What Is a Hydrogen Gas Generator?

A hydrogen gas generator is a device designed to produce hydrogen gas. It allows for the generation of hydrogen gas without the need for gas cylinders. Hydrogen gas finds applications in various fields, including research experiments, analytical instruments, and as fuel for fuel cell vehicles.
Uses of Hydrogen Gas Generators
Hydrogen gas is utilized in a wide range of applications, spanning from research and industrial sectors to general use.
1. Research Applications
Hydrogen gas serves as a carrier gas in gas chromatography (GC), as well as a fuel gas in experiments. It is commonly used as a fuel for hydrogen flame ion detectors (FID).
2. Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, hydrogen gas plays a significant role in various processes. This includes the desulfurization of petroleum products, serving as a raw material for ammonia synthesis, and acting as a hydrogen source for applications such as diamond synthesis via microwave plasma CVD and thin-film silicon production. Hydrogen and oxygen or air gas mixtures are used in burners due to their ability to maintain a stable flame at high temperatures without soot contamination.
Other promising applications involve the cleaning of silicon wafers using hydrogen-infused water, as well as the practical implementation of hydrogen-reduced ironmaking technologies aimed at reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
3. Fuel and General Use
Hydrogen gas holds potential in fuel cells for automobiles and household batteries. It is also employed in hydrogen fuel engines for power generation facilities and internal combustion engines in vehicles, contributing to the realization of carbon-neutral societies.
4. General Use
Hydrogen gas inhalers find applications in industries like cosmetics, medicine, sports, and relaxation.
Principle of Hydrogen Gas Generators
Hydrogen gas generators can be categorized based on the method they employ to produce hydrogen gas.
1. Electrolysis of Water
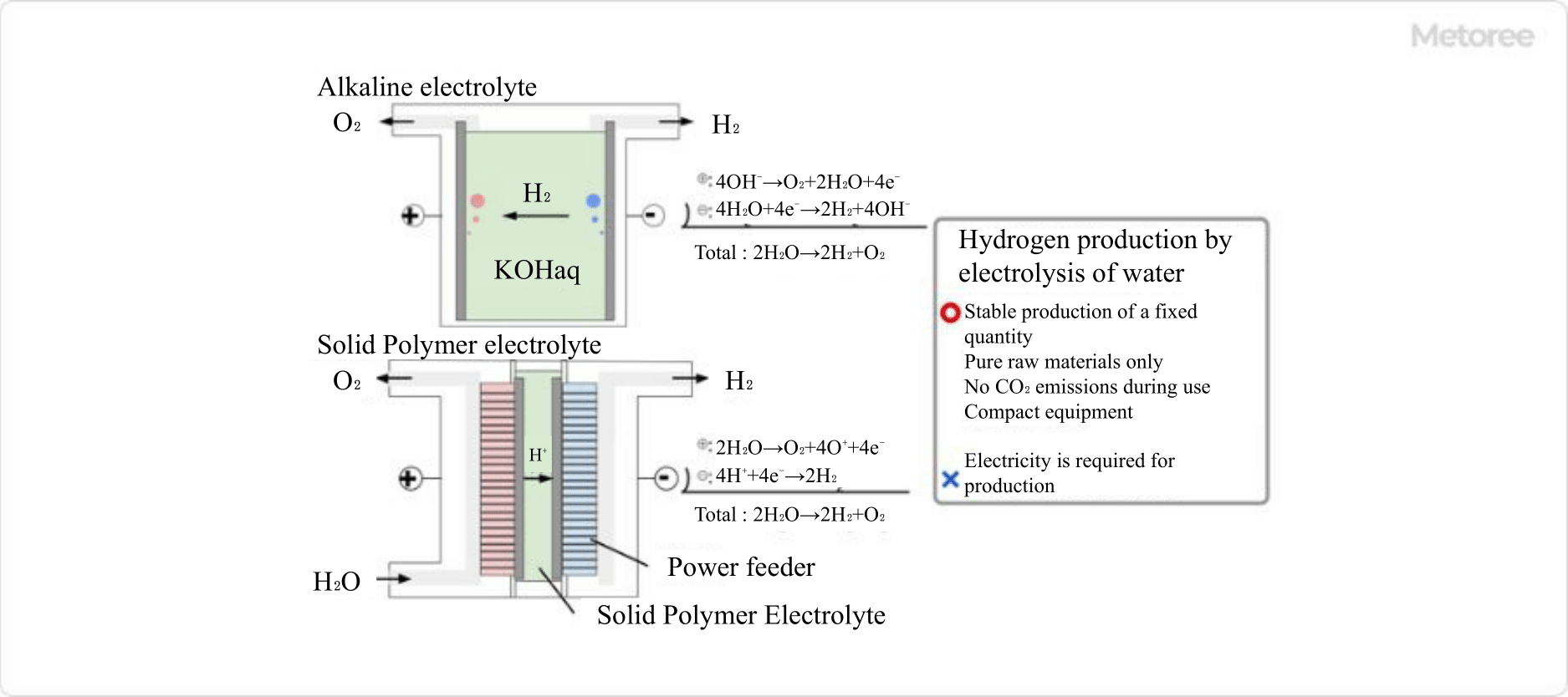
Figure 1. Production of hydrogen gas by electrolysis of water
Hydrogen and oxygen can be extracted through the electrolysis of water. While pure water has low efficiency in this process, it can be improved using electrolytes such as potassium hydroxide, solid polymer electrolytes, or ion-exchange membranes. Some hydrogen gas generators incorporate a purification system with a catalyst like palladium to enhance the purity of the produced hydrogen gas.
Electrolysis of water is suitable for producing hydrogen gas in small quantities and is ideal for research purposes and indoor use.
2. Steam Reforming
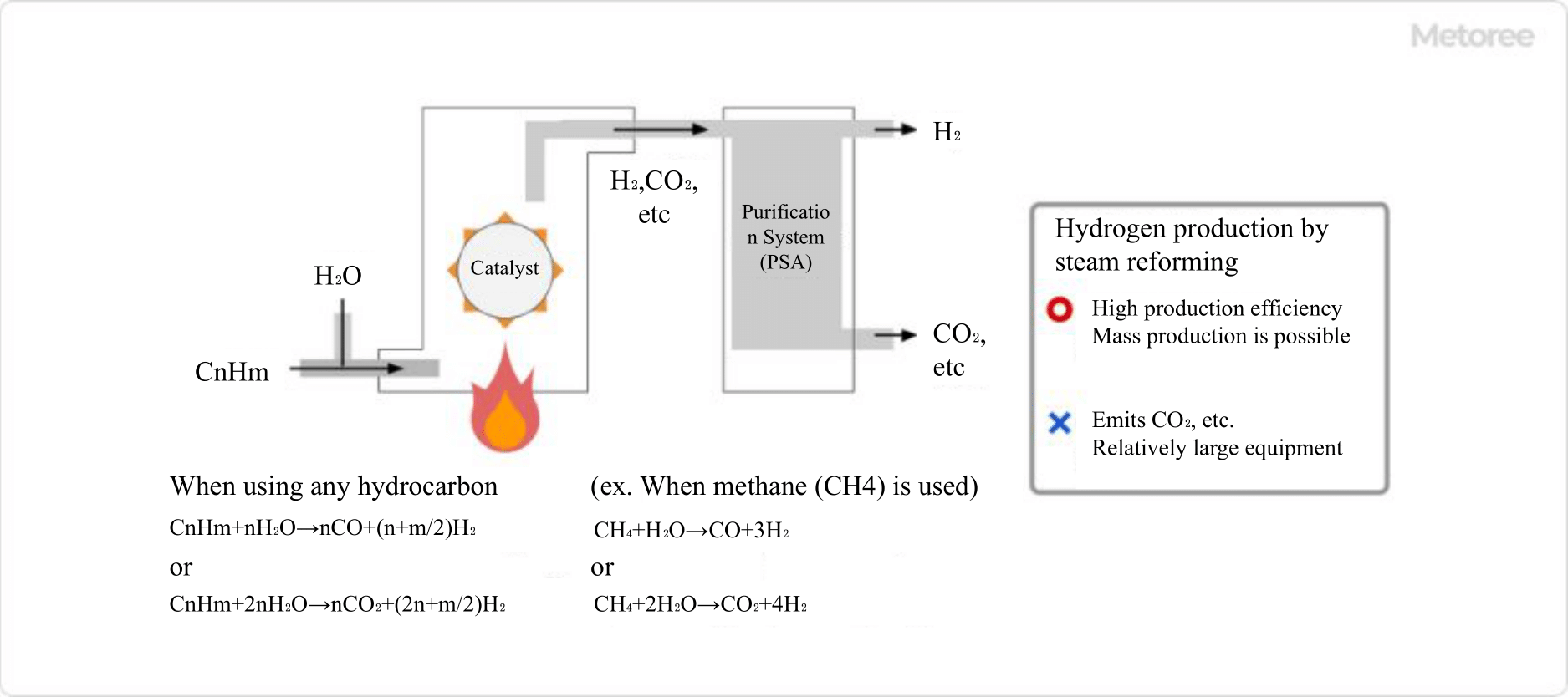
Figure 2. Production of hydrogen gas by steam reforming
Steam reforming involves the high-temperature steam reaction with hydrocarbons or coal in the presence of a catalyst, resulting in the generation of hydrogen gas. Carbon in the hydrocarbons combines with oxygen in the water to form carbon monoxide, effectively separating molecular hydrogen from both the hydrocarbons and water. The hydrogen produced via steam reforming often requires purification using methods like pressure fluctuation adsorption (PSA) due to impurities.
Steam reforming is commonly used in industrial applications to efficiently produce large volumes of hydrogen gas.
While there are various methods for hydrogen gas generation, the above two methods are the most prevalent.
Additional Information on Hydrogen Gas Generators
1. Advantages of Hydrogen Gas Generators Compared to Gas Cylinders
Hydrogen gas generators offer two key advantages compared to gas cylinders: reduced risk of gas leakage and elimination of the need for cylinder replacements.
Reduced Risk of Gas Leakage
Hydrogen gas is flammable and poses an explosion risk when mixed with oxygen. The risk of explosion is lower outdoors or in well-ventilated spaces due to hydrogen’s light and diffusive nature. However, in small, poorly ventilated areas, gas leakage from cylinders can lead to an increased risk of explosion if the hydrogen content in the air exceeds 4 vol%. There is also a potential for indoor asphyxiation.
Hydrogen gas generators can produce only the required amount of hydrogen gas, and excess gas is safely exhausted, significantly reducing the aforementioned risks. They are considered relatively safe for indoor use.
No Need for Cylinder Replacements
Once installed, hydrogen gas generators do not require cylinder replacements. This eliminates the need to transport and replace gas cylinders, reducing labor costs and carbon dioxide emissions.
2. Renewable Potential in Hydrogen Production
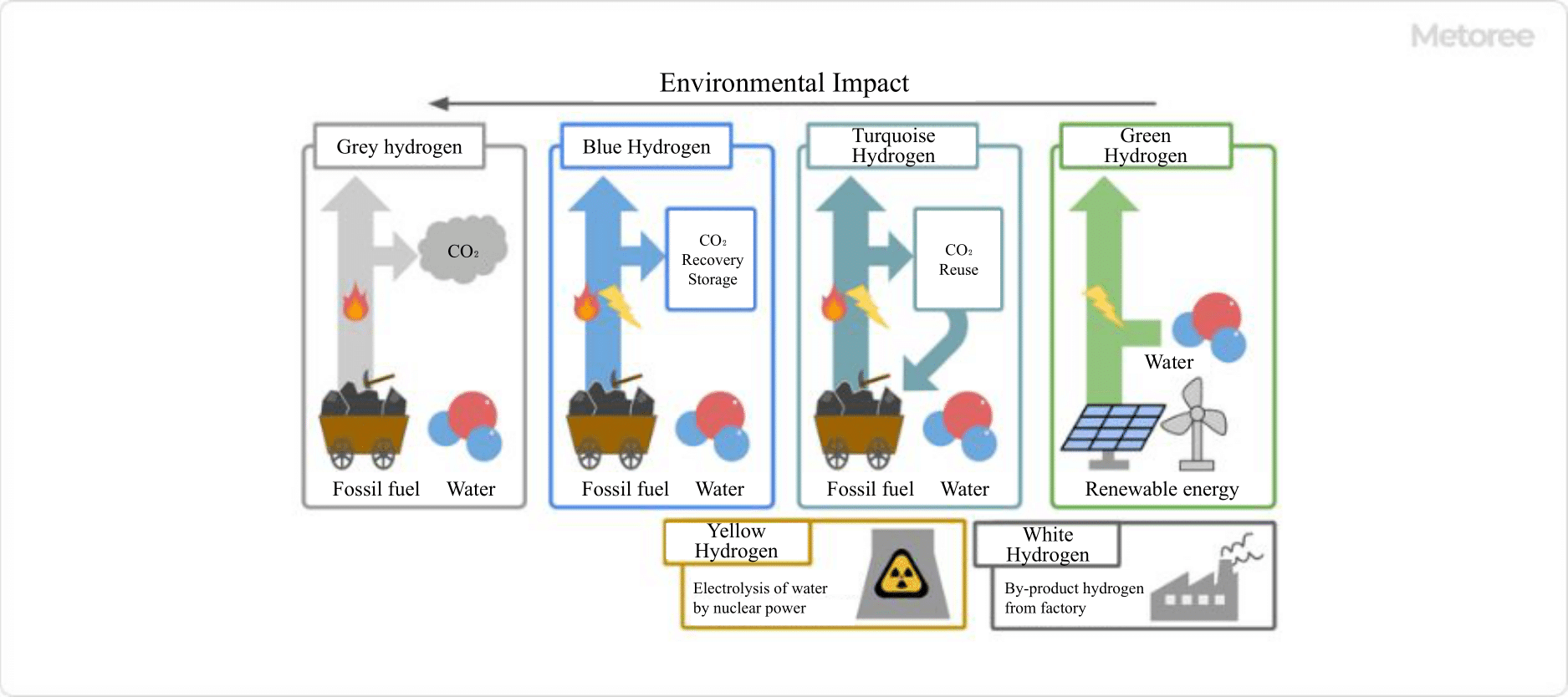
Figure 3. Color coding of hydrogen according to production method
Hydrogen is gaining attention as a clean energy source since its use results in the emission of only water, without carbon dioxide or other harmful substances.
However, in current scenarios, carbon dioxide and other emissions are associated with hydrogen gas production and transportation. To achieve truly clean energy use, the sum of carbon dioxide emissions from raw material acquisition to production and consumption must be reduced to less than zero. Hydrogen produced under these conditions is referred to as green hydrogen and is considered a completely clean energy source.
By generating hydrogen gas on-site, the need for transportation from production to consumption can be eliminated. Achieving green hydrogen production entails reducing carbon dioxide emissions to zero during hydrogen gas production. This can be achieved by using electricity from renewable sources like solar and wind power for electrolysis. Steam reforming with biomass is another method for producing green hydrogen, though it is less suitable for large-scale production due to raw material collection costs.
While still in the research phase, methods such as water and methane pyrolysis and artificial photosynthesis are being explored for green hydrogen production.