What Is a Stereolithography 3D Printer?
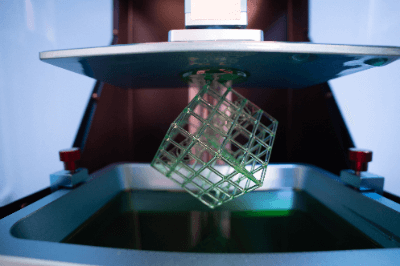
A stereolithography 3D printer is a 3D printer that utilizes the stereolithography method.
The stereolithography method is a technique for creating three-dimensional structures by curing and layering a material, which is cured by exposure to ultraviolet light, layer by layer. The material used is usually a liquid light-curable resin such as epoxy or acrylic resin.
Stereolithography 3D printing is the oldest of all the 3D printing technologies currently in practical use and is the most widely used method in the industry.
Uses of Stereolithography 3D Printers
Stereolithography 3D printers are employed for verifying designs, creating master models, and producing molds.
Due to their capability to produce highly precise, smooth-surfaced objects, stereolithography 3D printers can also be used for manufacturing final products.
The choice of printer types and materials depends on the intended use.
Principles of Stereolithography 3D Printers
In the optical fabrication method, 3D data is loaded into the printer, and the liquid resin is irradiated with ultraviolet light to create the model.
The process begins by creating the first layer, where the resin is cured by irradiating a laser beam onto a tank filled with light-curing resin liquid. Subsequently, the resin is lowered by one layer from the cured stacked surface, and the next layer is cured in the same manner. This process is repeated to build the model layer by layer.
Precise modeling can be achieved by setting a thin layer thickness, while thicker layers allow for faster and more efficient modeling.
Types of Stereolithography 3D Printers
There are several types of stereolithography 3D printers.
Here is a description of typical modeling methods.
1. Classification of Stereolithography 3D Printers Based on Modeling Direction
Stereolithography 3D printers can be classified into two types based on the direction in which modeling proceeds:
- Free surface method: Light is directed onto the modeling object from above, and modeling proceeds by stacking cured layers.
- Hanging method: The modeling object is suspended, and light is irradiated from below to advance the modeling.
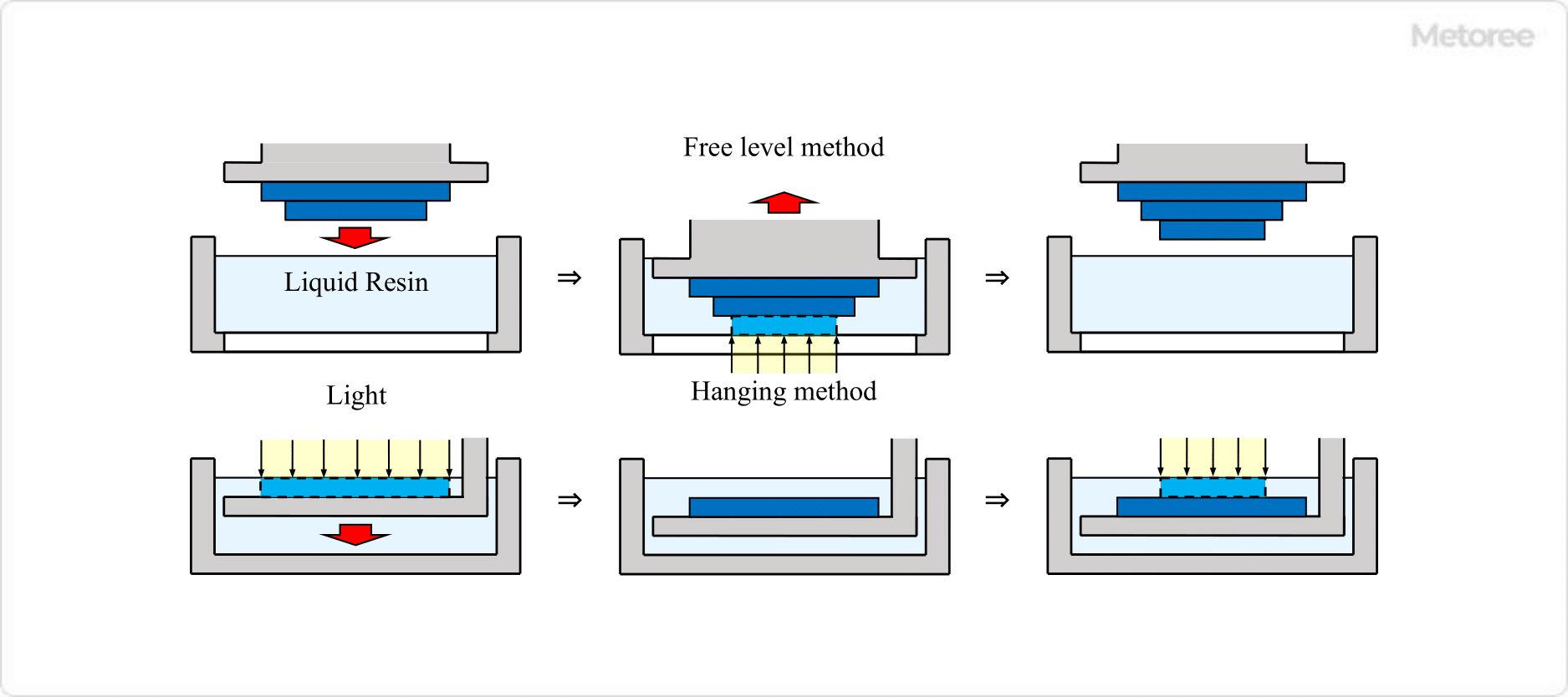
Figure 1. Classification based on modeling direction
2. Classifications of Stereolithography 3D Printers by the Way Light Is Applied
Stereolithography 3D printers can also be classified based on how light is applied. Three representative examples are:
- Laser scanning method: This method employs a laser-pointer-like light to draw lines of light.
- Projector method: A single layer of light is produced with a single irradiation.
- Liquid crystal panel method: Similar to the projector method, light is emitted from a surface, but this method uses a liquid crystal display instead of a projector to irradiate light.
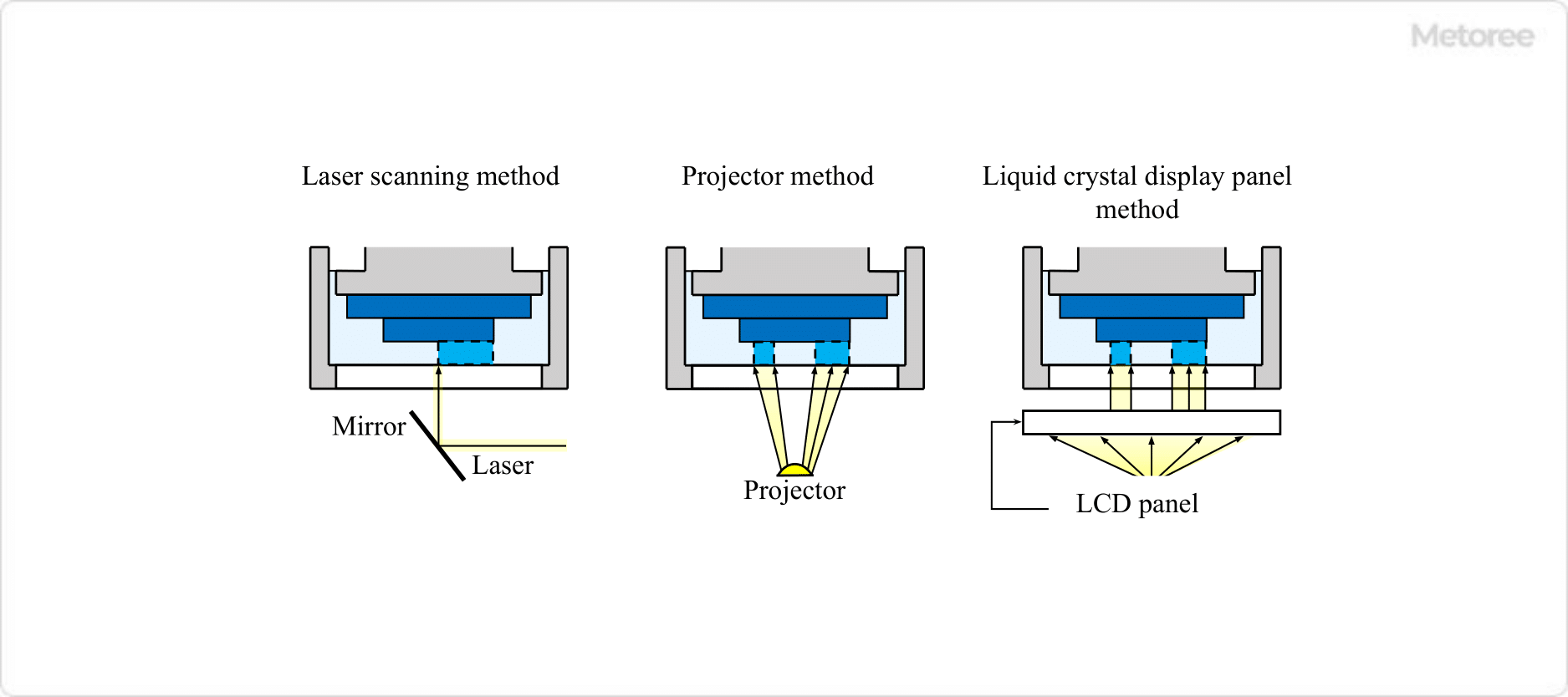
Figure 2. Classification is based on the way light is exposed
Other Information on Stereolithography 3D Printers
1. Features of Stereolithography 3D Printers
Stereolithography 3D printers have their advantages and disadvantages:
- Advantages: They can achieve high-precision modeling with smooth surfaces and are capable of relatively rapid production.
- Disadvantages: Stereolithography equipment and resins are costly, and post-processing is often required.
The light-curing resins used have distinct characteristics, and the choice of resin depends on the intended application. For example, epoxy resin is not resistant to sunlight, while acrylic resin is fragile, making it unsuitable for applications with high forces or durability requirements.
2. Stereolithography 3D Printers Procedure
The use of stereolithography 3D printers typically involves three steps: creation and conversion of 3D data, modeling, and post-processing.
- Creation and conversion of 3D data: 3D data of the object to be modeled is created using 3D CAD or a 3D scanner. This data is then converted into STL data and tool path data compatible with the selected 3D printer, which is subsequently loaded into the 3D printer.
- Modeling: The stereolithography 3D printer is used for the modeling process.
- Post-processing: Immediately after modeling, the surface of the model is cleaned with alcohol or other solvents to remove any uncured resin. Depending on the resin used, secondary curing may be performed to enhance strength. After these processes, support material, which is used to prevent deformation during printing, is removed.
3. Data Handled by Stereolithography 3D Printers
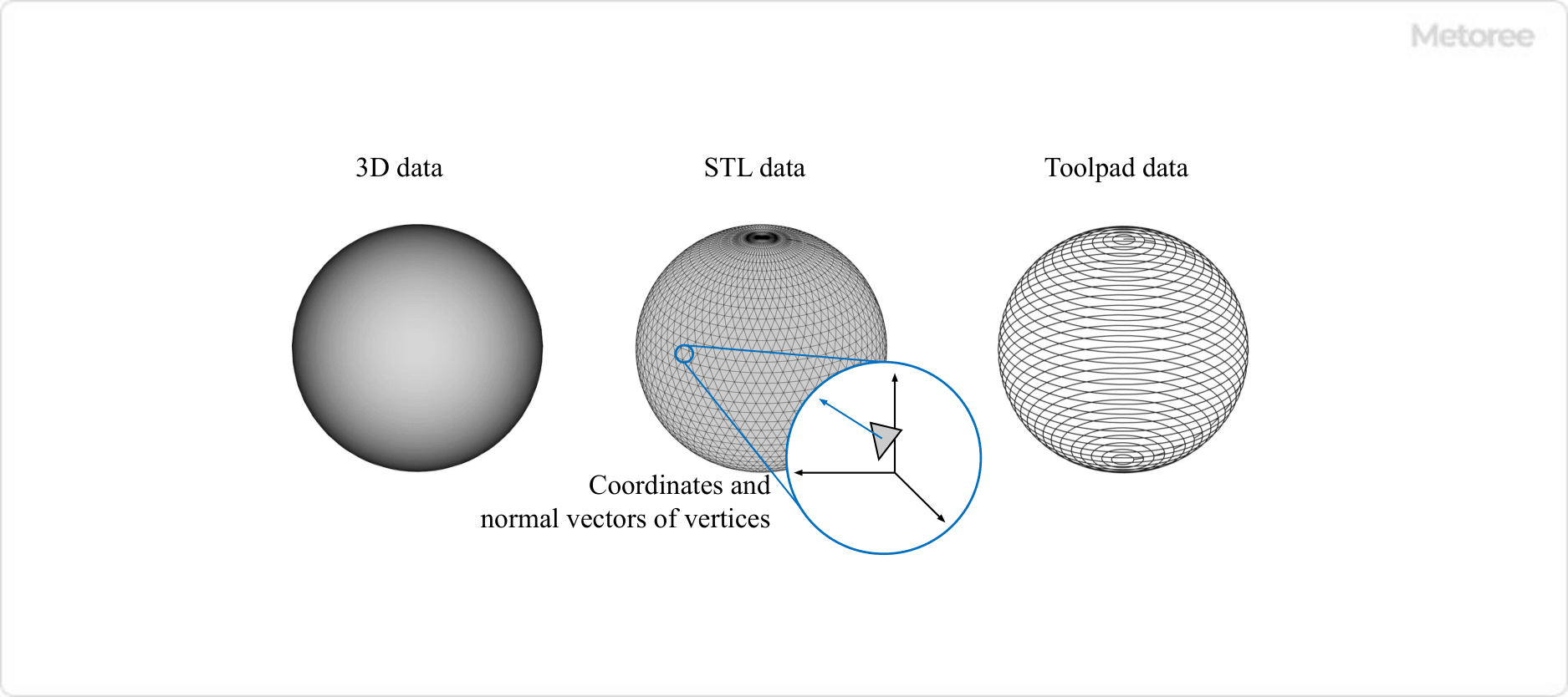
Figure 3. Data handled by stereolithography 3D printers
To proceed with stereolithography 3D printing, three types of data are essential: 3D data, STL data, and toolpath data.
- 3D data: 3D data can be created using 3D CAD software and 3D scanners. 3D CAD generates 3D data by designing the object on a computer. 3D scanners acquire 3D data by scanning physical objects. In recent years, some systems have allowed users to easily scan objects using smartphones and other devices.
- STL data: STL data represents 3D data as a collection of triangles, containing information such as coordinates and normal vectors of the triangle vertices. Many 3D CAD software can output STL data, but when creating STL data, it is necessary to check and correct the model to ensure it is not too flawed to be realistically modeled.
- Toolpath data: Toolpath data contains information on how the 3D printer operates to create the 3D model. The specific toolpath data varies depending on the 3D printer used, and the 3D printer must read this data to model the object.