What Is a Blind Flange?
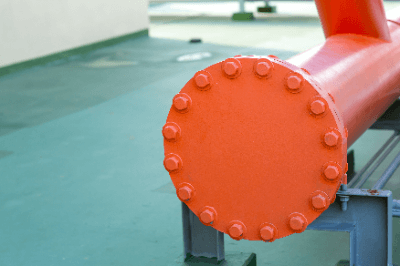
A blind flange, also known as a blank flange, is a fitting used in piping systems to terminate the flow of fluids. It is a type of flange that does not have a center opening, allowing it to effectively seal the end of a pipeline, duct, or other fluid transfer equipment.
Uses of Blind Flanges
Blind flanges are essential for creating a secure closure on piping systems, preventing the entry of foreign materials, and enabling easy access for inspection, cleaning, or modification. They find application in various settings including industrial plants, power generation facilities, and residential systems for emergency or temporary shutdowns.
Principle of Blind Flanges
The blind flange functions by creating a seal at the end of a pipe using a gasket placed between the flange and its mating surface. Bolts and nuts are then applied to clamp the flange in place, ensuring an even distribution of pressure to prevent leaks. The assembly must be tightened to a specific torque, often using a diagonal pattern, to ensure uniform sealing.
Types of Blind Flanges
The selection of blind flanges is based on factors such as the type of fluid, pressure, temperature, and flow rate. Key considerations include the nominal diameter, pressure rating, gasket seat type, and material of the flange:
- Nominal Diameter: Matches the diameter of the piping system, ranging from 10A to 1,500A in JIS standards.
- Nominal Pressure: Chosen based on the fluid pressure and temperature, with standards providing various classifications such as 5K to 63K for JIS and Class 150 to 2500 for ASME/ANSI.
- Gasket Seat Types: Include full-face, flat-face, fitted, and groove types, selected according to the gasket design.
- Material: Generally includes carbon steel and stainless steel, with specific alloys chosen based on environmental and operational requirements.
Other Information on Blind Flanges
Blind flanges adhere to several standards, including JIS, ASME/ANSI, ISO, and JPI, each specifying dimensions, materials, and performance criteria. Gasket selection is critical, with options ranging from joint seat gaskets to spiral wound and ring joint types, depending on the operational conditions.
1. Standard
Blind flanges adhere to several standards, including JIS, ASME/ANSI, ISO, and JPI, each specifying dimensions, materials, and performance criteria. Typical examples are as follows:
- ASME/ANSI B16.5 Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings, NPS1/2 Through NPS24 Metric/Inch Standard
- ISO 7005-1 Pipe flanges-Part 1: Steel flanges for industrial and general service piping systems.
2. Gasket
Gasket selection is critical, with options ranging from joint seat gaskets to spiral wound and ring joint types, depending on the operational conditions such as the temperature and pressure of the fluid.
Joint Seat Gasket
Made of carbon fiber, blended with rubber and vulcanized rolled into a sheet, cut to fit the flange seating surface dimensions.
Spiral Wound Gasket
Made by overlapping a V-shaped metal hoop (thin metal sheet) and filler (tape-like sealing material) and forming it into a spiral shape. They have high sealing performance and are often used with high-temperature, high-pressure fluids.
Ring Joint
Metal gaskets made of mild steel, stainless steel, Monel, and other materials in two cross-sectional shapes: oval and octagonal.