What Is Urea?

Figure 1. Basic Information on Urea
Urea, a nitrogen compound, is found in mammalian urine.
Known also as carbamide, urea decomposes into ammonia, cyanuric acid, and biuret when heated.
Urea can be synthesized through the hydrolysis of calcium cyanamide or dehydration of ammonium carbamate. It forms inclusion compounds with linear hydrocarbons and their derivatives, such as hexane. Its inclusion compounds with hydrogen peroxide are available commercially as solid-state oxidants.
Uses of Urea
Urea serves primarily as a fertilizer and urea resin raw material. It has applications as a diuretic, hypnotic, moisturizer, for extracting n-alkanes from petroleum, and in synthesizing hydrazine and melamine.
High-grade aqueous urea solutions purify nitrogen oxides in diesel and other vehicle emissions, known as the urea-SCR system.
In pharmaceuticals, urea is used for treating keratosis and dry skin, as a neuromuscular stimulant, and its aqueous solutions for evaluating protein solubilization and structural stability due to their protein denaturing properties.
Properties of Urea
Urea melts at approximately 133°C and decomposes to ammonia and other substances upon further heating. It is soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether, and turns purple when mixed with copper sulfate in water, indicating an alkaline solution.
Urea is deliquescent and exhibits nonlinear optical phenomena, where its response to intense light is not directly proportional.
Structure of Urea
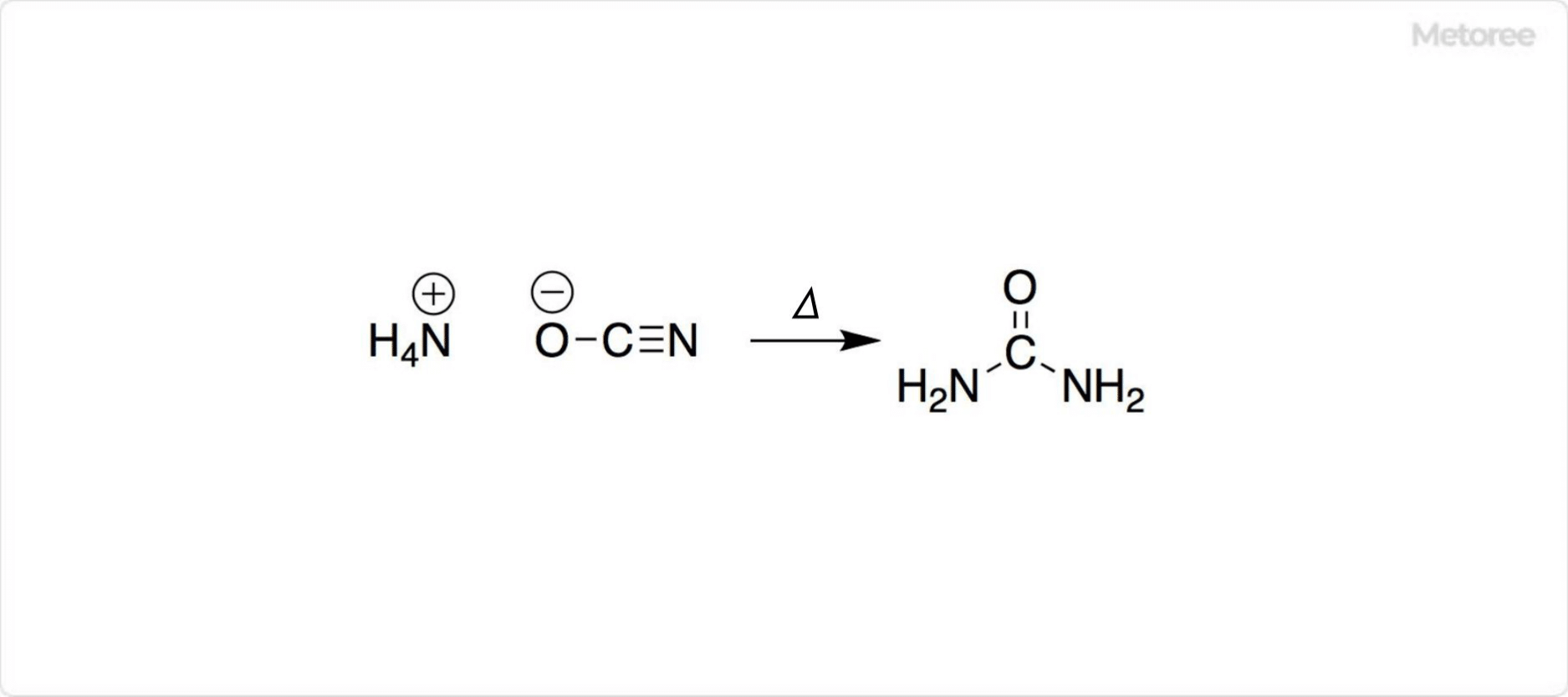
Figure 2. Urea Formation by Wöhler Synthesis
Urea, a colorless, odorless crystal with a molar mass of 60.06 g/mol (CO(NH2)2), was the first organic compound synthesized from inorganic materials, marking a milestone in organic chemistry history.
Friedrich Wöhler synthesized urea by heating ammonium cyanate, challenging the vitalism theory that only living organisms could produce organic compounds. The debate about whether urea is truly “organic” stems from its classification as an amide of carbonic acid, typically not considered an organic compound.
Other Information on Urea
1. Synthesis of Urea
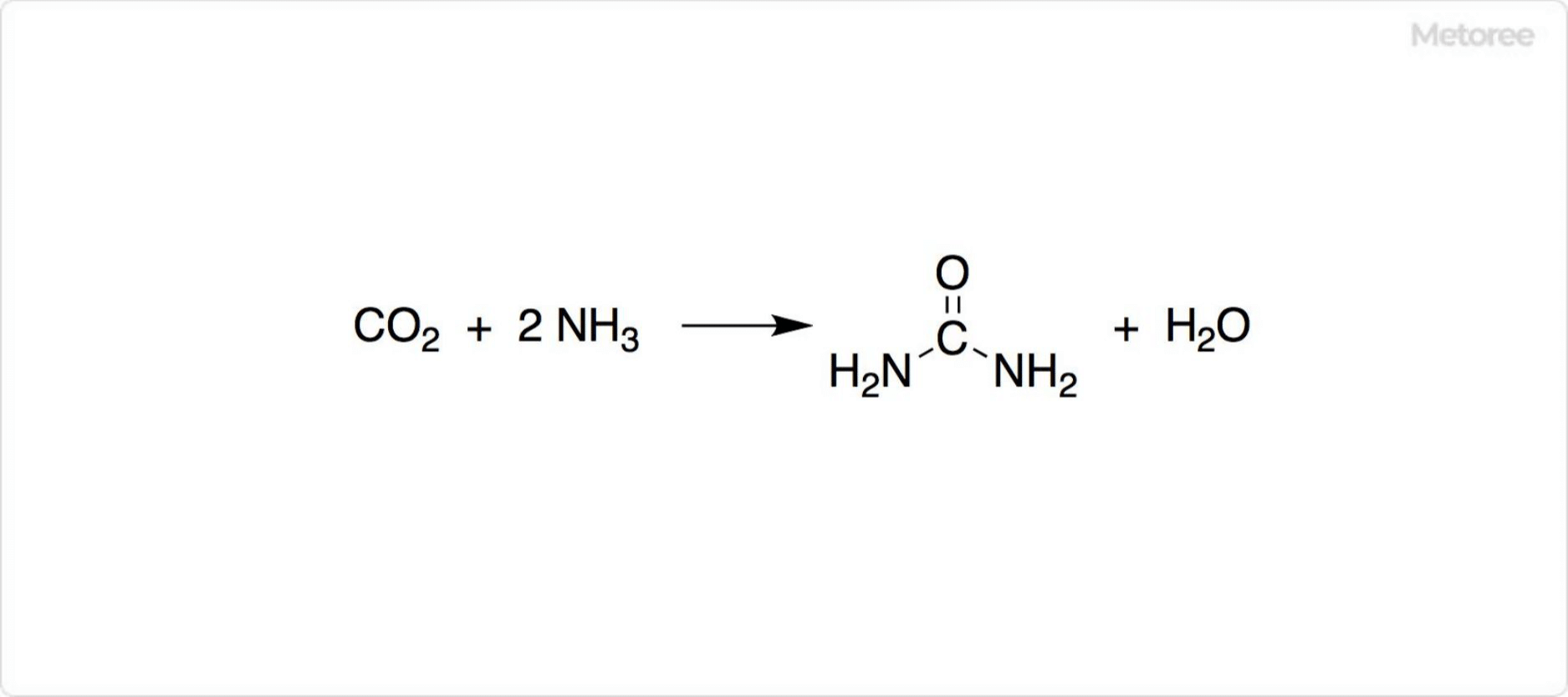
Figure 3. Industrial Urea Synthesis Method
Beyond Wöhler synthesis, urea is industrially produced from carbon dioxide and ammonia under conditions exceeding 120°C and 150 atmospheres.
2. Excretion of Nitrogen by Urea
Mammals, cartilaginous fish, and amphibians excrete nitrogen in the form of urea. In humans, excess nitrogen from proteins is converted to urea via the urea cycle and excreted in urine. Bony fish excrete ammonia, while most birds and reptiles excrete uric acid, a purine metabolism end product in humans and many primates, and a less water-soluble alternative to urea.
3. Urea Excretion and Health
Adults excrete about 30 grams of urea daily. Excessive stress can increase uric acid production, leading to gout if excretion is insufficient and crystals form.