What Is a Photovoltaic Cable?
 A Photovoltaic Cable is a cable for photovoltaic power generation. They are also called solar cables.
A Photovoltaic Cable is a cable for photovoltaic power generation. They are also called solar cables.
Electricity produced by photovoltaic power generation is direct current electricity.
Since cables for high-voltage use are sturdy and expensive with a shielding layer, it has been common practice to design cables to use low-voltage cables, keeping the voltage as low as possible.
Since the operating voltage was specified to be less than 1,500 VDC, it is now possible to design PV equipment with voltages between 600 V and 1,500 V.
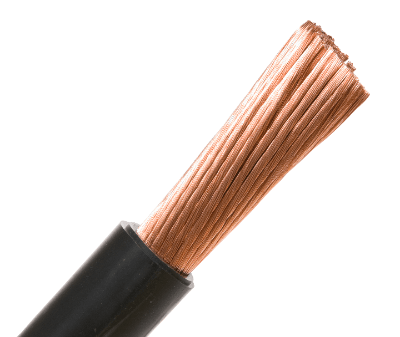
The structure has an electrical conductor that is covered with insulation and protected by an outer coating. The conductor is a soft copper wire with a cross-sectional area of 60 mm2 or less, or equivalent or stronger. The insulation must be a cross-linked polyolefin blend, cross-linked polyethylene blend, or ethylene rubber blend.
Uses of Photovoltaic Cable
Photovoltaic Cables are mainly used in photovoltaic power generation facilities.
The following are examples of applications for photovoltaic cables:
- Connection of solar panels
- Connection between PV modules and junction box
- Connection of junction box and power conditioner
Photovoltaic power generation equipment is largely divided into photovoltaic modules, junction boxes, and power conditioners.
Multiple photovoltaic modules are connected via a junction box and introduced into the power conditioner. At the power conditioner, electricity is transformed and converted to AC and connected to the power company’s grid.
Nowadays, PV cables with a voltage resistance of 600 V or higher are often used for installation, and high-voltage photovoltaic cables can reduce the number of junction boxes and other components, thus lowering the total cost of a PV installation.
Principle of Photovoltaic Cables
Photovoltaic Cables consist of a conductor, insulator, and sheath.
1. Conductor
The conductor is often made of soft copper stranded wire. Thin soft copper wire or tin-plated soft copper wire is collected and twisted together in multiple layers to provide flexibility. These are typical electrical conductors used where flexibility is required.
2. Insulator
Cross-linked polyolefin is used as an insulator. Polyolefin is a polymeric material made by polymerizing olefins and alkenes. Polyethylene and polypropylene are also included in polyolefins, which are used by adding a three-dimensional network structure to improve heat resistance and chemical resistance.
3. Sheath
The sheath is the outer shell of the cable and is made of materials such as polyvinyl chloride. It is resistant to sunlight, but its weakness is that it is vulnerable to low and high temperatures. The strength of vinyl chloride against sunlight is used to protect the inner cross-linked polyolefin layer, thereby enhancing the convenience of the cable.
Types of Photovoltaic Cable
Typical types of photovoltaic cable are as follows:
1. Photovoltaic Cable
This cable uses cross-linked polyethylene for both insulation and sheath. Cross-linked polyethylene is also used for CV cables, etc., so it consists of a familiar material. Generally, products with 1,500 V withstand voltage are sold.
2. QQ Cable
This cable uses cross-linked polyolefin for both the insulation and sheath, and, like photovoltaic cable, is generally sold with a withstand voltage of 1,500 V.
3. PP Cable
This cable uses ethylene rubber for the insulation and sheath. Since the material is rubber-based, it can be applied to moving parts.