What Is PCR Tube?
PCR Tubes are plastic tubes made specifically for use in PCR experiments. Polypropylene is usually used as the material, and a wide variety of sizes, shapes, and colors are available.
Uses of PCR Tubes
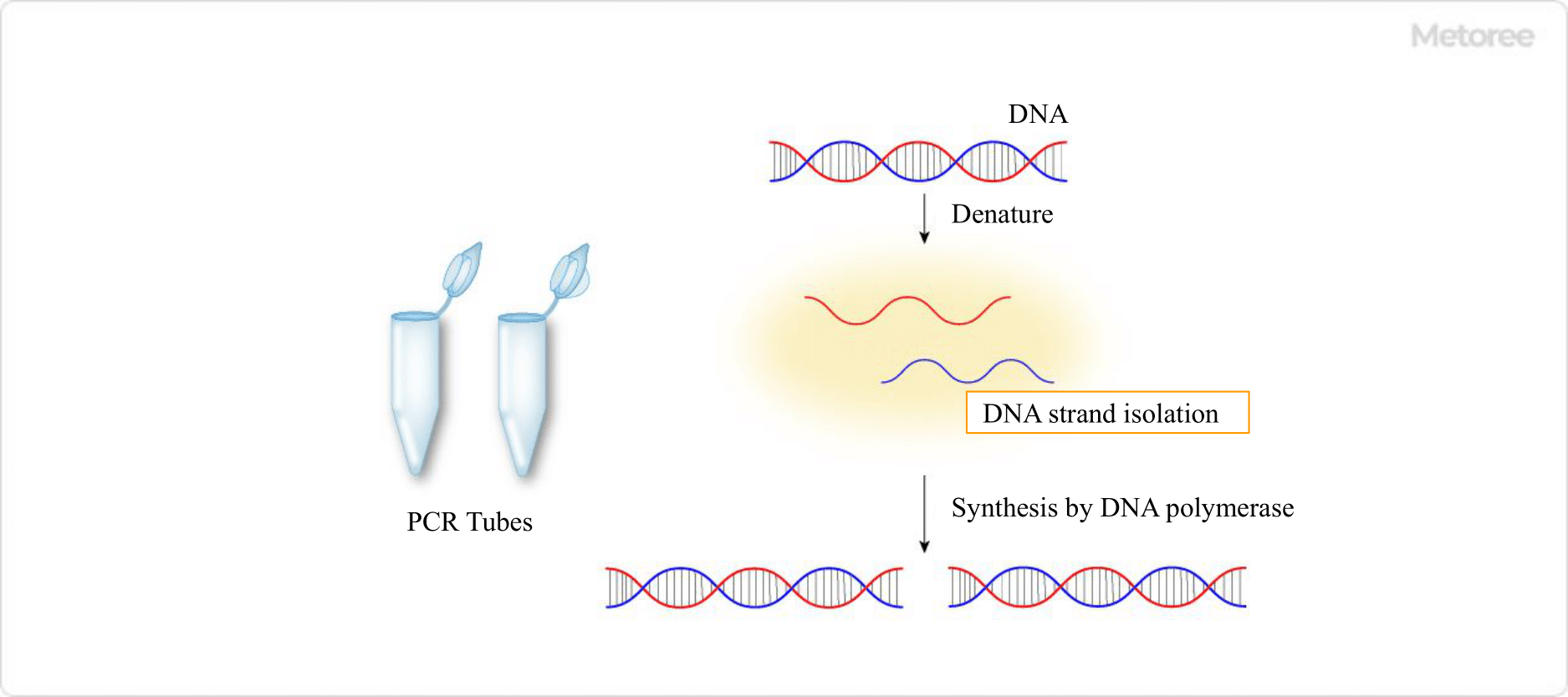
Figure 1. PCR tube and principle of PCR
PCR is an acronym for polymerase chain reaction, a technique that uses DNA polymerase to amplify a target DNA sequence from one to several million copies in a short period of time. Specifically, the series of reactions 1-3 below are called “cycles,” and by repeating 25-35 cycles, copies of the target DNA are synthesized exponentially.
- Denaturation: The double-stranded DNA template is heated to separate the DNA strands
- Annealing: short DNA molecules called primers are attached to adjacent regions of the target DNA
- Elongation: DNA polymerase synthesizes complementary strands of the template in the 3′-end direction starting from each primer
The device used to automatically control the temperature cycle and incubation time in PCR is a thermal cycler; PCR Tubes are manufactured for use in a thermal cycler. In order to select the correct PCR Tube, it is necessary to correctly understand the specifications of the thermal cycler you will be using.
In addition, since there are various types of PCR such as standard PCR, gradient PCR, real-time PCR, and qPCR, it is necessary to select the appropriate PCR for your purpose. At the same time, it is also important to properly prepare the experimental apparatus and reagents according to the type of experiment.
Structure of PCR Tube
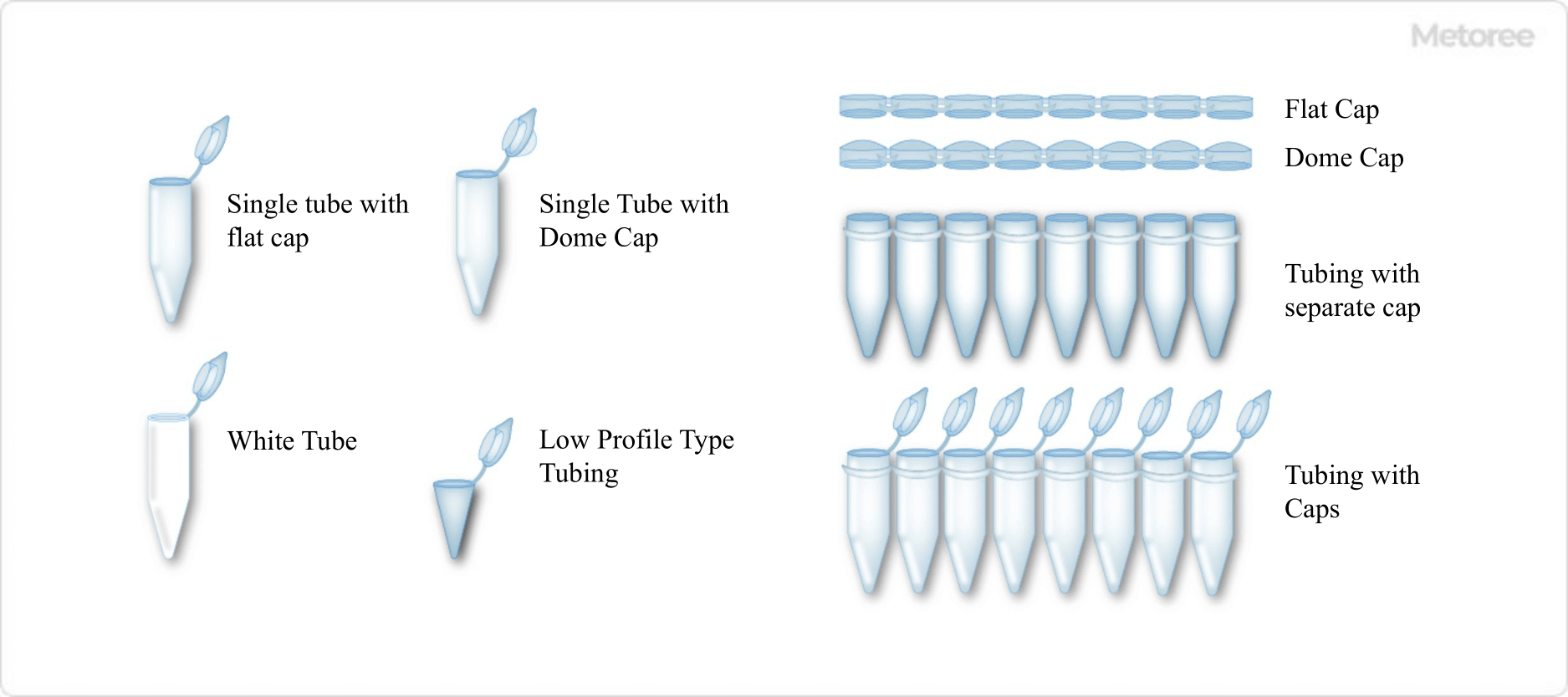
Figure 2. Various PCR tubes (Single tube) / Figure 3. Example of 8-row PCR tube
Polypropylene is usually used as the material. Polypropylene is chemically inert and can withstand rapid temperature changes during thermal cycling. In addition, the tube walls are manufactured to be thin and uniform to enhance heat transfer from the thermal cycler.
In addition, they are manufactured with the utmost care to ensure that they are free of dust and impurities such as endonucleases, pyrogens, DNA, lubricants, dyes, heavy metals, and fillers. This is because if the product becomes contaminated during manufacturing, dust particles can remain and interfere with PCR, or DNA fragments can serve as templates for nonspecific amplification, resulting in reduced experimental accuracy.
The structure consists of a tube portion that holds the sample and a cap portion, and is available in a single type with one separate tube, or an 8- or 12-tube type with multiple tubes.
There are two types of cap shapes: flat and domed, one with one cap per tube, and one with multiple caps in a row, which are separate from the tube.
There are two types of tube sections, one with a normal height (standard profile) and the other with a lower height (low profile). In addition to the transparent clear type, white ones are also available.
How to Select PCR Tubes
It is important to choose according to the type of experiment and to use the appropriate one for the thermal cycler you are using. For example, clear tubes (transparent type) make it easy to check the contents, while white tubes increase the sensitivity of qPCR by preventing fluorescence from refracting and diffusing outside the tube.
Domed caps allow rapid heat transfer from the thermal cycler, while flat caps can be marked with a marker and are easier to puncture with a needle during sample collection.
Low-profile tubes with a lower height minimize the space area in the reaction vessel, thus reducing the effects of evaporation and increasing the thermal conductivity compared to normal ones. Low-profile tubes are sometimes referred to as fast tubes because they are compatible with fast thermal blocks.
PCR Tubes are suitable for small- to medium-scale PCR experiments, and when the scale is larger, PCR plates are appropriate.