What Is Predictive Maintenance?
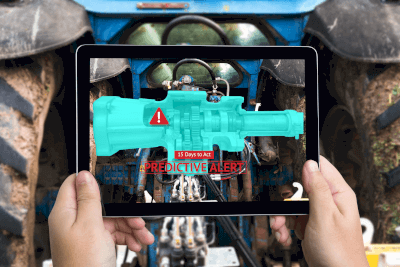
Predictive maintenance involves continuously monitoring and measuring the condition of equipment to detect early signs of deterioration, thereby facilitating timely replacement or repair of parts before failure occurs.
While similar to preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance differs in that it focuses on detecting deterioration early and performing maintenance only when necessary, reducing the likelihood of incurring extra costs associated with regular, scheduled replacements typical of preventive maintenance.
Given the retirement of skilled workers and the need for cost reduction, the manufacturing industry is increasingly adopting digital transformation (DX). Predictive maintenance, which identifies issues early, is being introduced alongside AI and machine learning systems, enhancing maintenance not just for individual parts but for entire facilities.
Difference Between Predictive Maintenance and Preventive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance entails continuous monitoring and measurement of equipment conditions to anticipate and address deterioration before failures or abnormalities occur. In contrast, preventive maintenance involves predetermined replacement frequencies for parts, leading to periodic replacements regardless of actual wear and tear. Predictive maintenance, however, relies on condition monitoring to perform maintenance as needed when deterioration is detected.
Implementing predictive maintenance requires a system for continuous measurement and monitoring, which can be costly and time-consuming to establish. However, it can reduce the costs associated with regular part replacements. Preventive maintenance, while incurring costs for replacing parts that may still be functional, is simpler to implement due to its defined replacement schedule.
Predictive Maintenance, Machine Learning, and AI
Predictive maintenance is defined by its continuous measurement and monitoring approach, with recent advancements in machine learning and AI being employed to determine what conditions signify deterioration. These technologies enable computers to learn from extensive historical data, distinguishing between ‘normal’ and ‘deteriorated’ conditions. With AI learning these patterns, future measurements can be accurately classified as normal or abnormal.
Examples of Predictive Maintenance
Amidst the retirement of experienced workers, increasing equipment complexity, and the need for cost-effective maintenance, the manufacturing industry is shifting from preventive to predictive maintenance through digital transformation (DX). Below, we introduce some specific examples of predictive maintenance.
Predictive Maintenance Using Vibration Sensors
One predictive maintenance method involves installing vibration sensors on factory equipment. By attaching sensors to bearings, motors, pumps, and other components, abnormal vibrations indicating deterioration can be detected. There are also explosion-proof vibration sensors for chemical plants and compatible sensors for food and beverage production lines.
Predictive Maintenance of Machinery and Equipment
Rather than focusing on individual equipment, entire production facilities are increasingly adopting predictive maintenance systems. These systems centralize and visualize measurement data from various equipment, making it easier to analyze. Some systems can learn from past data, failures, and anomalies, detecting issues previously only identifiable through skilled workers’ intuition and experience.