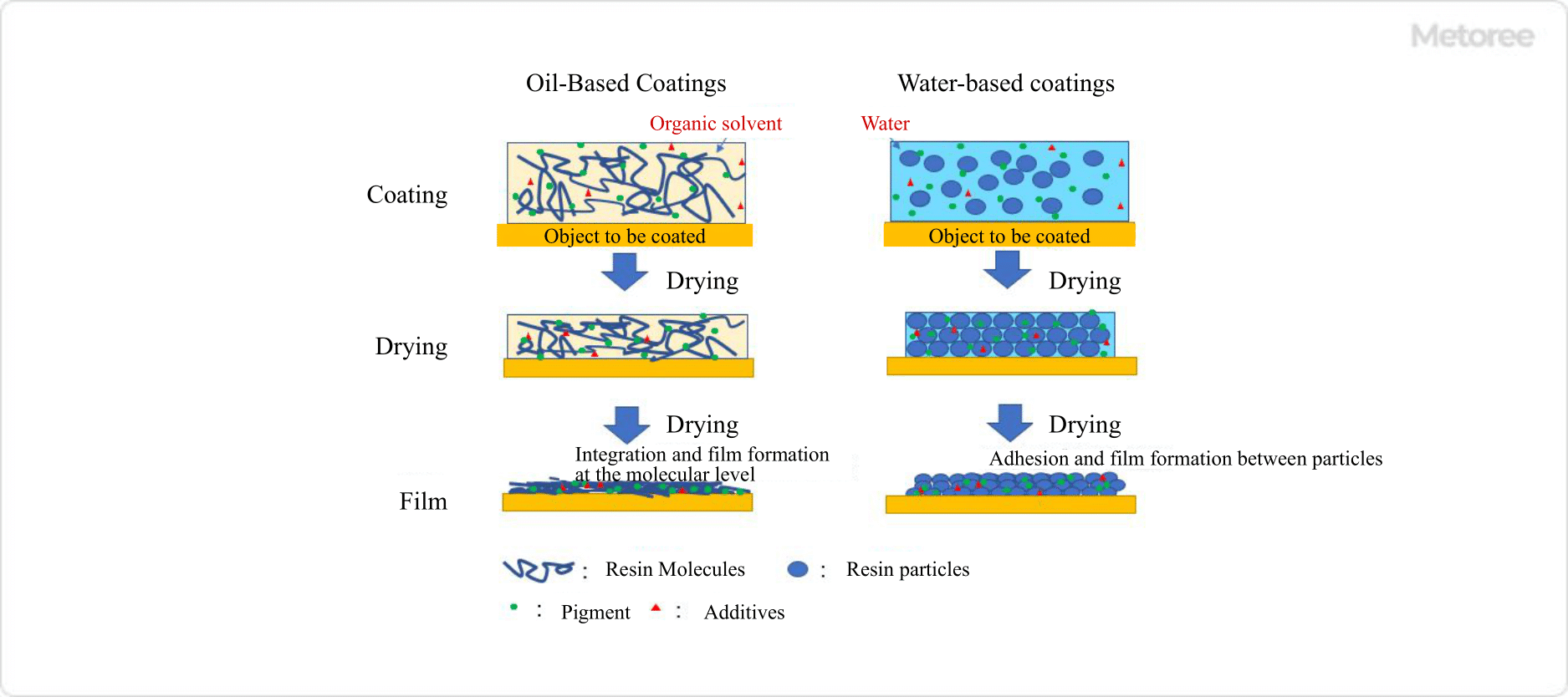
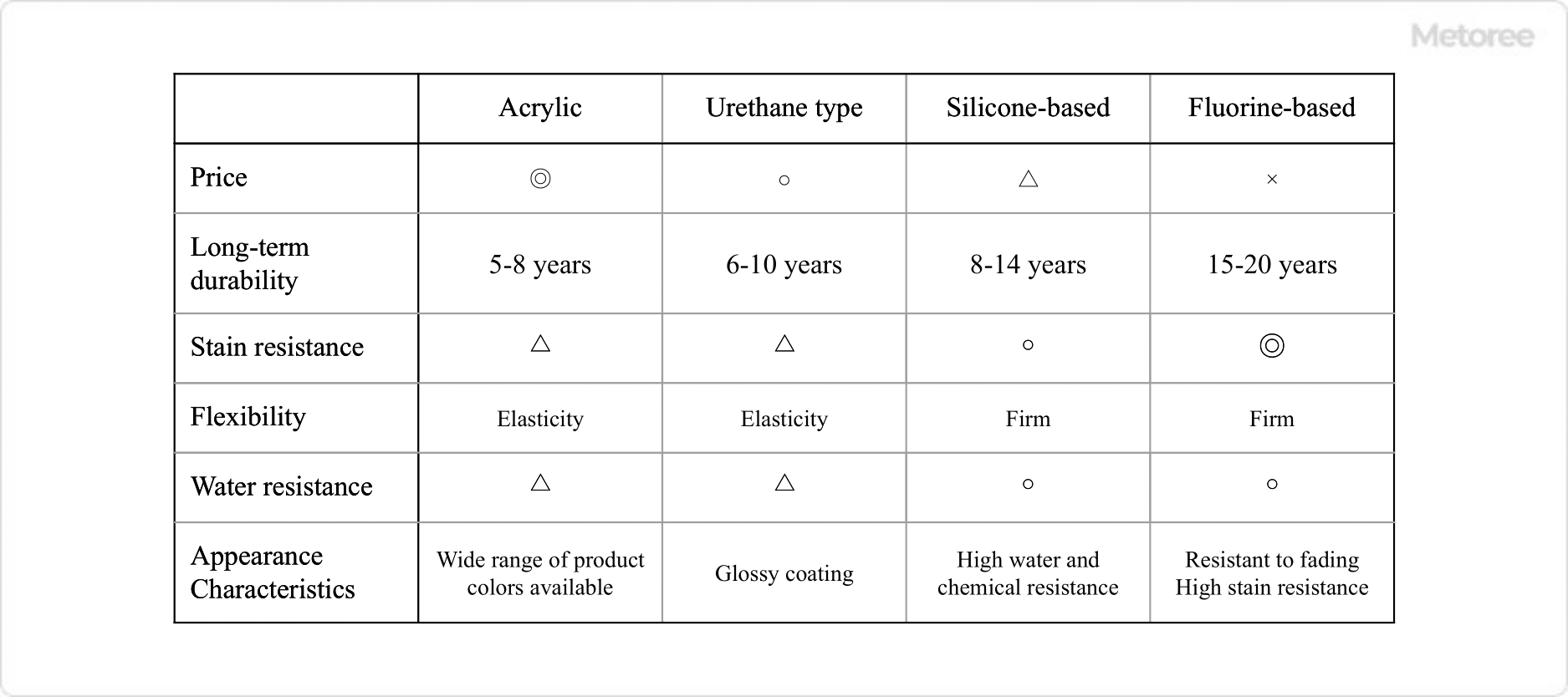
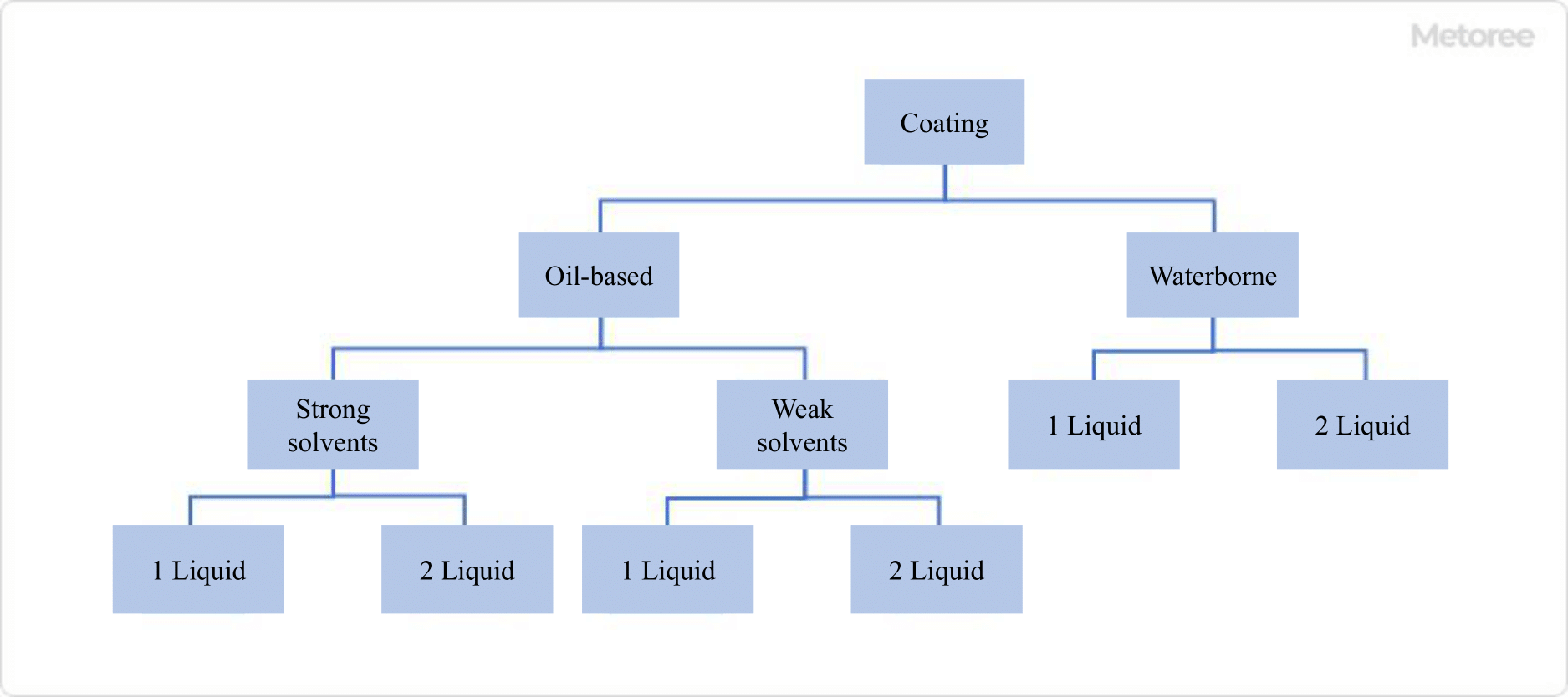
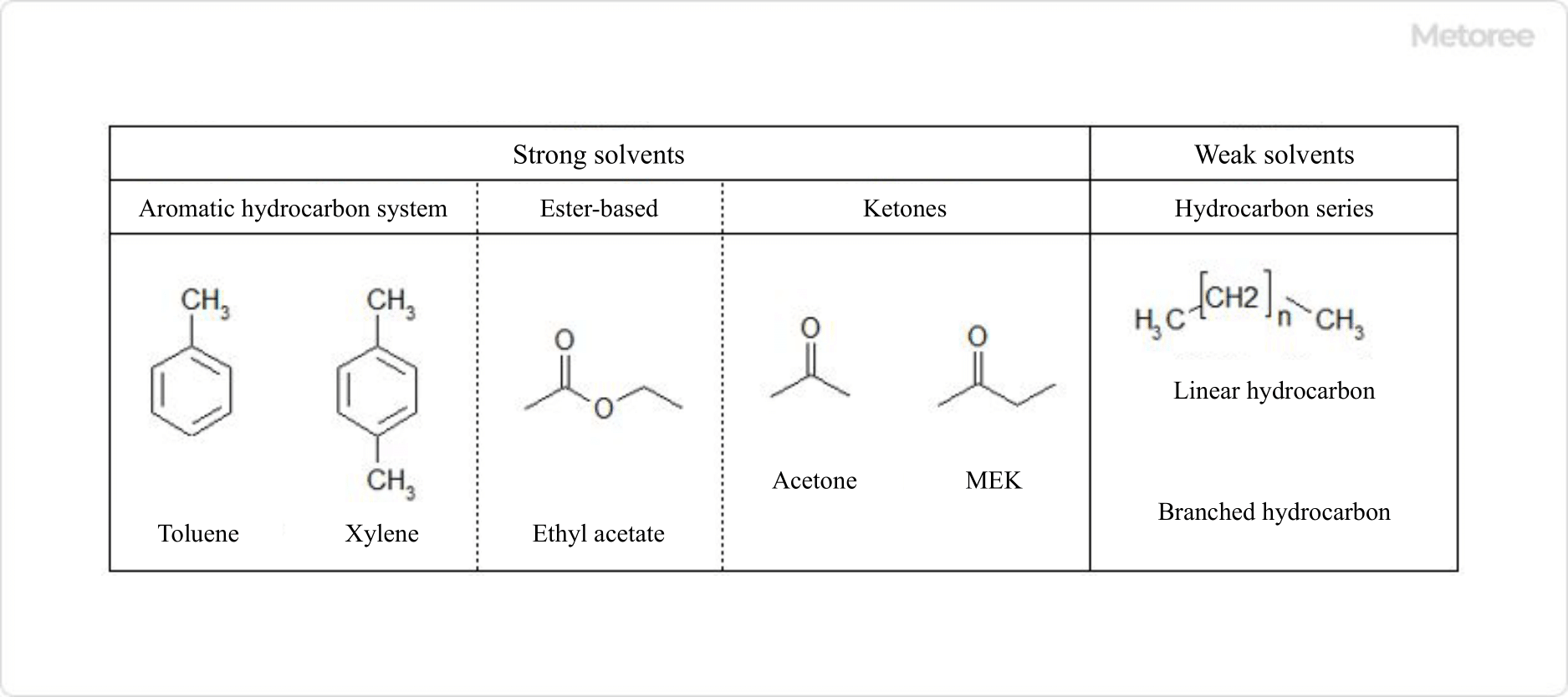
What Is a High-Pressure Hose Fitting?

A high-pressure hose fitting is a component (fitting) at the end of a hose to which a high-pressure hose is connected.
Like general hose fittings, there are different types of high-pressure hose fitting, depending on the application.
The hose fitting is selected according to the size (outer diameter) of the hose and its sealing performance (leakage) against fluid pressure. Especially in the case of high-pressure hoses, leakage of high-pressure fluid is dangerous, and a connection method with high-sealing performance must be used. Therefore, a screwed-in type with a tapered pipe thread, or a flanged type for higher pressure, is used.
Uses of High-Pressure Hose Fittings
High-pressure hose fittings are used to connect hoses to each other and to piping and equipment.
High-pressure hose fittings used for high-pressure fluids, such as steam, chemicals, gases, etc., are often threaded or flanged.
When used for air, where a small amount of leakage is not a concern, a coupler, or a one-touch type, may be preferred for its ease of connection and disconnection, making it more convenient to work with.
The most suitable high-pressure hose fittings material should be selected according to the type of fluid used and the environment in which it is used. In particular, selection should be made in consideration of pressure resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Principle of High-Pressure Hose Fittings
The principle of high-pressure hose fittings is the same as that of ordinary hose fittings.
In the case of the threaded type, the tapered male and female threads are tightly sealed together. By screwing in deeply, the tight fit gradually becomes stronger, and higher sealing performance can be obtained.
In the case of a flange type, the joint surfaces of the flanges are tightly sealed against each other. A gasket is generally inserted between the flanges to increase the adhesiveness of the flanges. The flanges are tightened with bolts and nuts to increase and maintain the adhesion. In this case, the bolts and nuts must be tightened evenly.
For this reason, bolts and nuts are generally tightened diagonally rather than in sequence. It is also important to tighten the bolts and nuts at the specified torque value for the gasket material and bolt/nut. The tightening torque is gradually increased in diagonal order until the required tightening torque value is reached.
In the case of screwed-in or flanged type for high-temperature fluid, the tightening of the threaded part may loosen due to thermal expansion after the actual flow of high-temperature fluid. In such cases, it is necessary to re-tighten the threaded part for the screwed type and the bolt/nut for the flanged type.