What Is a Conductive Tape?
A conductive tape is a type of tape that possesses conductive properties.
It is typically made from materials like aluminum or copper foil or contains conductive fillers, such as metal particles, within its adhesive layer. Conductive tape is known for its low electrical resistance. Given the variety available, choosing the right type of conductive tape for a specific application is crucial. Consider factors such as strength, flexibility, and whether a single-sided or double-sided adhesive is required.
This tape is often employed to shield equipment from external electromagnetic and electrostatic interference. It is applied near sources of noise or onto the surfaces of semiconductor devices.
By connecting one end of the conductive tape directly to the device’s ground line, it serves to absorb and dissipate external noise through the ground line, effectively safeguarding the equipment.
Applications of Conductive Tapes
1. Static Electricity and Electromagnetic Shielding
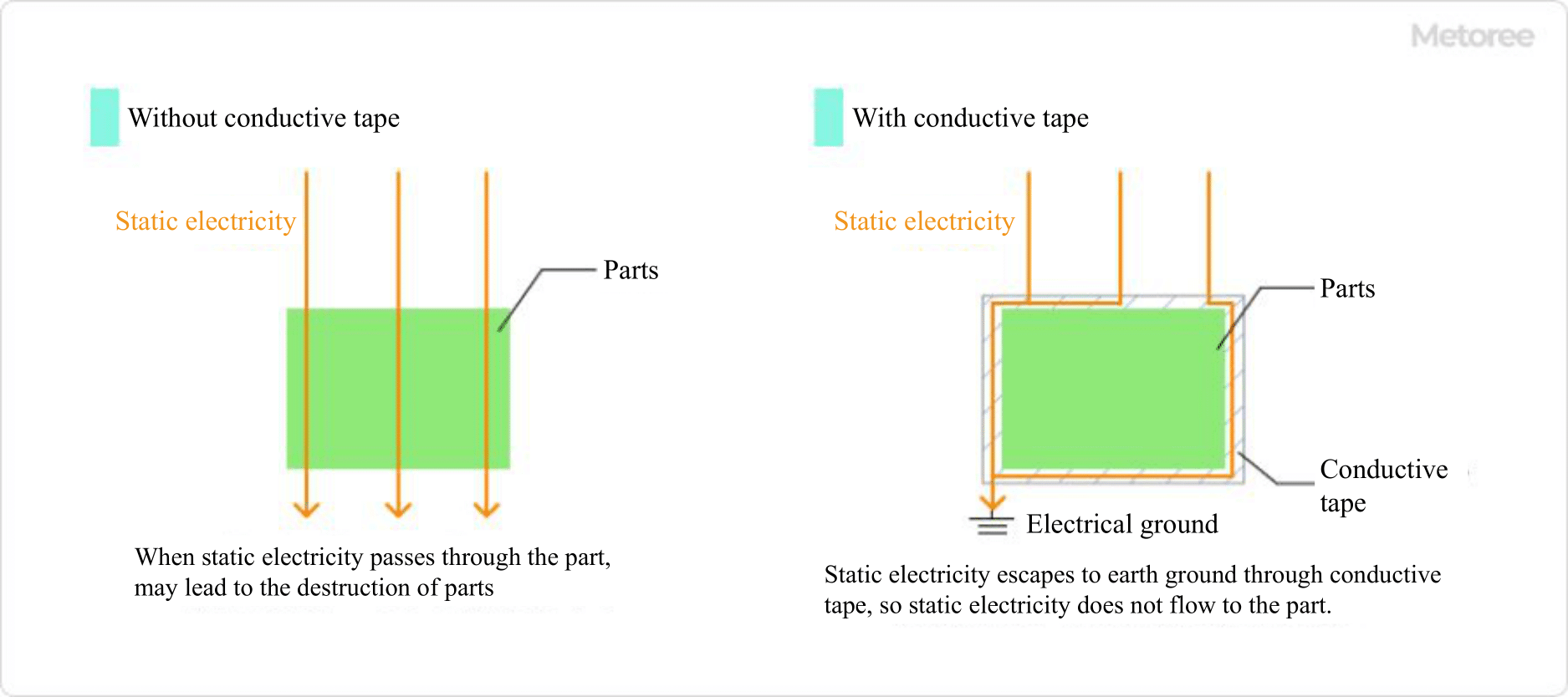
Figure 1. Protection of components using conductive tape
In a factory environment, a worker touching a product charged with static electricity can potentially damage semiconductor components on the electronic board inside the product, or even lead to partial destruction in the worst-case scenario.
To prevent such situations, measures like laying down conductive mats within the factory are necessary. These mats allow static electricity to flow from the product enclosure’s surface to the conductive mat on the worktable, grounding it in the process.
However, depending on the route static electricity takes into the equipment, it may reach the printed circuit board inside the product. In such cases, conductive mats alone may not suffice, and measures must be taken on the board level. Conductive tape is used to protect individual components by insulating them from static electricity and connecting them to the ground line.
2. Electrical Distribution Safety Measures
Conductive tape also serves as a safety measure in the distribution of electricity generated at power plants to offices and homes. While insulating tape is typically used to insulate cables from electricity, semi-conductive tape with slightly higher resistance is used in certain situations.
Cables containing a conductive layer can experience electric field concentration at specific points in the conductive layer if left unconnected when attached. Wrapping semi-conductive tape around the conductive layer helps alleviate this electric field stress.
3. Analytical Applications
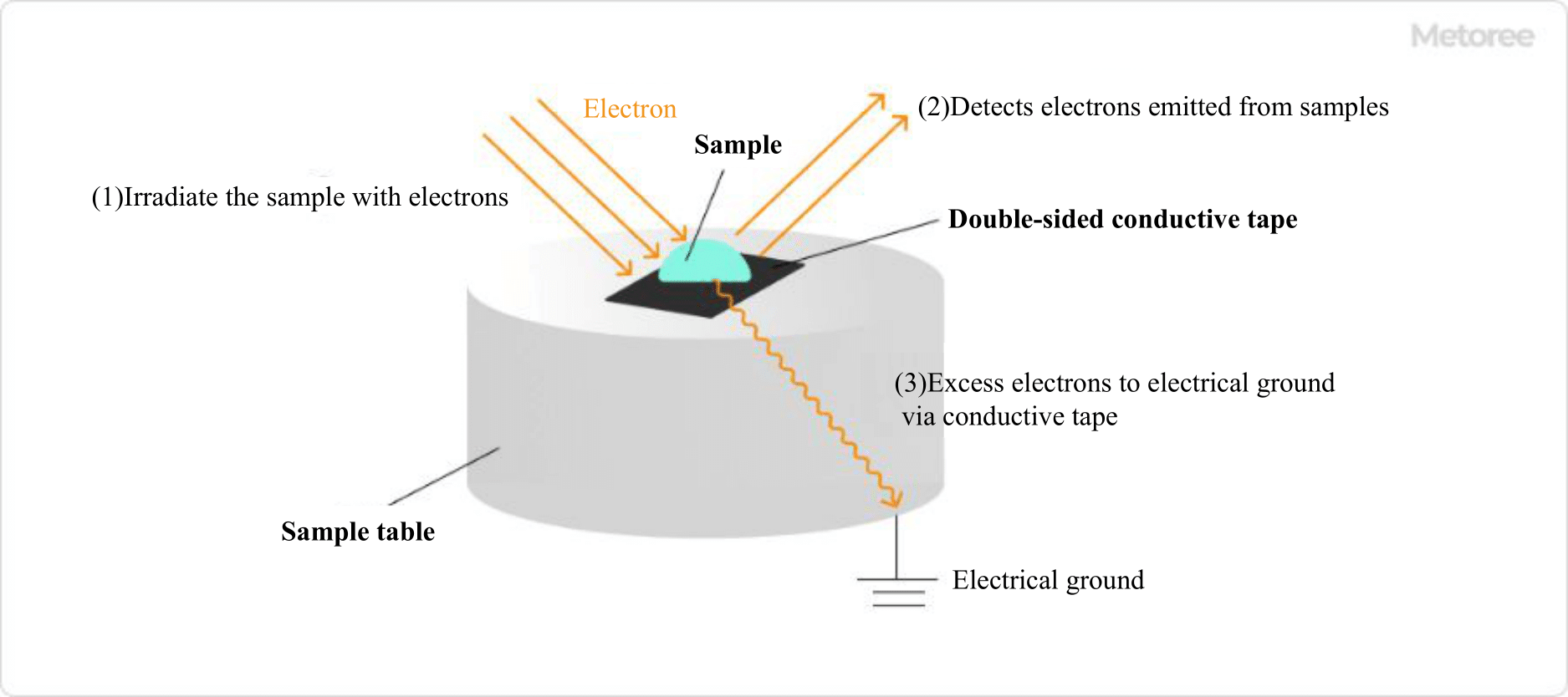
Figure 2. Role of conductive tape in SEM
When observing samples with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) or transmission electron microscope (TEM), commonly used in R&D applications, it is necessary to ensure that the sample is conductive. Conductive tape is applied to both sides of the specimen when it is placed on the observation table to provide a discharge path for irradiated electrons and prevent specimen charging during observation.
Principles of Conductive Tapes
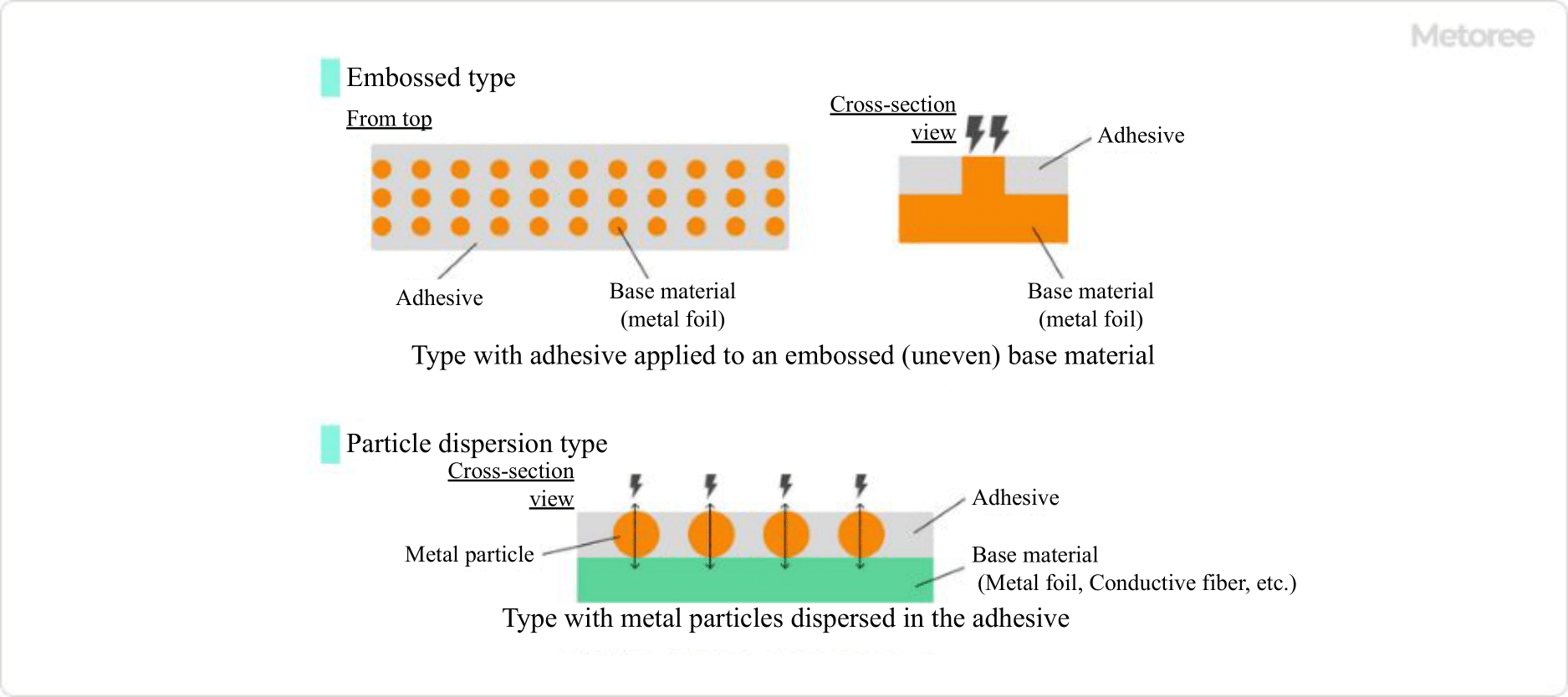
Figure 3. Structure principle of conductive tape
Conductive tape, like regular adhesive tape, consists of a base material and an adhesive. An adhesive is applied to embossed metal foil to impart conductivity, or metal particles are dispersed within the adhesive.
In addition to metallic foil, conductive tapes occasionally use conductive fibers with excellent flexibility as base materials. Conductive tapes with conductive fibers are often preferred for applications in moving or narrow equipment areas.
Types of Conductive Tapes
Among conductive tapes, there are specialized types like conductive carbon tape and transparent conductive tapes, designed for specific electronic equipment applications beyond just antistatic purposes.
1. Conductive Carbon Tape
Conductive carbon tape utilizes aluminum as the primary metal foil and incorporates a conductive filler of carbon powder within its adhesive layer. This results in the tape’s characteristic black color.
Conductive carbon tape is often used as a double-sided tape with adhesive layers on both sides of the metal foil. It finds application in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation and is suitable for analytical applications due to its minimal or absence of gas emission.
2. Transparent Conductive Tape
Some transparent conductive tapes are used in cleanroom environments. Products lacking anti-static measures are unsuitable for cleanrooms as they attract dust and contaminants, posing a risk to the controlled environment.
One example consists of a polybutylene terephthalate resin (PET) base material with a poly-conductive layer and an acrylic adhesive on the external side of the layer. These transparent conductive tapes offer excellent conductivity and transparency, making them ideal for highly adhesive electronic tape applications used in packaging static-sensitive components. They also function as adhesive tapes with anti-static specifications to mitigate peel-off charging.
Furthermore, they are employed as electrostatic chucks for CMOS, MEMS, power devices, and glass wafers in plasma and CVD processes.
Additional Information on Conductive Tapes
1. Mitigating Static Noise
Conductive sheets and tapes are used to prevent equipment damage caused by static electricity. Static electricity poses a significant challenge in factories, as it can potentially lead to component damage on internal circuit boards, even if unnoticed until product shipment.
To address this, it is crucial to implement local countermeasures using conductive tape in conjunction with broader approaches, such as the following:
- Increase Humidity in the Factory: Maintaining a constant humidity level within the factory helps reduce electrical resistance on equipment surfaces.
- Provide Grounding Wires: Supply workers with grounding wires for their wrists and other body parts to prevent static electricity generation.
- Lay Conductive Sheets: Use conductive sheets to provide a discharge path for static electricity, even if a worker becomes charged.
- Apply Conductive Tape to Equipment: Protect equipment by affixing conductive tape near potential noise entry points and on semiconductor device surfaces.
2. Solderable Conductive Tape
Metal conductive tapes, such as copper foil tape and aluminum foil tape, are developed for soldering to metal foil surfaces to establish electrical connections with other components. Conductive tapes, featuring adhesive properties, are easily applied to objects and are suitable for wiring work involving soldering.