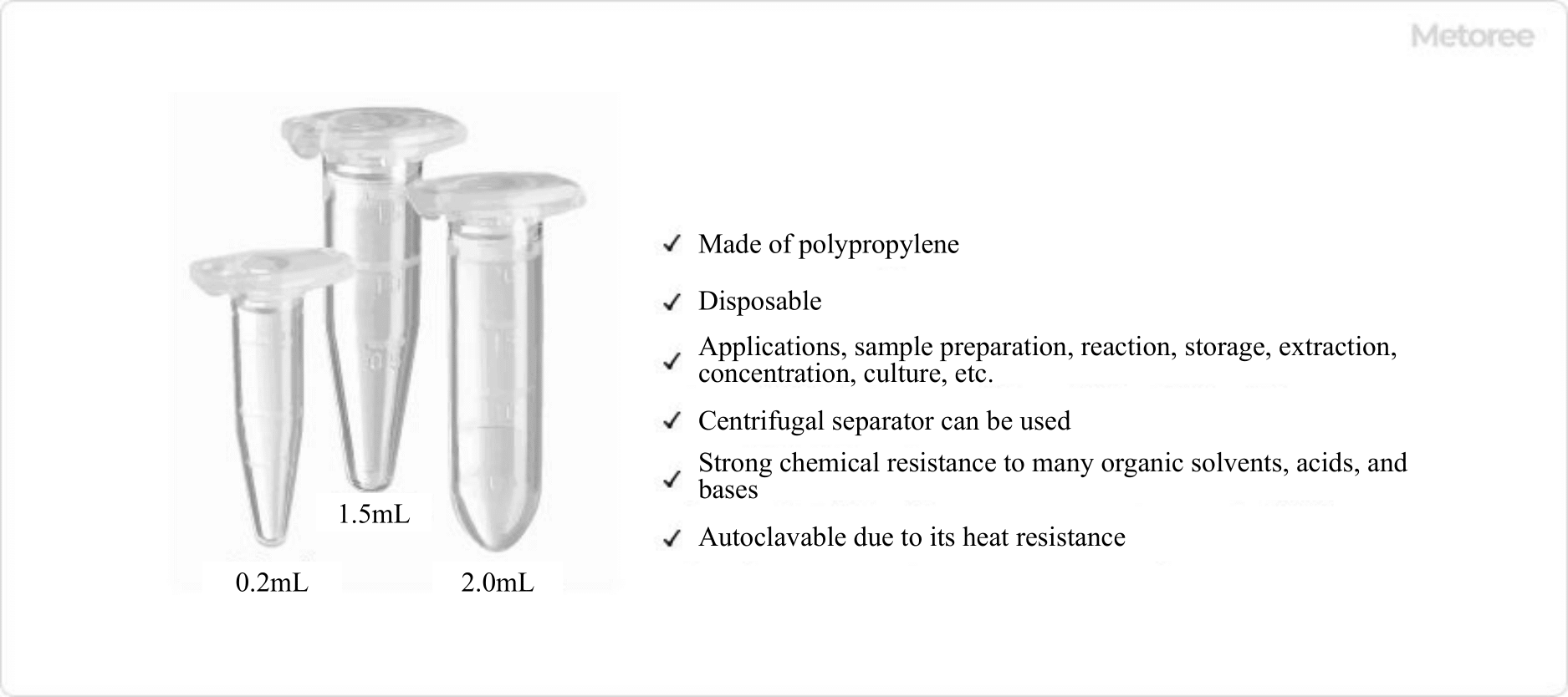
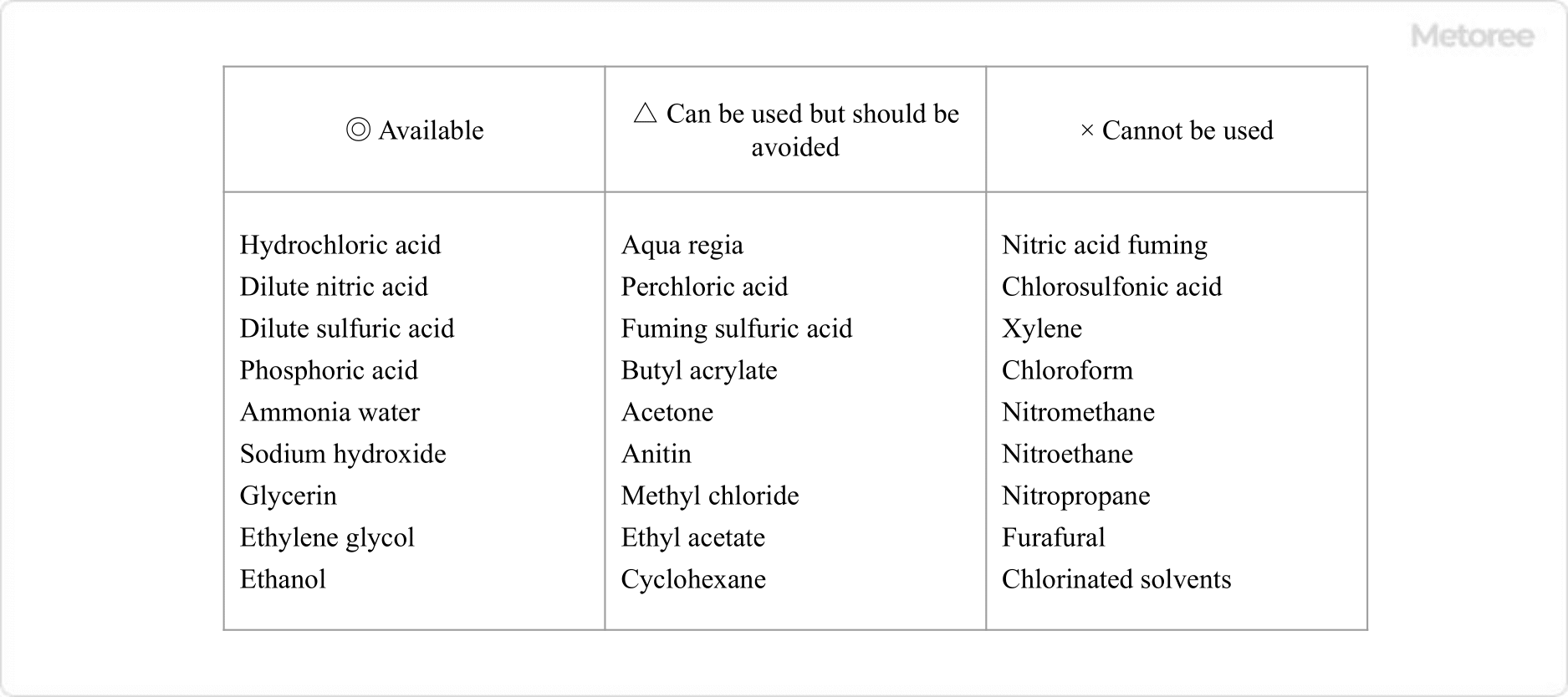
What Is a Measuring Pipette?

A measuring pipette is a type of glass volumeter. It has multiple scales engraved on its side, and can be used to collect and drop various volumes of liquids. A measuring pipette is classified into two types, Class A and Class B, according to the size of the tolerance.
Since measuring pipettes are less precise than whole pipettes, whole pipettes should be used when precise volume of liquid is required. On the other hand, measuring pipette is useful for experiments where strict accuracy is not required and the volume of liquid to be collected or dropped can be varied as desired.
Types and Uses of Measuring Pipettes
Measuring pipettes are instruments used in physical and chemical experiments, and are a type of volumetric instrument for measuring the volume of a liquid. Although less precise than whole pipettes, measuring pipettes are useful instruments for collecting and dropping liquids of various volumes because it has a scale on its side finely engraved to indicate the volume.
Because of the above features, measuring pipettes are used when the allowable error in solution preparation and collection is somewhat large, or when the amount of solution to be added to a sample can be varied arbitrarily. On the other hand, a whole pipette is used instead of a female pipette when accurate measuring pipetting is required, such as in the preparation of standard solutions for concentration measurement.
Accuracy of Measuring Pipettes
The tolerance of glass volumeters such as measuring pipettes is defined in the JIS standard (JIS R3505 Glass Volumeters). Measuring pipettes are classified into two classes, “Class A” and “Class B,” according to the JIS standard, with Class A having a smaller permissible volumetric error, i.e., requiring higher accuracy.
For both Class A and Class B, the permissible error is defined according to the total volume, and the larger the total volume, the smaller the relative value of the error. The tolerance for Class A is at most ±0.5% of the total volume, and for Class B ±1.0%. However, since this tolerance is based on the volume of water measured at 20°C, the actual error may be even greater depending on the temperature of the laboratory and the solvent collected.
Differences Between Measuring Pipettes, Whole Pipettes, and Komagome Pipettes
In addition to measuring pipettes, whole pipettes and komagome pipettes are sometimes used to collect liquids in experimental work. The major difference between these pipettes is accuracy.
Komagome pipettes are the least accurate of the three types above, but they can collect a fixed amount of liquid easily and quickly. The measuring pipettes are less precise than the whole pipette, but it is sufficiently more precise than the Komagome pipette, and it has a fine scale on the side, which is useful when you want to experiment by arbitrarily changing the collection volume with a certain degree of precision. Whole pipettes are the most accurate and are used when the volume of liquid needs to be measured precisely.

 An electromagnetic lock is a lock that uses the force of an electromagnet designed for emergency exits.
An electromagnetic lock is a lock that uses the force of an electromagnet designed for emergency exits.