What Is Diglyme?
Diglyme, or diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, is an organic compound known for its use as a high-boiling-point hydrophilic electron donor solvent in synthetic organic chemistry. Its chemical formula is C6H14O3, indicating its structure as two methoxylated ethylene glycol molecules. It is recognized and classified under various safety laws due to its toxicity and potential hazards.
Uses of Diglyme
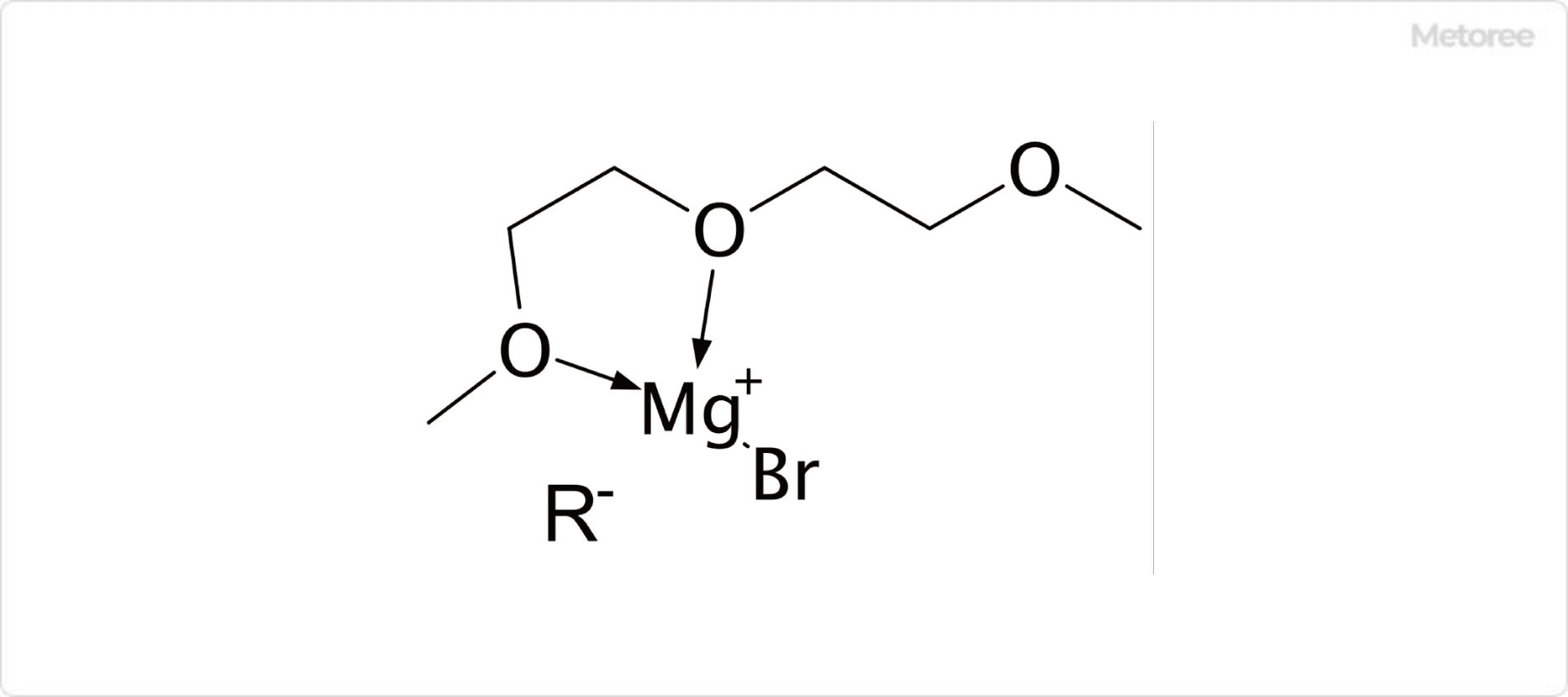
Figure 1. Example of Diglyme Coordination to Grignard Reagents
Diglyme serves various roles, including as a diluent, detergent, and reaction solvent, particularly with Grignard reagents and metal compounds. Its chelating ability to metal cations enhances reaction rates, making it valuable in reactions such as hydroborination with diborane.
Properties of Diglyme
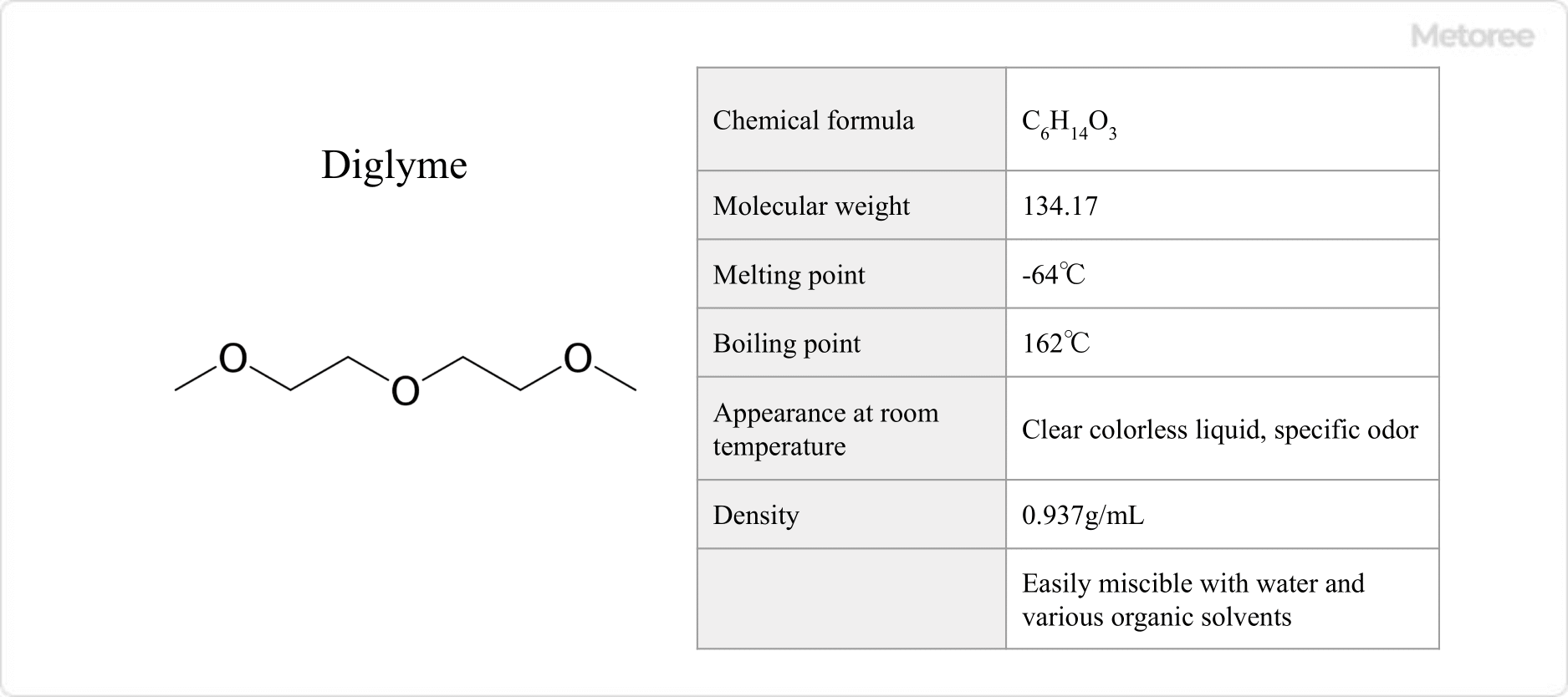
Figure 2. Basic Information on Diglyme
With a molecular weight of 134.18, diglyme is a clear, colorless liquid at room temperature, featuring a melting point of -68°C and a boiling point of 162°C. It is miscible with water and various organic solvents, displaying stability under basic conditions but reacting violently with strong oxidants.
Types of Diglyme
Available for both research and industrial applications, diglyme is sold in volumes from 25mL to 500mL for R&D and in larger containers like 16 kg cans and 200 kg drums for industrial use. Some formulations may include stabilizers such as BHT or contain minor impurities like water.
Other Information on Diglyme
1. Synthesis of Diglyme
The synthesis involves the reaction between dimethyl ether and ethylene oxide in the presence of an acid catalyst, leading to diglyme’s production.
2. Chemical Reactions Using Diglyme as a Solvent
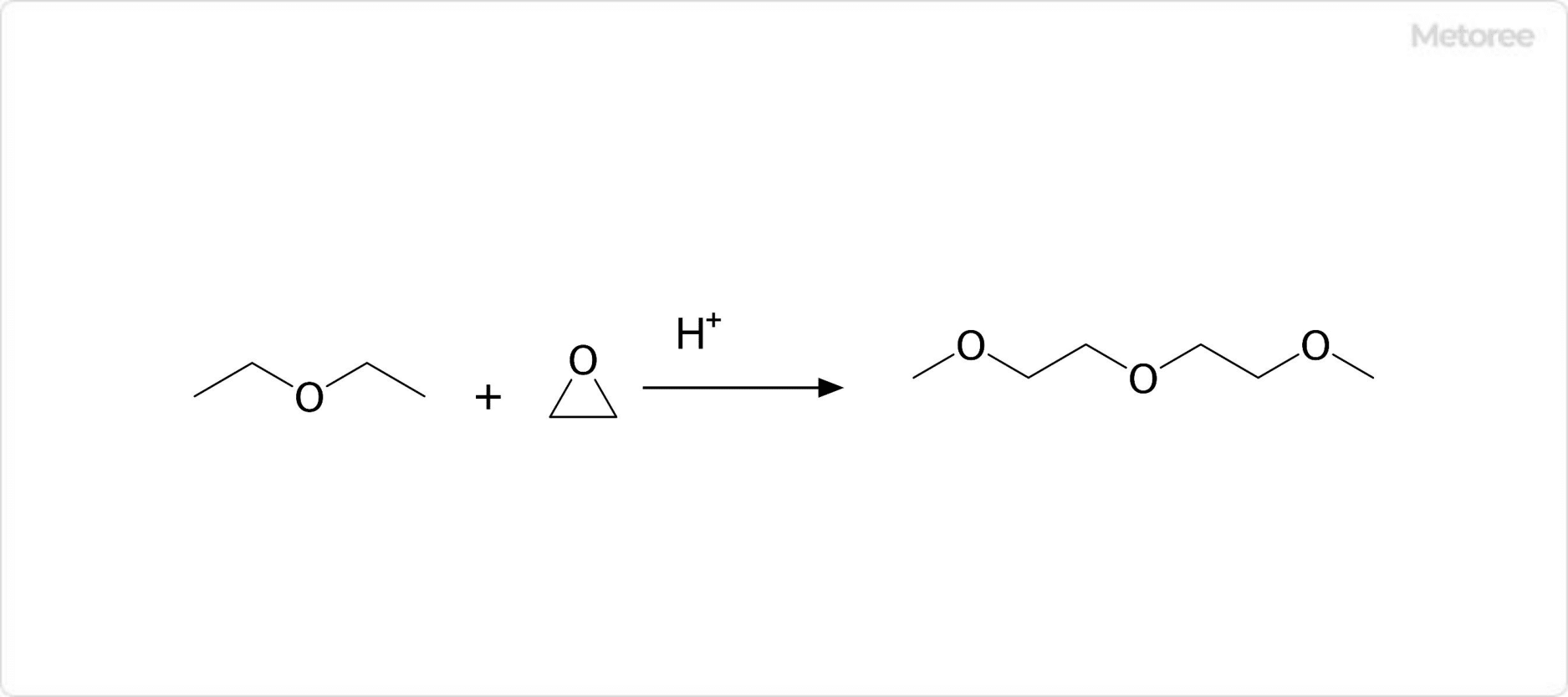
Figure 3. Example of Reaction Using Diglyme as a Solvent
Utilized for its ability to chelate metal cations, diglyme is a preferred solvent in various synthetic reactions, including reductions and hydroborination-amination processes.
3. Safety of Diglyme
As a hazardous substance, diglyme requires careful handling, appropriate protective equipment, and adherence to safety regulations due to its flammability and health risks.