polycarbonate Resin Global Market Share
Polycarbonate Resin is used in an extremely wide range of applications, and production facilities are located in various regions. By capital, American manufacturers account for 36%, European manufacturers, mainly from Germany and Belgium, 25%, and Japanese manufacturers, 38%.
2. Processing of Polycarbonate Resin
Polycarbonate resin is a thermoplastic resin that softens when heated. It can be cut like acrylic resin, bent with heat, and welded with solvents.
It can also be used in a manner similar to metalworking to create workpieces that take advantage of its properties. For this reason, there are a number of businesses that make their living processing polycarbonate resin.