What Is a Power Unit?
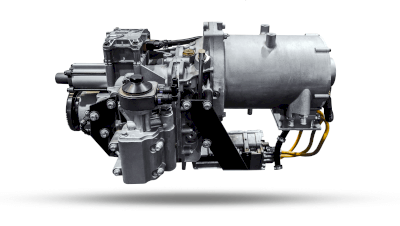
A power unit is a device that generates power, such as an engine or motor for automobiles and other vehicles.
It is used as a power source for large equipment, such as various industrial devices. Since a power unit consists of an internal combustion engine, several motors, and a generator, it is called a power unit as an integrated power source.
Diesel engines are often used as internal combustion engines. The power generated by the diesel engine is transmitted to the hydraulic pumps and other devices to operate the machine.
Uses of Power Units
Power units are used to operate a variety of large machines. Examples include drainage pumps, oil pumps, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and communications equipment. In these cases, hydraulic power units are often used.
Power units are also used to power F1 cars in Formula 1, a form of motorsports. The power unit is not only powered by a conventional engine but also by a hybrid turbocharged engine, which has been improved to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
Principle of Power Units
Power units can be used to operate various industrial machines by using the power generated by diesel engines and other engines through multiple motors and other devices. While power units have long been used in industrial applications, recent years have seen the development of power units in Formula One.
Power units in F1 consist of an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger and battery, and hybrid devices, such as an energy recovery system. Computer control of these devices can improve fuel efficiency, engine performance, and exhaust emissions. Thus, Power units are becoming increasingly sophisticated in the automotive industry.
On the other hand, the term for devices including engines, transmissions, and clutches in automobiles is power plant. The term power plant is also used to refer to a power plant.
Other Information on Power Units
1. History of F1 Power Units
For more than 50 years after the start of F1, F1 cars have been running on fuel. F1 is not only a motorsport but also a development of next-generation technology.
In light of the depletion of oil and fossil fuels and environmental issues, F1 introduced a hybrid power unit in 2014. This power unit is packed with technology that produces high power with a small displacement.
2. Structure of the F1 Power Unit
The F1 power unit consists of the following components.
ICE
The ICE is an internal combustion engine, the equivalent of an engine. Previously, unimaginably high-power engines were used, but now they are defined as engines with a displacement of 1.6 liters and six cylinders.
TC
A TC, also called a turbocharger, uses the exhaust gas emitted from the engine to compress and feed air to the engine. By sending a large amount of compressed air, the power of the engine is increased dramatically.
The MGU-H, which is linked to the turbocharger, is a thermal energy regeneration system. It assists the rotation of the turbocharger. This, together with heat recovery, alleviates turbo lag, which is the biggest crying point of turbochargers.
MGU-K
The MGU-K is a kinetic energy regeneration system, which corresponds to a generator in a general hybrid vehicle.
The electric energy is sent to a battery for storage. The MGU-K also has a motor drive function, which uses the electrical energy in the battery to provide driving power as a motor.
MGU-H
The MGU-H is a thermal energy regeneration system that converts thermal energy from exhaust gases into electrical energy.
The converted electrical energy is stored in a battery, and the battery’s electrical energy is used to assist the turbocharger.
Other
- ES
A battery that stores the converted electrical energy. - CE
An electronic device that controls the Power Unit.