What Is Die Casting Die?
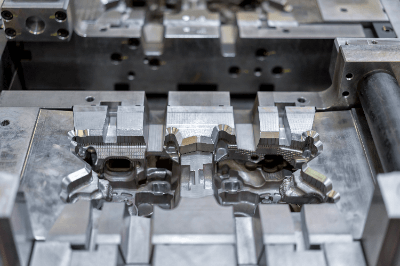 Die casting is a type of casting method in which molten material is heated and poured into a mold.
Die casting is a type of casting method in which molten material is heated and poured into a mold.
The materials to be melted are metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. The manufacturing process is automated and suitable for mass production. An advantage is low cost, since once a die is made, it can be used continuously.
The term “Casting Die” refers not only to the manufacturing method but also to the product itself made by this method. Compared to other casting methods, die casting has a shorter history since the method was established, and new methods are being created even today.
Uses of Casting Die
1. Automotive Parts
Die casting is used in a wide variety of automotive parts, including parts of the body, covers around water pumps, engines, transmissions, compressors for air conditioners, and other parts with complex shapes.
Recently, with the need for electrification and weight reduction, they are also used in parts around power steering and covers for control units. Aluminum die casting is often used for automotive parts because they are often complex and require good heat dissipation; although there are alternatives using ABS and other resins, aluminum die casting is still an essential part of automotive parts today.
2. Home Appliances
Casting Die products are also used in familiar home appliances such as TVs, air conditioners, washing machines, and electric cookers.
Like automotive parts, many home appliances are precision products, and mass production is required. Therefore, Casting Die is used because of its ability to handle complex shapes and to keep production costs low.
3. Other Products
Casting Die products also contribute to miniaturization and weight reduction. Therefore, they are often used for products that require lightness, such as golf equipment, cameras, fishing equipment, OA equipment, and cell phones.
Principle of Die Casting Die
There are several types of Casting Die. The general construction method is the following procedure:
- The fixed and movable molds of the Casting Die are pressed together with great force.
- Molten metal is injected into the space between them at a high pressure of several tens of megapascals.
- When the hot water hardens, the movable mold is moved to remove the part.
Special methods are as follows:
1. Vacuum Casting Die Method
After the molds are pressed together, air is removed to create a vacuum. After the vacuum is created, hot water is injected and the product is removed. Since air is removed, oxides are suppressed and high quality products can be produced.
2. Non-Porous Casting Die Method
After the molds are pressed together, the inside of the mold is filled with oxygen. After filling, hot water is injected and the product is removed. This method has the feature of preventing the generation of nests due to the decompression caused by the oxidation reaction. This method is suitable for products that require strength.
3. Local Pressure Casting Die
After the molds are aligned, hot water is injected. When the hot water is half solidified, the mold is partially re-pressurized. By re-pressurizing, hot water can be replenished to the area where shrinkage has occurred during solidification, thus making it possible to produce products with fewer cracks.
Other Information on Casting Die
1. The Difference Between Casting Die and Casting
Casting is a method of forming products by pouring liquid metal melted in a high-temperature furnace into molds made of sand, metal, or wax. Basically, no external force is applied, but the liquid metal’s own weight and subsequent flow is used.
Casting Die, on the other hand, is a further development of casting, in which liquid metal is injected into a mold under pressure to form it.
In casting, the high-temperature liquid metal is not so fluid that it takes time to spread to every corner of the mold under its own weight alone. Furthermore, it shrinks as it solidifies, so dimensional changes and wrinkles created during flow are likely to cause defects.
On the other hand, in Casting Die, pressure is applied to the liquid metal and injected into the mold, so the metal is quickly spread to all corners of the mold. Because it is formed under pressure, it has high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface roughness. This allows for high productivity in mass production.
Another major difference from casting is that finishing and inspection processes can be reduced due to the high quality.
2. Disadvantages of Casting Die
Undercut shapes are disadvantageous
Casting Die is used to extrude the product after molding, and it is difficult to extrude horizontal holes or flange parts that are perpendicular to the direction of extrusion. Such parts are called undercut shapes. To make products with undercuts, we use cores that can be removed after casting. This makes the mold more complex and increases the manufacturing cost.
Lower strength than cast products
In Casting Die, high-temperature liquid metal is forced into the product at high speed and high pressure, causing air that cannot escape and evaporated gases from the mold release agent that separates the mold from the product to be entrained in the product. This inevitably results in the inclusion of internal defects and a reduction in strength.
When plastic forming is applied by external force, such as hot forging or cold forging, it is possible to crush these defects, and thus the strength of the product is superior to that of Casting Die. Recently, however, Casting Die methods have been developed that solve this problem.
High initial cost
The disadvantage of Casting Die is that the initial cost is high because of the complicated mold shape and the need to use expensive materials with excellent resistance to heat and aluminum corrosion. In addition, since the die is repeatedly subjected to high temperature and high pressure loads hundreds or thousands of times a day, it does not have a long service life, resulting in high running costs.