What Is a Delivery Hose?
A delivery hose is a rubber or synthetic resin hose reinforced with materials such as steel wire or polyester thread.
It is used in plumbing work because it is bendable, lightweight, and easy to cut and install. There is a wide range of inner diameters from 20 mm to 300 mm and wall thicknesses from 2 mm to 16 mm. The hose material, reinforcement material, and dimensions are selected based on the flow rate, flow velocity, allowable pressure, ambient environment, installation conditions, and bending radius, among other factors.
Uses of Delivery Hoses
1. Fuel Delivery
Delivery hoses are crucial tools used for fuel delivery. They are utilized in various settings, such as gas stations, aviation fuel delivery, and industrial fuel delivery, to transport fuel efficiently and safely.
2. Transportation of Liquid Chemicals
Delivery hoses are employed to transport a variety of liquid chemicals, including chemicals and liquid raw materials. Special materials and coatings provide chemical resistance and allow for the safe transport of these substances without compromising their properties.
3. Food Industry
In the food industry, delivery hoses transport liquid and powder ingredients and products. They ensure efficient supply while maintaining the quality of food.
4. Supply of Construction Materials
Delivery hoses are also utilized to supply building materials such as concrete, cement, and sand at construction sites. They are effective for supplying materials at high elevations or when access to tight spaces is challenging.
5. Agriculture
In agriculture, delivery hoses spray and deliver liquids such as pesticides and fertilizers. They ensure even distribution while maintaining crop health.
6. Industrial Water Supply
Delivery hoses are used to supply cooling and processing water in industrial facilities. Flexible hoses facilitate the delivery of water to specific locations.
7. Cleaning Operations
Delivery hoses are also used in the cleaning industry for high-pressure washing and spraying detergents. They support efficient cleaning operations and improve environmental and hygienic conditions.
Principles of Delivery Hoses
1. Flexibility and Durability
Delivery hoses are made of high-quality synthetic rubber, plastic, or a combination of the two. This flexibility and durability allow the hoses to bend, stretch, and contract while still ensuring the reliable transport of materials.
2. Internal Structure
The interior of delivery hoses is designed to allow an unobstructed flow of liquids and gases. Smooth inner walls and appropriate diameters minimize fluid resistance and promote efficient flow.
3. Safety and Efficiency
Delivery hoses provide both safety and efficiency in the transportation of materials. Accurate flow control and proper pressure management ensure efficient movement and safe use of materials.
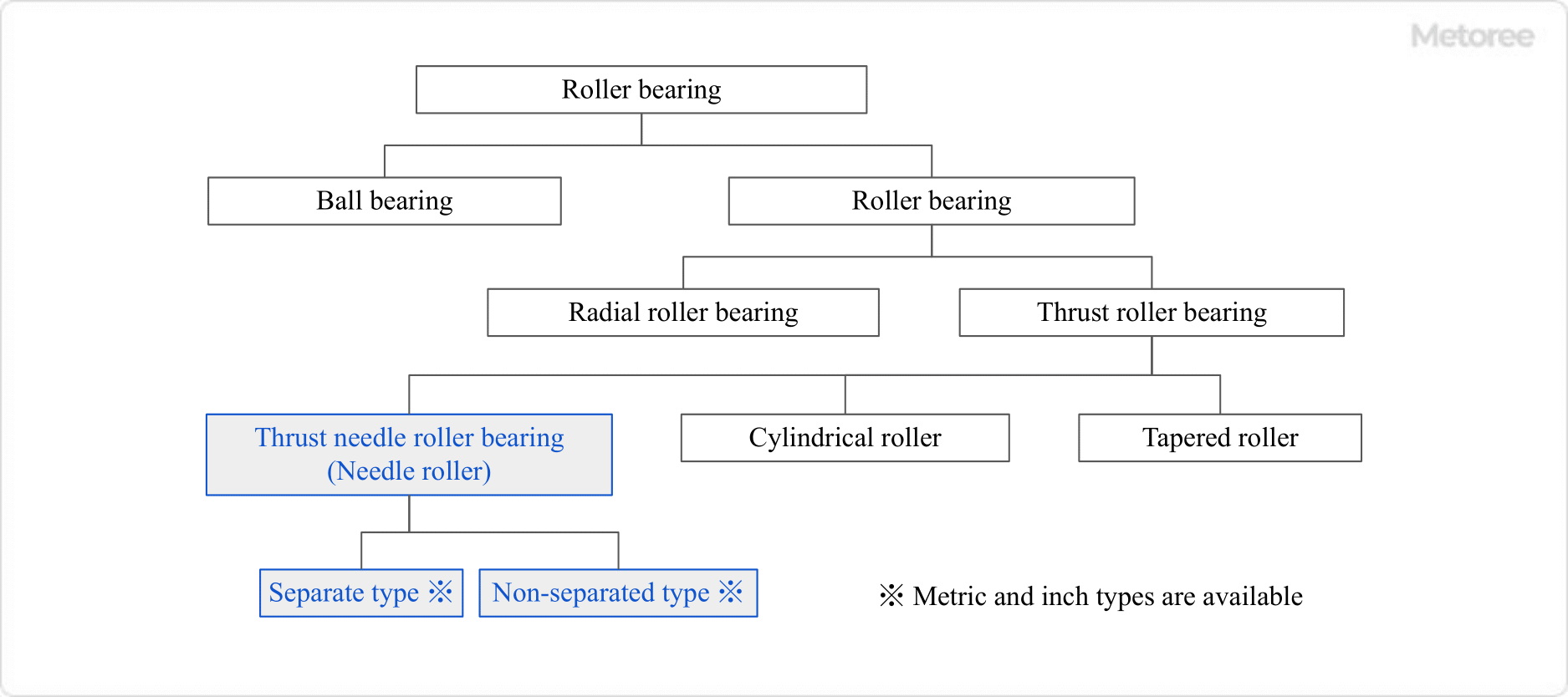
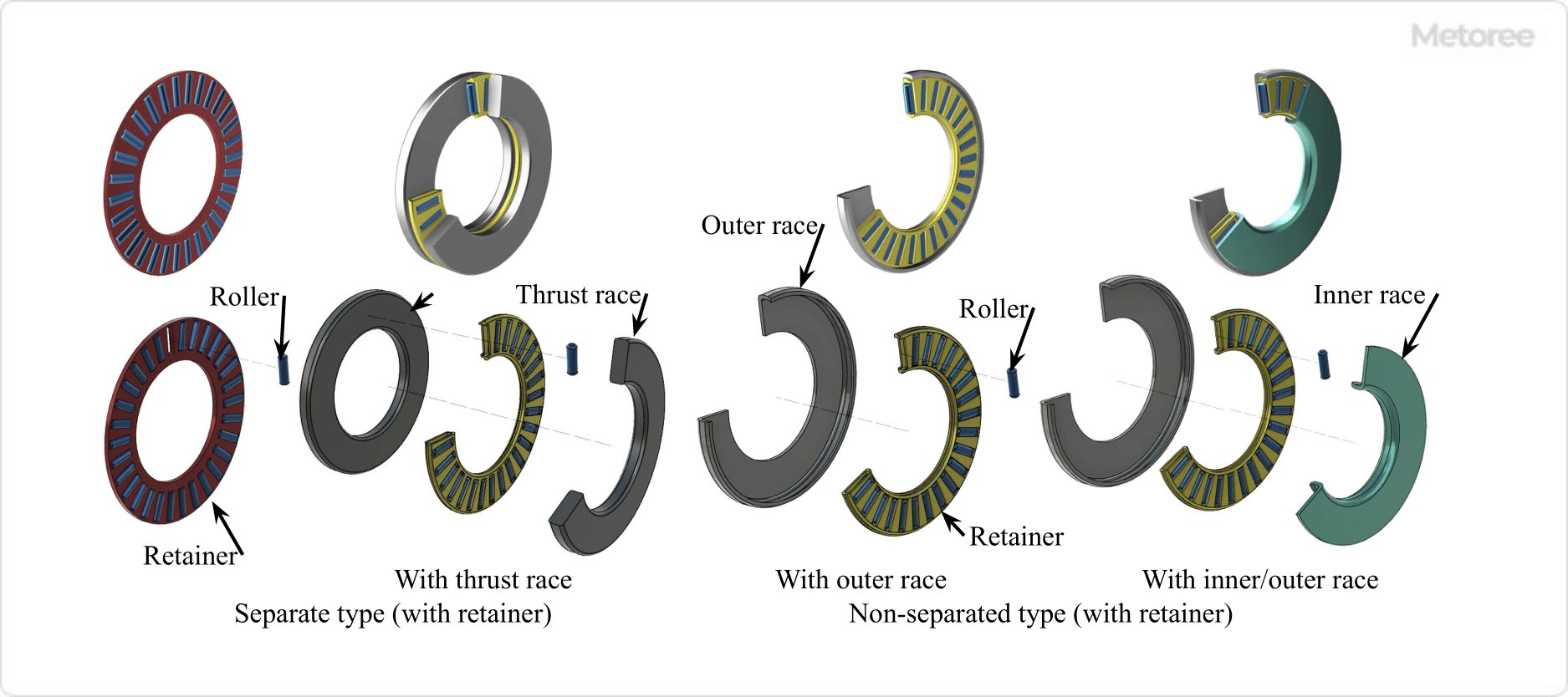
Types of Delivery Hoses
1. Hoses for Transporting Chemical Substances
Hoses are utilized in the chemical and manufacturing industries to transport various chemicals. These hoses feature high chemical resistance and are suitable for moving various corrosive and hazardous materials.
2. Food Grade Hoses
Food-grade hoses are employed in the food industry to transport materials such as liquids and powders. They must meet safety standards and be safe from contact with food products.
3. Fuel Hose
Fuel hoses are used for supplying fuel and refueling vehicles. They must be resistant to fuel and ensure a tight, leak-proof connection.
4. Air Compression Hose
This hose is utilized at industrial sites and for automobile maintenance, supplying air from air compressors and powering tools. Pressure resistance and abrasion resistance are crucial.
5. Water Supply Hose
Used in homes and commercial facilities, water hoses are employed for water supply and irrigation. Water resistance and durability are required, making them suitable for indoor and outdoor use.
6. Medical Hoses
Hoses used in medical equipment and settings are employed to supply fluids and gases. They require cleanliness and durability and are designed for various medical environments.
7. Vibration Absorbing Hoses
These hoses have a special construction that absorbs and does not transmit vibrations from machinery and equipment. They are used in certain machines and systems to reduce damage and noise caused by vibration.
Other Information on Delivery Hoses
1. Selection of Appropriate Material
Delivery hoses are selected based on the characteristics of the materials to be conveyed. Factors such as chemical resistance, temperature resistance, and pressure resistance are considered to select the most suitable hose for the material’s nature.
2. Importance of Connections
Delivery hoses must be securely connected to the pumps, valves, nozzles, etc., being used. A firm connection prevents leakage or spillage of the substance and ensures safe transport.
3. Consideration of Operating Environment
Delivery hoses are selected based on the environment in which they will be used. To meet different conditions indoors, outdoors, and in various industries, characteristics such as weather resistance and chemical resistance are considered.


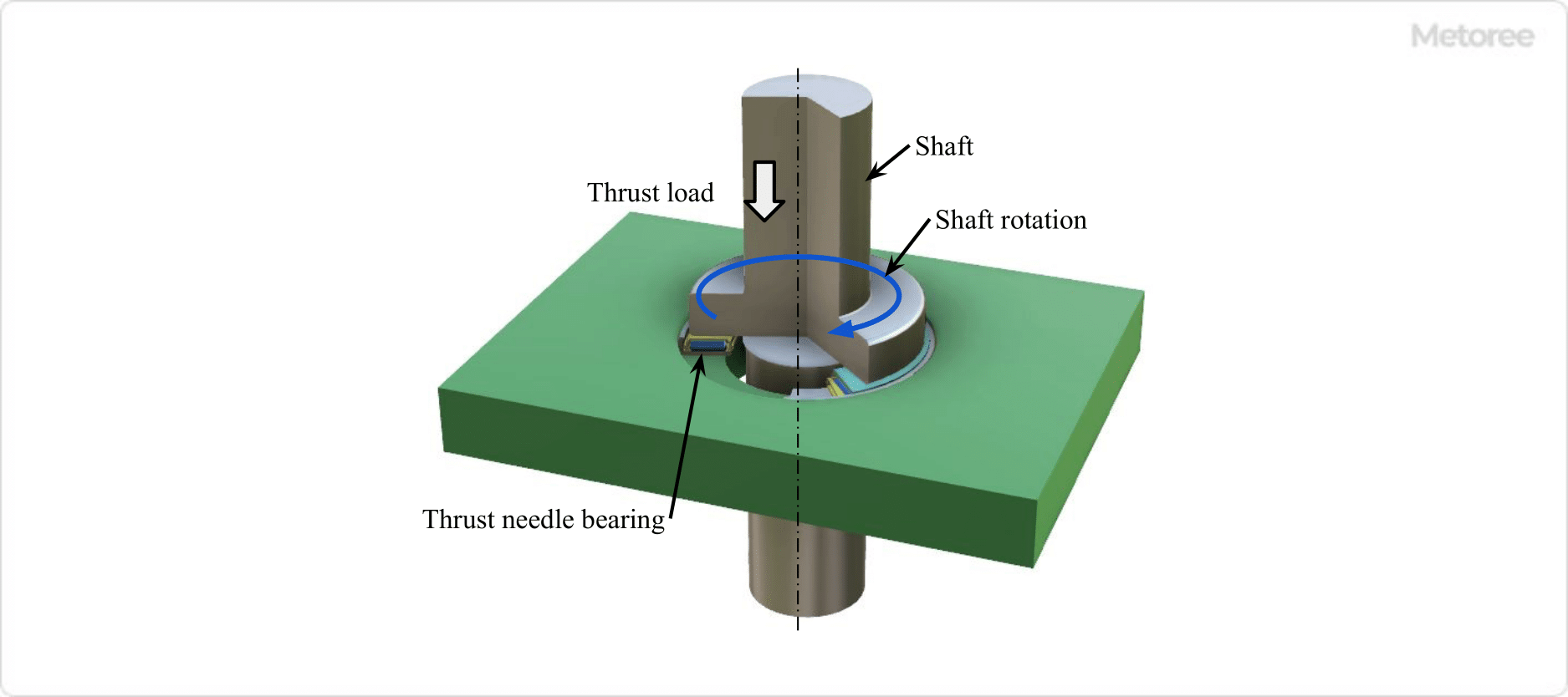
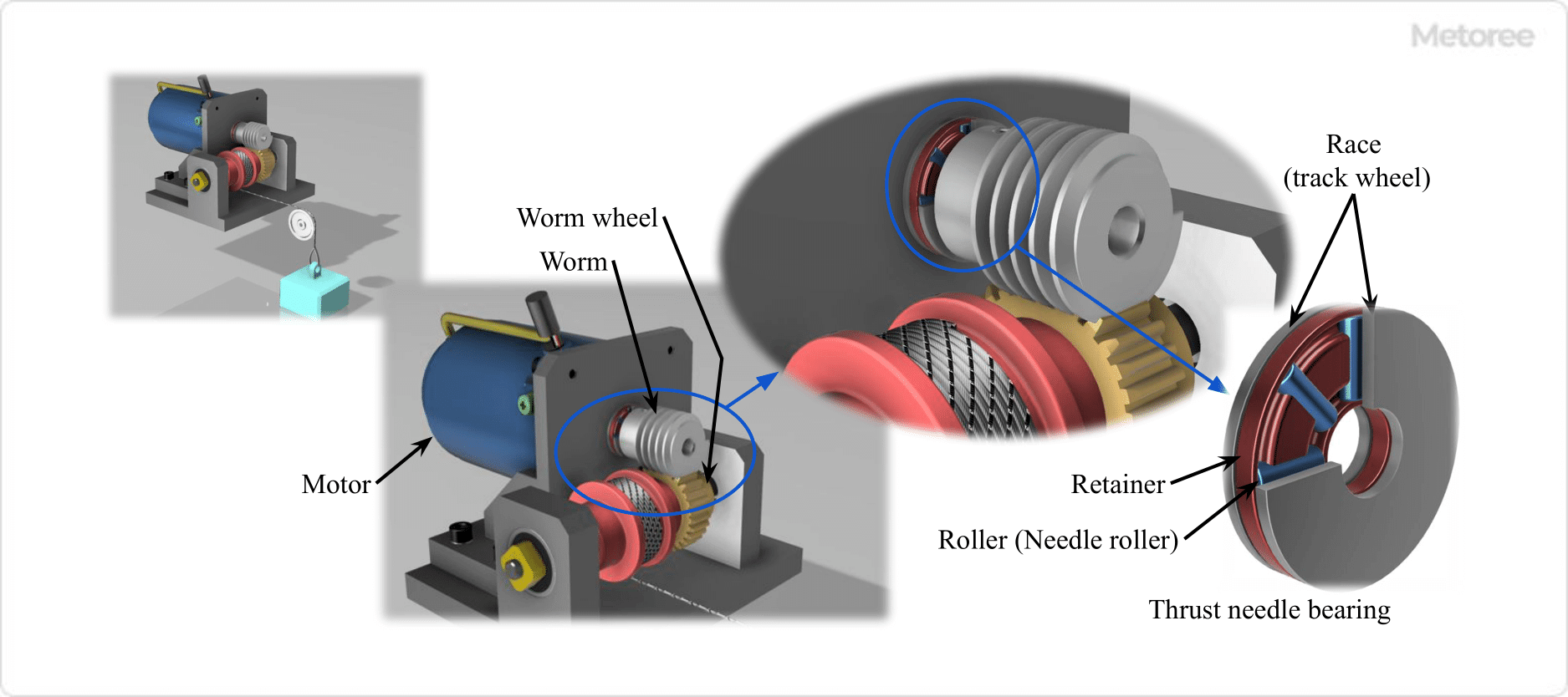
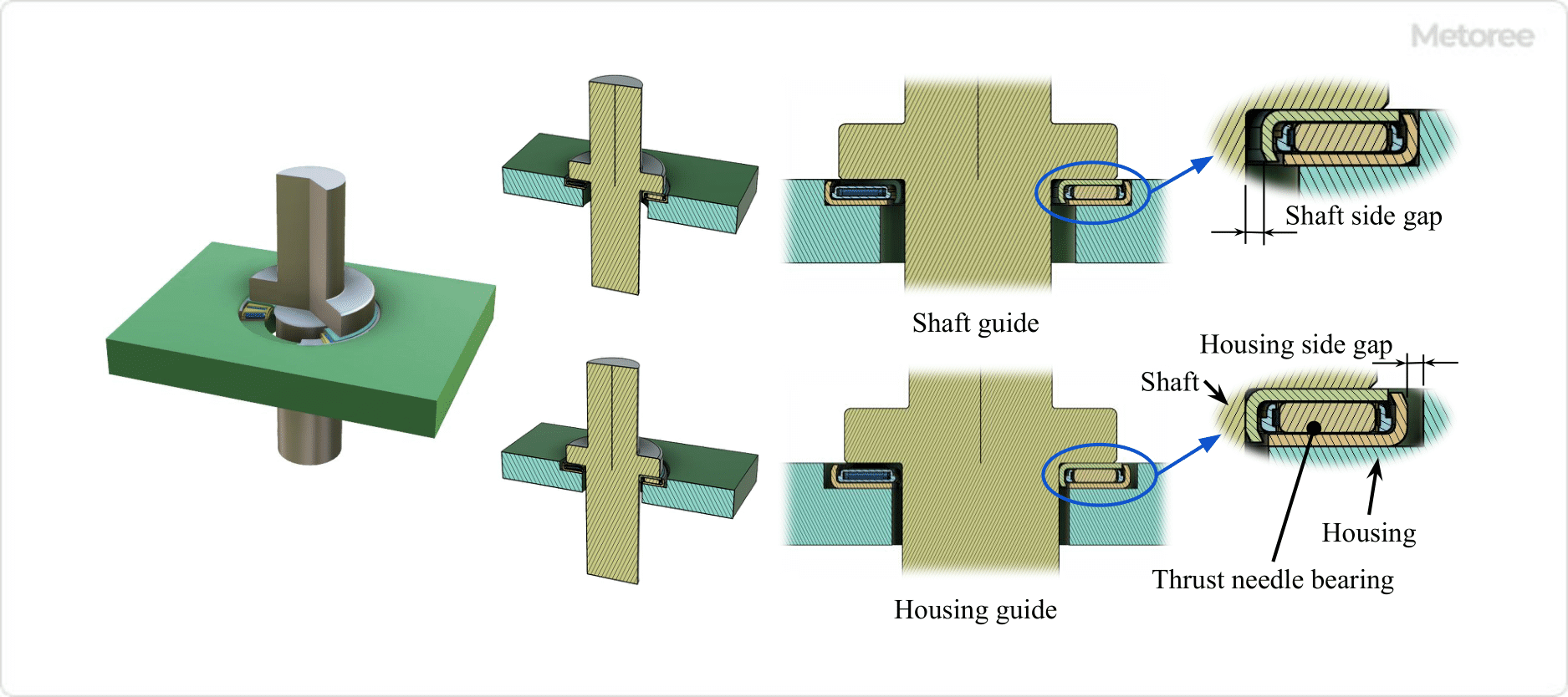
 A joint boot is a protective rubber device used in automotive joints like constant velocity joints and ball joints. They seal in lubricating
A joint boot is a protective rubber device used in automotive joints like constant velocity joints and ball joints. They seal in lubricating 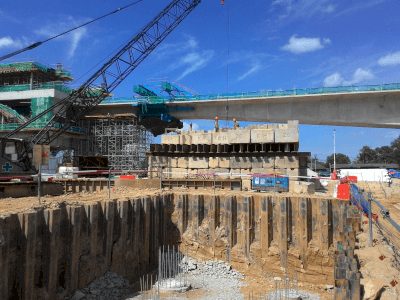 Sheet pile shoring is a construction technique used for supporting earth in excavation and burial projects. This method involves creating a shallow trench and placing plates on either side to retain the earth. The setup is supported by cut beams, which are adjustable to change the spacing between the plates. Known for its simplicity, sheet pile shoring requires few parts and can be easily assembled and disassembled by a small team.
Sheet pile shoring is a construction technique used for supporting earth in excavation and burial projects. This method involves creating a shallow trench and placing plates on either side to retain the earth. The setup is supported by cut beams, which are adjustable to change the spacing between the plates. Known for its simplicity, sheet pile shoring requires few parts and can be easily assembled and disassembled by a small team.